|版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。
关于头文件重复包含的问题,以前一直不太清楚,今天特意翻了一下参考书和网上查阅资料,有了如下的理解:
这样说明,如果定义了头文件A.h,B.h和源文件C.cpp。如果我们在A.h中写上一个函数,在B.h中include A.h,然后再在C.cpp中include A.h和B.h,这样我们就会出现重复包含的问题,如下图:

下面看下问题代码:


1 //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// A.h files 2 3 //用于测试头文件的重复包含和重定义的问题 4 #include <iostream> 5 using namespacestd; 6 7 int sub(int a, intb) 8 { 9 std::cout << "sub: a-b = " << a - b <<std::endl; 10 return a -b; 11 } 12 13 int add(int a, intb) 14 { 15 std::cout << "sub: a+b = " << a + b <<std::endl; 16 17 return a +b; 18 } 19 20 21 //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// B.h files 22 23 #include <iostream> 24 using namespacestd; 25 26 #include "A.h" 27 28 int mul(int a, intb) 29 { 30 std::cout << "sub: a*b = " << a * b <<std::endl; 31 32 return a *b; 33 } 34 35 36 37 ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////C.cpp files 38 39 #include <iostream> 40 using namespacestd; 41 42 #include "A.h" 43 #include "B.h" 44 45 int main(void) 46 { 47 48 //add(1, 2); 49 //sub(45, 45); 50 51 return 0; 52 }
出错截图:
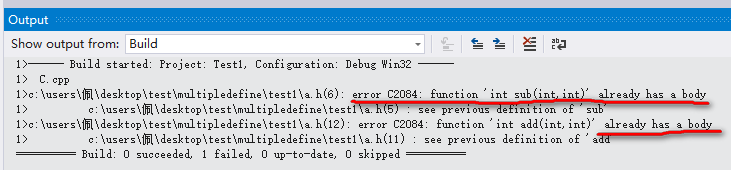
*.出错分析:
我们可以看到错误代码的提示:error C2084: function 'int sub(int,int)' already has a body,这说明sub函数已经存在了一个。这是什么原因,因为在B.h中我们通过#include "A.h"导入了A.h的头文件。而我们都知道头文件处理简单的来说就是将A.h中文件中的所有的东西全部的复制到#include <A.h>的定义所在的文件处。既然如此我们就可这样的理解,如下代码:


1 //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// A.h files 2 3 //用于测试头文件的重复包含和重定义的问题 4 #include <iostream> 5 using namespacestd; 6 7 int sub(int a, intb) 8 { 9 std::cout << "sub: a-b = " << a - b <<std::endl; 10 return a -b; 11 } 12 13 int add(int a, intb) 14 { 15 std::cout << "sub: a+b = " << a + b <<std::endl; 16 17 return a +b; 18 } 19 20 21 //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// B.h files 22 23 #include <iostream> 24 using namespacestd; 25 26 //#include "A.h" 27 //#include "A.h"就是相当于将A.h中的内容copy到了B.h中 28 29 ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 30 //copy部分A.h中的函数,如下: 31 int sub(int a, intb) 32 { 33 std::cout << "sub: a-b = " << a - b <<std::endl; 34 return a -b; 35 } 36 37 int add(int a, intb) 38 { 39 std::cout << "sub: a+b = " << a + b <<std::endl; 40 41 return a +b; 42 } 43 //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 44 45 int mul(int a, intb) 46 { 47 std::cout << "sub: a*b = " << a * b <<std::endl; 48 49 return a *b; 50 } 51 52 53 54 ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////C.cpp files 55 56 #include <iostream> 57 using namespacestd; 58 59 #include "A.h" 60 #include "B.h" 61 62 //这里的A.h和B.h中的内容也会copy到C.cpp中来 63 64 int main(void) 65 { 66 67 //add(1, 2); 68 //sub(45, 45); 69 70 return 0; 71 }
那么,这样看之后,我们就可以发现一个问题,在A.h中有两个函数sub()和add()定义;在B.h中同样的包含了两个函数sub()和add()定义,当A.h和B.h单独分开始这样还不会有问题。但是我们在看下C.cpp文件中有:#include "A.h" 和 #include "B.h"。这样的话又重复的将A.h和B.h文件中的内容复制到了C.cpp中,那么这样就出现问题了,在A.h和B.h中的相同函数全部复制到C.cpp中。那么在编译的时候编译器就会发现重定义了两个相同的函数,也就是上面的错误。编译上面Multiple define error: 2中的代码同样出现于Multiple define error: 1中的一样的错误。
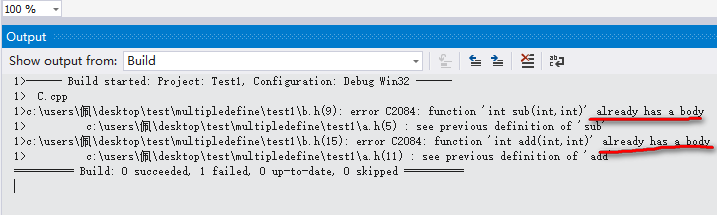
因此,总的来说,头文件重复包含的问题往往是重定义的问题。下面我们有两种方式解决头文件的重复包含:一个是条件编译的#ifndef...#endif 和 #pragma once.
如下代码示例:
////////// C.cpp files
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "A.h"
#include "B.h"
int main(void)
{
add(1, 2);
sub(45, 45);
return 0;
}
/////////// A.h files
//用于测试头文件的重复包含和重定义的问题
#ifndef _A_H_
#define _A_H_
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int sub(int a, int b)
{
std::cout << "sub: a-b = " << a - b << std::endl;
return a - b;
}
int add(int a, int b)
{
std::cout << "sub: a+b = " << a + b << std::endl;
return a + b;
}
#endif // _A_H_
///////////// B.h files
#ifndef _B_H_
#define _B_H_
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "A.h"
int mul(int a, int b)
{
std::cout << "sub: a*b = " << a * b << std::endl;
return a * b;
}
#endif // _B_H_
*.如上代码加入#ifndef...#endif就消除了重定义的问题了。其实这种方法消除的原理是在当编译器遇到第2(3,....)遍同样的头文件时,因为已经编译了一次,在后面在遇到的时候,编译器自动忽略文件中的内容。
/////////// C.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "A.h"
#include "B.h"
int main(void)
{
add(1, 2);
sub(45, 45);
return 0;
}
//////////////// A.h
//用于测试头文件的重复包含和重定义的问题
//#ifndef _A_H_
//#define _A_H_
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int sub(int a, int b)
{
std::cout << "sub: a-b = " << a - b << std::endl;
return a - b;
}
int add(int a, int b)
{
std::cout << "sub: a+b = " << a + b << std::endl;
return a + b;
}
//#endif // _A_H_
///////////////////// B.h
//#ifndef _B_H_
//#define _B_H_
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "A.h"
int mul(int a, int b)
{
std::cout << "sub: a*b = " << a * b << std::endl;
return a * b;
}
//#endif // _B_H_
*.#pragma once同样能消除头文件的重复包含的问题。见下运行实例图:
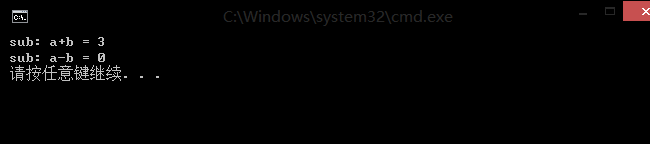
同样的上面的#ifndef...#endif 和 #pragma once 并不能完全消除所有的重定义问题。如下代码:


1 ////////////////////// A.h 2 3 #ifndef _A_H_ 4 #define _A_H_ 5 6 int a = 10; 7 8 #include <iostream> 9 using namespacestd; 10 11 int sub(int a, intb) 12 { 13 std::cout << "sub: a-b = " << a - b <<std::endl; 14 return a -b; 15 } 16 17 int add(int a, intb) 18 { 19 std::cout << "sub: a+b = " << a + b <<std::endl; 20 21 return a +b; 22 } 23 24 #endif //_A_H_ 25 26 27 //////////////////// B.h 28 29 #ifndef _B_H_ 30 #define _B_H_ 31 32 #include <iostream> 33 using namespacestd; 34 //#include "A.h" 35 36 int a = 5; 37 38 int mul(int a, intb) 39 { 40 std::cout << "sub: a*b = " << a * b <<std::endl; 41 42 return a *b; 43 } 44 45 #endif //_B_H_
Multiple define error: 3出现如下错误:
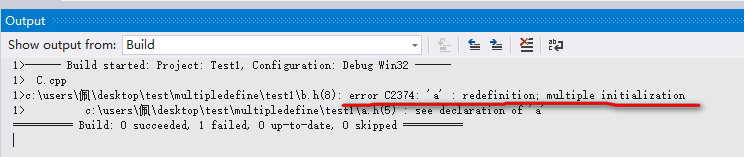
看上面的代码,我们已将a变量的声明放在了条件编译之中,但是还是出现了重定义的问题,这是什么原因呢?在C++静态变量中有三种类型,其中有一种外部链接型的静态变量。而全局变量在声明的时候没有加上修饰词static,因此这种变量是属于外部链接型的变量。而外部链接的变量对于在同一个工程文件的所有文件中都是可见的,所以在其中一个文件中定义的外部链接变量a,同时在另一个文件中也定义。或者在包含头文件的时候重复包含了某一个定义了外部变量的头文件,就会导致在同一个工程文件形成的程序中将包含两个一样的变量(同样函数定义(Multiple define error:2)也是一样会产生同样的错误)。
如何解决呢?解决的方法就是在a变量前加上extern修饰符即可;如下:
extern int a = 10;
因此,在头文件的定义中,我们最好不要将函数定义和变量的声明放到头文件中。但是下面的几种确实头文件常包含的内容:
函数声明 使用#define或者const定义的符号常量 类声明 结构体声明 模板声明 内联函数
如下:
#ifndef _B_H_
#define _B_H_
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "A.h"
#define pi 3.1415
const int value = 100;
int add(int a, int b);
class bb
{
//......
};
struct bbb
{
//......
};
inline void bbbb(int a, int b)
{
cout << "a+b = " << a+b << endl;
}
int mul(int a, int b);
//{
// std::cout << "sub: a*b = " << a * b << std::endl;
//
// return a * b;
//}
#endif // _B_H_其中函数声明不用说都知道,类声明和结构体声明在头文件中不会导致重定义是因为类和结构体中的不会创建变量只是在源文件中声明结构体变量的时候。因此不会出现重定义问题。内联函数和模板的声明这两个我还没有查到具体的原因(待续)。
-----------如有错误,希望大家多多指正-----------