HNSW
分层的可导航小世界(Hierarchical Navigable Small World, HNSW)
特点
1、一种基于图的数据结构
2、使用贪婪搜索算法的变体进行ANN搜索,每次选择最接近查询的未访问的相邻元素时,它都会从元素到另一个元素地遍历整个图,直到达到停止条件
原理参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/u011233351/article/details/85116719
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/80552211?utm_source=wechat_session
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38156298/article/details/100085892
一、什么特征作为输入
1、原始特征,图像本身作为输入,显然这种情况不说效果如何,最起码数据量上就会很大,对RAM要求极大。一般不会作为输入特征
2、SIFT特征, 图像处理中有很多特征提取方法,其中SIFT有代表性。当然也可以选择其他。这样大大的降低数据量的同时,也能起到降维的作用。将有效特征作为相似度比较的依据比较合理。
3、DEEP特征,目前神经网络比较流行,可以利用这个方法提取特征。
4、其他特征
特征选择有一个原则:归一化的降维的主要特征。去除冗余点,这对我们后续的相似度检测有着很大的好处。
二、参数M、efConstruction和max_elements
1、M - the number of bi-directional links created for every new element during construction.
M的合理范围在[2,200]。M越高,对于本身具有高维特征的数据集来讲,recall可能越高,性能越好;M越低,对于本身具有低维特征的数据集来讲,性能越好。
建议M:12,16,32。因为特征已经选择过了,维度一般不会太高。
2、efConstruction - the parameter has the same meaning as ef, but controls the index_time/index_accuracy.
ef - the size of the dynamic list for the nearest neighbors (used during the search).
efConstruction越大,构造时间越长,index quality越好。有时,efConstruction增加的过快并不能提升index quality。有一种方法可以检查efConstruction的选择是否可以接受。计算recall,当ef=efConstruction,在M值时,如果recall低于0.9,那么可以适当增加efConstruction的数值。
3、max_elements - 检索的最大元素。
这个参数取决于你创建的索引库的特征数量。如果你想要在1000,0000个特征中检测是否有相似的图像时,这个max_elements就要设置为1000,0000. 当然这也要看RAM是否支持这么多数据同时加载进来。
三、demo
https://github.com/pengzerong/hnsw-test
流程
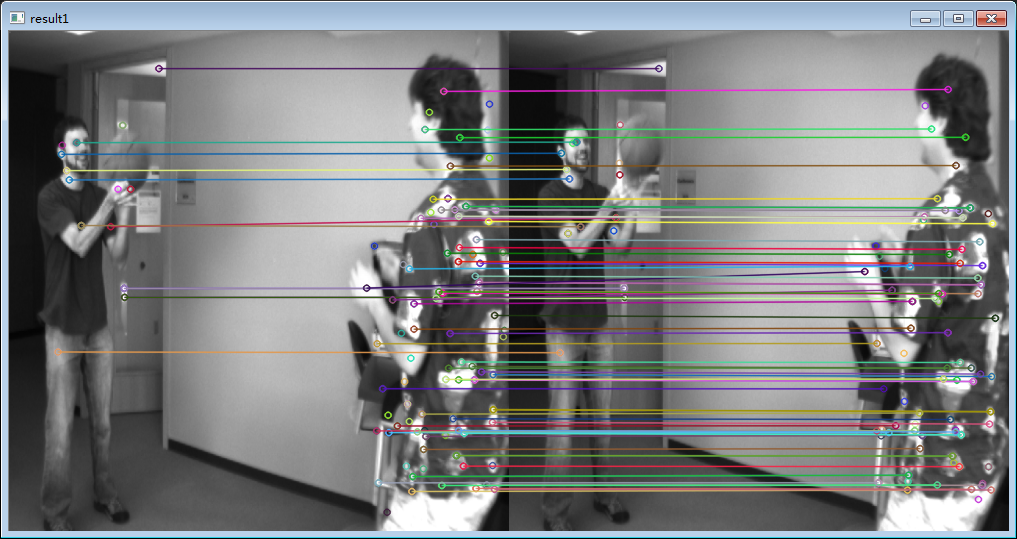
1、读取两幅图像,分别对两张图提取SIFT特征
Mat srcImg1 = imread("basketball1.png", 1); Mat srcImg2 = imread("basketball2.png", 1); if (srcImg1.empty() || srcImg2.empty()) return -1; Ptr<cv::Feature2D> detector = xfeatures2d::SIFT::create(128); std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints1, keypoints2; Mat descriptors1, descriptors2; // 提取图片的特征点及特征点描述 detector->detect(srcImg1, keypoints1); detector->compute(srcImg1, keypoints1, descriptors1); rootSift(descriptors1); detector->detect(srcImg2, keypoints2); detector->compute(srcImg2, keypoints2, descriptors2); rootSift(descriptors2);
2、特征归一化
void rootSift(Mat &descriptors, const float eps = 1e-7) { // Compute sums for L1 Norm Mat sums_vec; descriptors = abs(descriptors); //otherwise we draw sqrt of negative vals reduce(descriptors, sums_vec, 1 /*sum over columns*/, CV_REDUCE_SUM, CV_32FC1); for (int row = 0; row < descriptors.rows; row++) { int offset = row * descriptors.cols; for (int col = 0; col < descriptors.cols; col++) { descriptors.at<float>(offset + col) = sqrt(descriptors.at<float>(offset + col) / (sums_vec.at<float>(row) + eps) /*L1-Normalize*/); } // L2 distance normalize(descriptors.row(row), descriptors.row(row), 1.0, 0.0, NORM_L2); } return; }
3、创建HNSW
size_t maxCount = descriptors1.rows; int M = 32; int efConstruction = 100;// TestFindSelf,140以下有不能查找到自己的情况 int vecdim = descriptors1.cols;// 特征维度 hnswlib::InnerProductSpace *L2Space = new hnswlib::InnerProductSpace(vecdim); hnswlib::HierarchicalNSW<float> *hnsw = new hnswlib::HierarchicalNSW<float>(L2Space, maxCount, M, efConstruction); int count = 0; for (size_t i = 0; i < descriptors1.rows; i++) { float *mass = new float[vecdim]; for (size_t j = 0; j < vecdim; j++) { mass[j] = descriptors1.at<float>(i, j); } hnsw->addPoint((void*)mass, count); ++count; delete[] mass; }
4、匹配特征点,筛选出可以用来配准的特征点
int nn = 3; std::vector<DMatch> matchPoints; Mat indices, dists; for (size_t i = 0; i < descriptors2.rows; i++) { float *mass = new float[vecdim]; for (size_t j = 0; j < vecdim; j++) { mass[j] = descriptors2.at<float>(i, j); } std::priority_queue<std::pair<float, hnswlib::labeltype>> candidates = hnsw->searchKnn((void*)mass, nn); delete[] mass; for (int k = 0; k < nn; k++) { double dAngle = abs(keypoints2.at(i).angle - keypoints1.at(candidates.top().second).angle); if (abs(candidates.top().first) < 0.1 && dAngle < 10) { std::cout << i << " angle diff: " << dAngle << ", dist: " << candidates.top().first << " "<< candidates.top().second << std::endl; DMatch dmatches(candidates.top().second, i, candidates.top().first); matchPoints.push_back(dmatches); } candidates.pop(); } }
5、匹配效果