首先看一个例子,当我使用不同方法将一个源map拷贝到另一个map后,改变源map,复制后的map理应不受影响
importjava.math.BigDecimal; importjava.util.HashMap; importjava.util.Iterator; importjava.util.Map; importjava.util.Map.Entry; public classMapTest { public static voidmain(String[] args) { Map<String, BigDecimal> detailsmap = new HashMap<String, BigDecimal>(); Map<String, BigDecimal> detailsmapByEquals = new HashMap<String, BigDecimal>(); Map<String, BigDecimal> detailsmapByPutAll = new HashMap<String, BigDecimal>(); Map<String, BigDecimal> detailsmapByIterator = new HashMap<String, BigDecimal>(); detailsmap.put("key1", new BigDecimal("123.22")); detailsmap.put("key2", new BigDecimal("156.2")); //通过“=”的方式复制map对象 detailsmapByEquals =detailsmap; //通过putAll的方式复制map对象 detailsmapByPutAll.putAll(detailsmap); //通过iterator的方式复制map对象 mapCopy(detailsmapByIterator, detailsmap); System.out.println("detailsmap 的内容为:" +detailsmap); detailsmap.remove("key2"); System.out.println("移除key2的 detailsmap 的内容为:" +detailsmap); System.out.println("通过 “=” 复制的map当前值为:" +detailsmapByEquals); System.out.println("通过 “putAll方法” 复制的map当前值为:" +detailsmapByPutAll); System.out.println("通过 “iterator方法” 复制的map当前值为:" +detailsmapByIterator); } public static voidmapCopy(Map detailsmapByIterator, Map detailsmap) { //将detailsmap内容拷贝到detailsmapByIterator if (detailsmapByIterator == null) { detailsmapByIterator = newHashMap(); } if(detailsmap == null){ return; } Iterator it =detailsmap.entrySet().iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ Map.Entry entry =(Entry) it.next(); Object key =entry.getKey(); detailsmapByIterator.put(key, detailsmap.get(key) != null?detailsmap.get(key):""); } } }
查看输出:

可以看到通过“=”复制的map内容随源map的改变而改变,而通过putAll方法和Iterator复制的map则不受源map改变的影响。
2. Map的两种拷贝类型Map的拷贝分为两种情况:
- 浅拷贝:只拷贝对象的引用,两个引用仍然指向同一个对象,在内存中占用同一块内存。被拷贝对象的所有变量都含有与原来的对象相同的值,而所有的对其他对象的引用仍然指向原来的对象。即浅拷贝仅仅拷贝对象的引用,而不拷贝它所引用的对象。
- 深拷贝:被拷贝对象的所有变量都含有与原来的对象相同的值,除去那些引用其他对象的变量。那些引用其他对象的变量将指向被拷贝过的新对象,而不再是原有的那些被引用的对象。即深拷贝把要拷贝的对象所引用的对象都拷贝了一遍。
如示例中的三种拷贝方法:针对map中的数据为统一的、简单的基本数据类型,当拷贝的数据通过“=”复制map的方法为浅拷贝,putAll方法为深拷贝,iterator遍历添加的方式为深拷贝。
3. putAll方法并非深拷贝两种深拷贝方法,iterator遍历添加的方式,由于是重新创建了一个对象,且遍历添加源Map的元素,因此在内存中另开辟了一块内存,毋庸置疑是深拷贝;而对于putAll方法参考其源码:
/** * Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this map. * These mappings will replace any mappings that this map had for * any of the keys currently in the specified map. * * @paramm mappings to be stored in this map * @throwsNullPointerException if the specified map is null */ public void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V>m) { int numKeysToBeAdded =m.size(); if (numKeysToBeAdded == 0) return; /* * Expand the map if the map if the number of mappings to be added * is greater than or equal to threshold. This is conservative; the * obvious condition is (m.size() + size) >= threshold, but this * condition could result in a map with twice the appropriate capacity, * if the keys to be added overlap with the keys already in this map. * By using the conservative calculation, we subject ourself * to at most one extra resize. */ if (numKeysToBeAdded >threshold) { int targetCapacity = (int)(numKeysToBeAdded / loadFactor + 1); if (targetCapacity >MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) targetCapacity =MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; int newCapacity =table.length; while (newCapacity <targetCapacity) newCapacity <<= 1; if (newCapacity >table.length) resize(newCapacity); } for (Map.Entry<? extends K, ? extends V>e : m.entrySet()) put(e.getKey(), e.getValue()); }
通过源码可以看到putAll() 方法的实现仅仅是将源Map的第一层put进Map中,这种方式对于value为基本类型的map复制是实现深拷贝的效果的,但是当value为对象时,是不会奏效的。这里简单使用源Map内嵌Map的方式测试putAll方法,看其是否实现了深层次的复制:
importjava.util.HashMap; importjava.util.Map; public classMapDeepCopy { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public static voidmain(String[] args) { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); Map<String, Object> mapCopy = new HashMap<String, Object>(); //Map中要嵌套Map Map mapInner = newHashMap(); mapInner.put("num", "100"); map.put("key1", mapInner); map.put("key2", "600"); //复制 mapCopy.putAll(map); System.out.println("使用“putAll”方法复制map到mapCopy中,此时mapCopy值为:————"+mapCopy); //更改复制之后的map中内嵌map的内容 ((Map) mapCopy.get("key1")).put("num", "200"); System.out.println("更改复制之后的mapCopy内容,更改之后mapCopy值为:————"+mapCopy); System.out.println("此时源map map的值为:————"+map);//源Map也被改变 } }
输出如下,说明map和mapCopy中的mapInner元素使用的还是同一块内存:

有一种方法,是使用序列化的方式来实现对象的深拷贝,但是前提是,对象必须是实现了Serializable接口才可以,Map本身没有实现Serializable 这个接口,所以这种方式不能序列化Map,也就是不能深拷贝Map。但是HashMap是可以的,因为它实现了Serializable。下面的方式,基于HashMap来讲,非Map的拷贝。
/** * @Title: 对象深度克隆---使用序列化进行深拷贝 * @Description: 使用序列化的方式来实现对象的深拷贝,但是前提是,对象必须是实现了 Serializable接口才可以,Map本身没有实现 Serializable 这个接口,所以这种方式不能序列化Map,也就是不能深拷贝Map。但是HashMap是可以的,因为它 实现了Serializable。 * @paramobj * @returnT */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public static <T extends Serializable>T clone(T obj) { T clonedObj = null; try{ ByteArrayOutputStream baos = newByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream oos = newObjectOutputStream(baos); oos.writeObject(obj); oos.close(); ByteArrayInputStream bais = newByteArrayInputStream( baos.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream ois = newObjectInputStream(bais); clonedObj =(T) ois.readObject(); ois.close(); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } returnclonedObj; }
调用
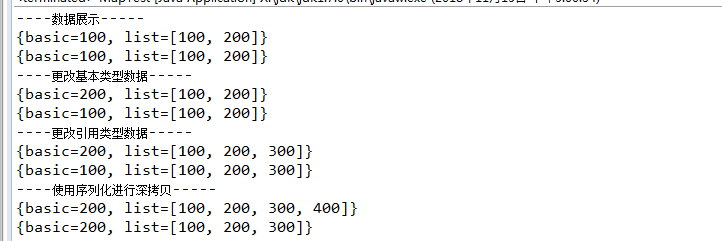
importjava.io.ByteArrayInputStream; importjava.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; importjava.io.ObjectInputStream; importjava.io.ObjectOutputStream; importjava.io.Serializable; importjava.util.ArrayList; importjava.util.HashMap; importjava.util.List; public classMapTest { public static voidmain(String[] args) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); list.add(100); list.add(200); HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); //放基本类型数据 map.put("basic", 100); //放对象 map.put("list", list); HashMap<String, Object> mapNew = new HashMap<String, Object>(); mapNew.putAll(map); System.out.println("----数据展示-----"); System.out.println(map); System.out.println(mapNew); System.out.println("----更改基本类型数据-----"); map.put("basic", 200); System.out.println(map); System.out.println(mapNew); System.out.println("----更改引用类型数据-----"); list.add(300); System.out.println(map); System.out.println(mapNew); System.out.println("----使用序列化进行深拷贝-----"); mapNew =clone(map); list.add(400); System.out.println(map); System.out.println(mapNew); } }
输出如下:
附:
【4. Map深拷贝的实现】转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/cxxjohnson/p/6258742.html