本文通过迁移学习将训练好的VGG16模型应用到图像的多标签分类问题中。该项目数据来自于Kaggle,每张图片可同时属于多个标签。模型的准确度使用F score进行量化,如下表所示:
| 标签 | 预测为Positive(1) | 预测为Negative(0) |
|---|---|---|
| 真值为Positive(1) | TP | FN |
| 真值为Negative(0) | FP | TN |
例如真实标签是(1,0,1,1,0,0), 预测标签是(1,1,0,1,1,0), 则TP=2, FN=1, FP=2, TN=1。$$Precision=frac{TP}{TP+FP}, ext{ }Recall=frac{TP}{TP+FN}, ext{ }F{\_}score=frac{(1+eta^2)*Presicion*Recall}{Recall+eta^2*Precision}$$其中$eta$越小,F score中Precision的权重越大,$eta$等于0时F score就变为Precision;$eta$越大,F score中Recall的权重越大,$eta$趋于无穷大时F score就变为Recall。可以在Keras中自定义该函数(y_pred表示预测概率):
from tensorflow.keras import backend # calculate fbeta score for multi-label classification def fbeta(y_true, y_pred, beta=2): # clip predictions y_pred = backend.clip(y_pred, 0, 1) # calculate elements for each sample tp = backend.sum(backend.round(backend.clip(y_true * y_pred, 0, 1)), axis=1) fp = backend.sum(backend.round(backend.clip(y_pred - y_true, 0, 1)), axis=1) fn = backend.sum(backend.round(backend.clip(y_true - y_pred, 0, 1)), axis=1) # calculate precision p = tp / (tp + fp + backend.epsilon()) # calculate recall r = tp / (tp + fn + backend.epsilon()) # calculate fbeta, averaged across samples bb = beta ** 2 fbeta_score = backend.mean((1 + bb) * (p * r) / (bb * p + r + backend.epsilon())) return fbeta_score
此外在损失函数的使用上多标签分类和多类别(multi-class)分类也有区别,多标签分类使用binary_crossentropy,假设一个样本的真实标签是(1,0,1,1,0,0),预测概率是(0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.7, 0.9, 0.2): $$binary{\_}crossentropy ext{ }loss=-(ln 0.2 + ln 0.7 + ln 0.4 + ln 0.7 + ln 0.1 + ln 0.8)/6=0.96$$另外多标签分类输出层的激活函数选择sigmoid而非softmax。模型架构如下所示:
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Flatten from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam from tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16 from tensorflow.keras.models import Model def define_model(in_shape=(128, 128, 3), out_shape=17): # load model base_model = VGG16(weights='imagenet', include_top=False, input_shape=in_shape) # mark loaded layers as not trainable for layer in base_model.layers: layer.trainable = False # make the last block trainable tune_layers = [layer.name for layer in base_model.layers if layer.name.startswith('block5_')] for layer_name in tune_layers: base_model.get_layer(layer_name).trainable = True # add new classifier layers flat1 = Flatten()(base_model.layers[-1].output) class1 = Dense(128, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='he_uniform')(flat1) output = Dense(out_shape, activation='sigmoid')(class1) # define new model model = Model(inputs=base_model.input, outputs=output) # compile model opt = Adam(learning_rate=1e-3) model.compile(optimizer=opt, loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=[fbeta]) model.summary() return model
从Kaggle网站上下载数据并解压,将其处理成可被模型读取的数据格式


from os import listdir from numpy import zeros, asarray, savez_compressed from pandas import read_csv from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import load_img, img_to_array # create a mapping of tags to integers given the loaded mapping file def create_tag_mapping(mapping_csv): labels = set() # create a set of all known tags for i in range(len(mapping_csv)): tags = mapping_csv['tags'][i].split(' ') # convert spaced separated tags into an array of tags labels.update(tags) # add tags to the set of known labels labels = sorted(list(labels)) # convert set of labels to a sorted list # dict that maps labels to integers, and the reverse labels_map = {labels[i]:i for i in range(len(labels))} inv_labels_map = {i:labels[i] for i in range(len(labels))} return labels_map, inv_labels_map # create a mapping of filename to a list of tags def create_file_mapping(mapping_csv): mapping = dict() for i in range(len(mapping_csv)): name, tags = mapping_csv['image_name'][i], mapping_csv['tags'][i] mapping[name] = tags.split(' ') return mapping # create a one hot encoding for one list of tags def one_hot_encode(tags, mapping): encoding = zeros(len(mapping), dtype='uint8') # create empty vector # mark 1 for each tag in the vector for tag in tags: encoding[mapping[tag]] = 1 return encoding # load all images into memory def load_dataset(path, file_mapping, tag_mapping): photos, targets = list(), list() # enumerate files in the directory for filename in listdir(path): photo = load_img(path + filename, target_size=(128,128)) # load image photo = img_to_array(photo, dtype='uint8') # convert to numpy array tags = file_mapping[filename[:-4]] # get tags target = one_hot_encode(tags, tag_mapping) # one hot encode tags photos.append(photo) targets.append(target) X = asarray(photos, dtype='uint8') y = asarray(targets, dtype='uint8') return X, y filename = 'train_v2.csv' # load the target file mapping_csv = read_csv(filename) tag_mapping, _ = create_tag_mapping(mapping_csv) # create a mapping of tags to integers file_mapping = create_file_mapping(mapping_csv) # create a mapping of filenames to tag lists folder = 'train-jpg/' # load the jpeg images X, y = load_dataset(folder, file_mapping, tag_mapping) print(X.shape, y.shape) savez_compressed('planet_data.npz', X, y) # save both arrays to one file in compressed format
接下来再建立两个辅助函数,第一个函数用来分割训练集和验证集,第二个函数用来画出模型在训练过程中的学习曲线


import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # load train and test dataset def load_dataset(): # load dataset data = np.load('planet_data.npz') X, y = data['arr_0'], data['arr_1'] # separate into train and test datasets trainX, testX, trainY, testY = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=1) print(trainX.shape, trainY.shape, testX.shape, testY.shape) return trainX, trainY, testX, testY # plot diagnostic learning curves def summarize_diagnostics(history): # plot loss pyplot.subplot(121) pyplot.title('Cross Entropy Loss') pyplot.plot(history.history['loss'], color='blue', label='train') pyplot.plot(history.history['val_loss'], color='orange', label='test') # plot accuracy pyplot.subplot(122) pyplot.title('Fbeta') pyplot.plot(history.history['fbeta'], color='blue', label='train') pyplot.plot(history.history['val_fbeta'], color='orange', label='test') pyplot.show()
使用数据扩充技术(Data Augmentation)对模型进行训练
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator from tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import preprocess_input from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint trainX, trainY, testX, testY = load_dataset() # load dataset # create data generator using augmentation # vertical flip is reasonable since the pictures are satellite images train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(horizontal_flip=True, vertical_flip=True, rotation_range=90, preprocessing_function=preprocess_input) test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(preprocessing_function=preprocess_input) # prepare generators train_it = train_datagen.flow(trainX, trainY, batch_size=128) test_it = test_datagen.flow(testX, testY, batch_size=128) # define model model = define_model() # fit model # When one epoch ends, the validation generator will yield validation_steps batches, then average the evaluation results of all batches checkpointer = ModelCheckpoint(filepath='./weights.best.vgg16.hdf5', verbose=1, save_best_only=True) history = model.fit_generator(train_it, steps_per_epoch=len(train_it), validation_data=test_it, validation_steps=len(test_it), epochs=15, callbacks=[checkpointer], verbose=0) # evaluate optimal model # For simplicity, the validation set is used to test the model here. In fact an entirely new test set should have been used. model.load_weights('./weights.best.vgg16.hdf5') #load stored optimal coefficients loss, fbeta = model.evaluate_generator(test_it, steps=len(test_it), verbose=0) print('> loss=%.3f, fbeta=%.3f' % (loss, fbeta)) # loss=0.108, fbeta=0.884 model.save('final_model.h5') # learning curves summarize_diagnostics(history)
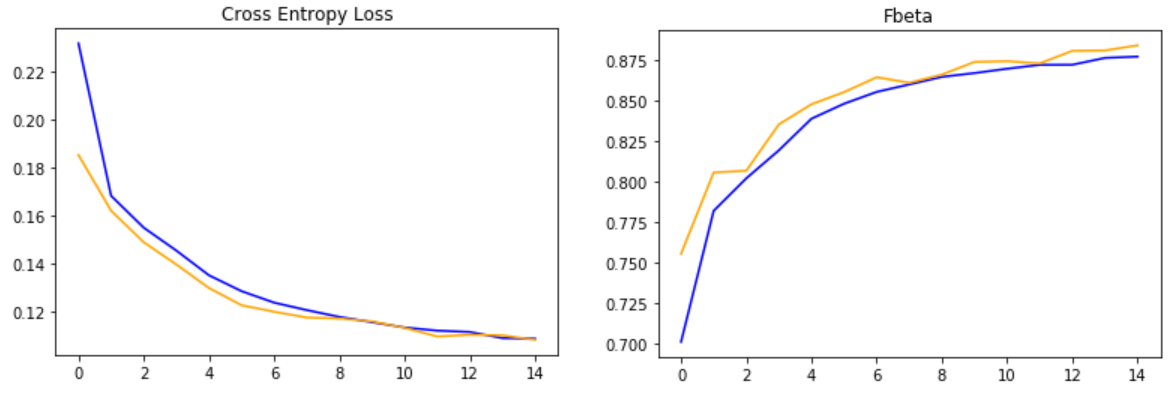
蓝线代表训练集,黄线代表验证集