1、生成正态分布数据并绘制概率分布图
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 根据均值、标准差,求指定范围的正态分布概率值
def normfun(x, mu, sigma):
pdf = np.exp(-((x - mu)**2)/(2*sigma**2)) / (sigma * np.sqrt(2*np.pi))
return pdf
# result = np.random.randint(-65, 80, size=100) # 最小值,最大值,数量
result = np.random.normal(15, 44, 100) # 均值为0.5,方差为1
print(result)
x = np.arange(min(result), max(result), 0.1)
# 设定 y 轴,载入刚才的正态分布函数
print(result.mean(), result.std())
y = normfun(x, result.mean(), result.std())
plt.plot(x, y) # 这里画出理论的正态分布概率曲线
# 这里画出实际的参数概率与取值关系
plt.hist(result, bins=10, rwidth=0.8, density=True) # bins个柱状图,宽度是rwidth(0~1),=1没有缝隙
plt.title('distribution')
plt.xlabel('temperature')
plt.ylabel('probability')
# 输出
plt.show() # 最后图片的概率和不为1是因为正态分布是从负无穷到正无穷,这里指截取了数据最小值到最大值的分布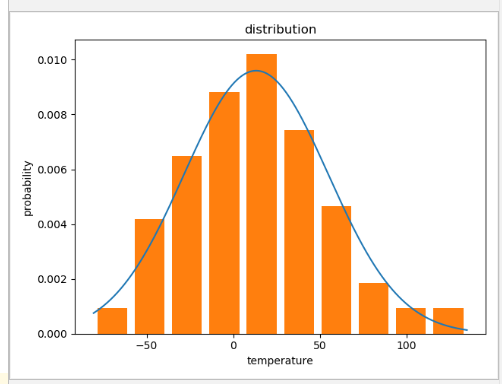
根据范围生成正态分布:
result = np.random.randint(-65, 80, size=100) # 最小值,最大值,数量
根据均值、方差生成正态分布:
result = np.random.normal(15, 44, 100) # 均值为0.5,方差为1
2、判断一个序列是否符合正态分布
import numpy as np from scipy import stats pts = 1000 np.random.seed(28041990) a = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=pts) # 生成1个正态分布,均值为0,标准差为1,100个点 b = np.random.normal(2, 1, size=pts) # 生成1个正态分布,均值为2,标准差为1, 100个点 x = np.concatenate((a, b)) # 把两个正态分布连接起来,所以理论上变成了非正态分布序列 k2, p = stats.normaltest(x) alpha = 1e-3 print("p = {:g}".format(p)) # 原假设:x是一个正态分布 if p < alpha: # null hypothesis: x comes from a normal distribution print("The null hypothesis can be rejected") # 原假设可被拒绝,即不是正态分布 else: print("The null hypothesis cannot be rejected") # 原假设不可被拒绝,即使正态分布
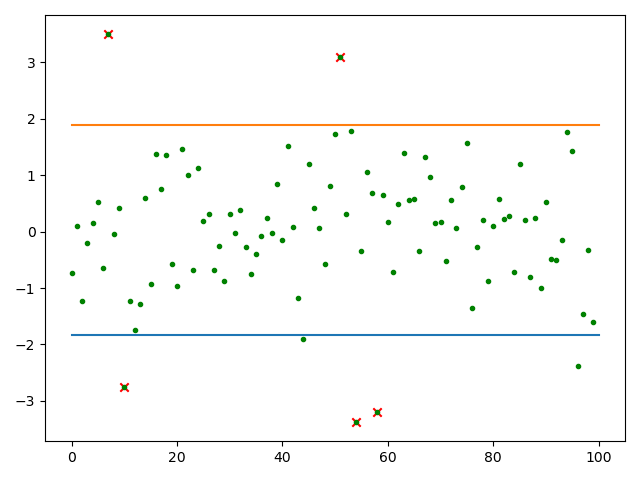
3、求置信区间、异常值
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import stats import pandas as pd # 求列表数据的异常点 def get_outer_data(data_list): df = pd.DataFrame(data_list, columns=['value']) df = df.iloc[:, 0] # 计算下四分位数和上四分位 Q1 = df.quantile(q=0.25) Q3 = df.quantile(q=0.75) # 基于1.5倍的四分位差计算上下须对应的值 low_whisker = Q1 - 1.5 * (Q3 - Q1) up_whisker = Q3 + 1.5 * (Q3 - Q1) # 寻找异常点 kk = df[(df > up_whisker) | (df < low_whisker)] data1 = pd.DataFrame({'id': kk.index, '异常值': kk}) return data1 N = 100 result = np.random.normal(0, 1, N) # result = np.random.randint(-65, 80, size=N) # 最小值,最大值,数量 mean, std = result.mean(), result.std(ddof=1) # 求均值和标准差 # 计算置信区间,这里的0.9是置信水平 conf_intveral = stats.norm.interval(0.9, loc=mean, scale=std) # 90%概率 print('置信区间:', conf_intveral) x = np.arange(0, len(result), 1) # 求异常值 outer = get_outer_data(result) print(outer, type(outer)) x1 = outer.iloc[:, 0] y1 = outer.iloc[:, 1] plt.scatter(x1, y1, marker='x', color='r') # 所有离散点 plt.scatter(x, result, marker='.', color='g') # 异常点 plt.plot([0, len(result)], [conf_intveral[0], conf_intveral[0]]) plt.plot([0, len(result)], [conf_intveral[1], conf_intveral[1]]) plt.show()
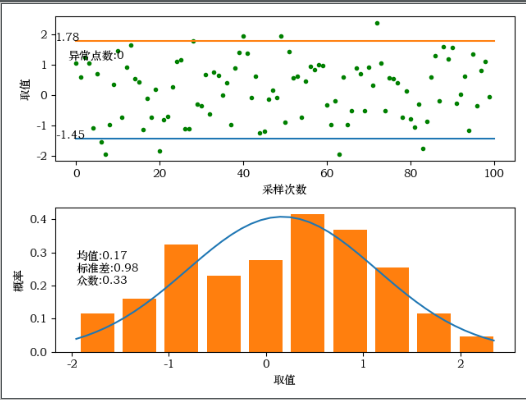
4、采样点离散图和概率图
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy import stats import pandas as pd import time print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%D %H:%M:%S')) # 根据均值、标准差,求指定范围的正态分布概率值 def _normfun(x, mu, sigma): pdf = np.exp(-((x - mu)**2)/(2*sigma**2)) / (sigma * np.sqrt(2*np.pi)) return pdf # 求列表数据的异常点 def get_outer_data(data_list): df = pd.DataFrame(data_list, columns=['value']) df = df.iloc[:, 0] # 计算下四分位数和上四分位 Q1 = df.quantile(q=0.25) Q3 = df.quantile(q=0.75) # 基于1.5倍的四分位差计算上下须对应的值 low_whisker = Q1 - 1.5 * (Q3 - Q1) up_whisker = Q3 + 1.5 * (Q3 - Q1) # 寻找异常点 kk = df[(df > up_whisker) | (df < low_whisker)] data1 = pd.DataFrame({'id': kk.index, '异常值': kk}) return data1 N = 100 result = np.random.normal(0, 1, N) # result = np.random.randint(-65, 80, size=N) # 最小值,最大值,数量 # result = [100]*100 # 取值全相同 # result = np.array(result) mean, std = result.mean(), result.std(ddof=1) # 求均值和标准差 # 计算置信区间,这里的0.9是置信水平 if std == 0: # 如果所有值都相同即标准差为0则无法计算置信区间 conf_intveral = [min(result)-1, max(result)+1] else: conf_intveral = stats.norm.interval(0.9, loc=mean, scale=std) # 90%概率 # print('置信区间:', conf_intveral) # 求异常值 outer = get_outer_data(result) # 绘制离散图 fig = plt.figure() fig.add_subplot(2, 1, 1) plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.3) x = np.arange(0, len(result), 1) plt.scatter(x, result, marker='.', color='g') # 画所有离散点 plt.scatter(outer.iloc[:, 0], outer.iloc[:, 1], marker='x', color='r') # 画异常离散点 plt.plot([0, len(result)], [conf_intveral[0], conf_intveral[0]]) # 置信区间线条 plt.plot([0, len(result)], [conf_intveral[1], conf_intveral[1]]) # 置信区间线条 plt.text(0, conf_intveral[0], '{:.2f}'.format(conf_intveral[0])) # 置信区间数字显示 plt.text(0, conf_intveral[1], '{:.2f}'.format(conf_intveral[1])) # 置信区间数字显示 info = 'outer count:{}'.format(len(outer.iloc[:, 0])) plt.text(min(x), max(result)-((max(result)-min(result)) / 2), info) # 异常点数显示 plt.xlabel('sample count') plt.ylabel('value') # 绘制概率图 if std != 0: # 如果所有取值都相同 fig.add_subplot(2, 1, 2) x = np.arange(min(result), max(result), 0.1) y = _normfun(x, result.mean(), result.std()) plt.plot(x, y) # 这里画出理论的正态分布概率曲线 plt.hist(result, bins=10, rwidth=0.8, density=True) # bins个柱状图,宽度是rwidth(0~1),=1没有缝隙 info = 'mean:{:.2f} std:{:.2f} mode num:{:.2f}'.format(mean, std, np.median(result)) plt.text(min(x), max(y) / 2, info) plt.xlabel('value') plt.ylabel('Probability') else: fig.add_subplot(2, 1, 2) info = 'non-normal distribution!! mean:{:.2f} std:{:.2f} mode num:{:.2f}'.format(mean, std, np.median(result)) plt.text(0.5, 0.5, info) plt.xlabel('value') plt.ylabel('Probability') plt.savefig('./distribution.jpg') plt.show() print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%D %H:%M:%S'))