上一篇博客我们介绍了remote模式下Actor的创建,其实与local的创建并没有太大区别,一般情况下还是使用LocalActorRef创建了Actor。那么发消息是否意味着也是相同的呢?
既然actorOf还是委托给了LocalActorRef,那么在本地创建的Actor发消息还是跟以前一样的,那么如果如何给远程的Actor发消息呢?我们一般是通过actorSelection或者给远程Actor发送一个Identify消息,来接收对应的ActorRef,然后再发消息。我们来分析一下这两者的区别。
首先来看actorSelection,不管是用ActorSystem或者ActorContext的actorSelection方法,最终都是调用了ActorRefFactory对应的方法。
/**
* Construct an [[akka.actor.ActorSelection]] from the given path, which is
* parsed for wildcards (these are replaced by regular expressions
* internally). No attempt is made to verify the existence of any part of
* the supplied path, it is recommended to send a message and gather the
* replies in order to resolve the matching set of actors.
*/
def actorSelection(path: String): ActorSelection = path match {
case RelativeActorPath(elems) ⇒
if (elems.isEmpty) ActorSelection(provider.deadLetters, "")
else if (elems.head.isEmpty) ActorSelection(provider.rootGuardian, elems.tail)
else ActorSelection(lookupRoot, elems)
case ActorPathExtractor(address, elems) ⇒
ActorSelection(provider.rootGuardianAt(address), elems)
case _ ⇒
ActorSelection(provider.deadLetters, "")
}
我们发现它支持两种类型的path:RelativeActorPath、ActorPathExtractor。
/**
* Extractor for so-called “relative actor paths” as in “relative URI”, not in
* “relative to some actor”. Examples:
*
* * "grand/child"
* * "/user/hello/world"
*/
object RelativeActorPath extends PathUtils {
def unapply(addr: String): Option[immutable.Seq[String]] = {
try {
val uri = new URI(addr)
if (uri.isAbsolute) None
else Some(split(uri.getRawPath, uri.getRawFragment))
} catch {
case _: URISyntaxException ⇒ None
}
}
}
RelativeActorPath提取器比较简单,就是创建了一个URI对象,然后判断其是否为Absolute,如果是就返回None,如果不是就返回对应的elemes。对于远程Actor,我们一般会指定主机名、端口号,例如akka.tcp://actorSystemName@10.0.0.1:2552/user/actorName,根据URI的定义,这个URI的schema是akka.tcp,很显然是Absolute,那就会返回None。
/**
* Given an ActorPath it returns the Address and the path elements if the path is well-formed
*/
object ActorPathExtractor extends PathUtils {
def unapply(addr: String): Option[(Address, immutable.Iterable[String])] =
try {
val uri = new URI(addr)
uri.getRawPath match {
case null ⇒ None
case path ⇒ AddressFromURIString.unapply(uri).map((_, split(path, uri.getRawFragment).drop(1)))
}
} catch {
case _: URISyntaxException ⇒ None
}
}
ActorPathExtractor这个提取器的名称定义的是有问题的,既然actorSelection只支持两种类型的路径选择:本地和远程。第一个解析器定义成相对路径,那么后面一个就直接是绝对路径好了啊,为啥用ActorPathExtractor这样蹩脚的命名?难道本地模式下,就不是ActorPath提取器了?我们来看看对于akka.tcp://actorSystemName@10.0.0.1:2552/user/actorName提取出了什么。经调试,address是akka.tcp://actorSystemName@10.0.0.1:2552,elems就是后面的user、actorName了。
也就是说remote模式下,如果有host、prot等信息就会返回ActorSelection(provider.rootGuardianAt(address), elems)这个类。不过好像无论哪种情况都返回这个类,好尴尬啊,但传入的第一个参数是不同的:provider.rootGuardianAt(address)。也就是说actorSelection这个函数是不区分当前的模式的,只要含有host/port就会传入provider.rootGuardianAt(address),否则就传入provider.rootGuardian。如果在local模式下,也强制用actorSelection查找远程Actor会发生什么呢?我们来看看LocalActorRefProvider。
override def rootGuardianAt(address: Address): ActorRef =
if (address == rootPath.address) rootGuardian
else deadLetters
local模式下,如果待查询actor的地址就是本地地址,则直接在本地返回查找;否则就返回deadLetters。其实是无法查找远程actor的。那么RemoteActorRefProvider呢?
def rootGuardianAt(address: Address): ActorRef = {
if (hasAddress(address)) rootGuardian
else try {
new RemoteActorRef(transport, transport.localAddressForRemote(address),
RootActorPath(address), Nobody, props = None, deploy = None)
} catch {
case NonFatal(e) ⇒
log.error(e, "No root guardian at [{}]", address)
new EmptyLocalActorRef(this, RootActorPath(address), eventStream)
}
}
当然了,它也会判断一下本地地址是否包含待查询地址(防止多网卡或其他特殊情况),如果包含,则意味着是本地Actor交给rootGuardian;否则就创建RemoteActorRef。
分析到这里我们知道了,其实在remote模式下,actorSelection返回了一个RemoteActorRef,还记得这个类的作用嘛?我们之前简单分析过,它其实是对远程Acotor的一个本地网络代理,也就是说所有通过actorSelection发送给远程actor的消息,都会经过他中转。
我们继续分析ActorSelection的源码
/**
* Construct an ActorSelection from the given string representing a path
* relative to the given target. This operation has to create all the
* matching magic, so it is preferable to cache its result if the
* intention is to send messages frequently.
*/
def apply(anchorRef: ActorRef, elements: Iterable[String]): ActorSelection = {
val compiled: immutable.IndexedSeq[SelectionPathElement] = elements.collect({
case x if !x.isEmpty ⇒
if ((x.indexOf('?') != -1) || (x.indexOf('*') != -1)) SelectChildPattern(x)
else if (x == "..") SelectParent
else SelectChildName(x)
})(scala.collection.breakOut)
new ActorSelection with ScalaActorSelection {
override val anchor = anchorRef
override val path = compiled
}
}
很显然这里的anchorRef是上面创建的RemoteActorRef实例,其中ActorSelection的anchor(锚定)是anchorRef。至此,一个ActorSelection创建完毕。那么如何发消息呢?这就需要分析tell或者!方法了。
def tell(msg: Any, sender: ActorRef): Unit =
ActorSelection.deliverSelection(anchor.asInstanceOf[InternalActorRef], sender,
ActorSelectionMessage(msg, path, wildcardFanOut = false))
其实乍一看,我们应该明白,这就是在deliverSelection函数内部,把消息封装成ActorSelectionMessage发送给了anchor。
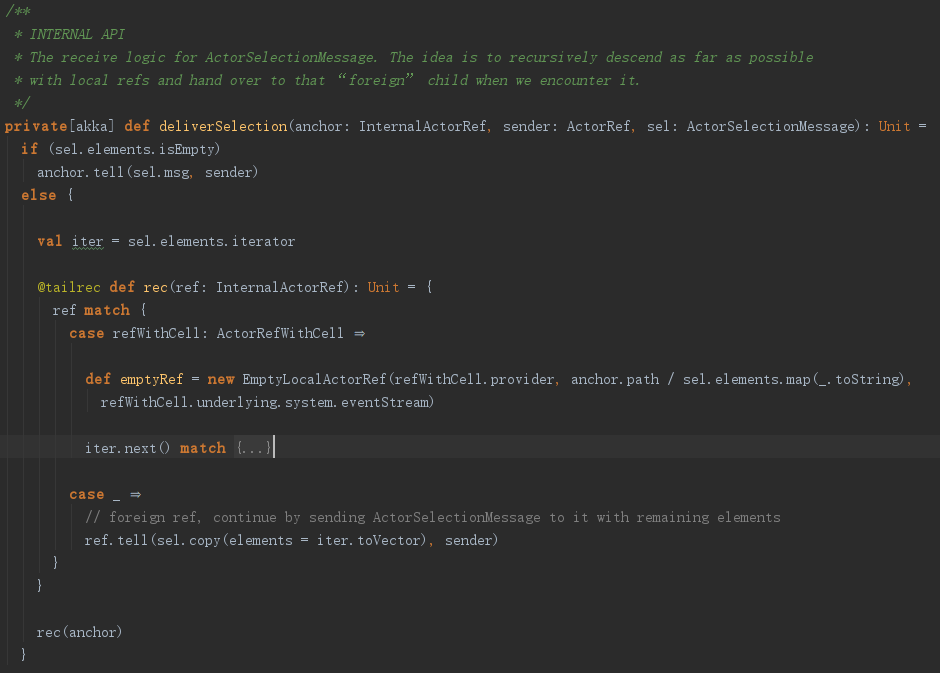
该函数首先判断sel的elements是否为空,很显然不为空,进入rec函数。该函数比较复杂而且还是一个尾递归函数,但我们知道此处的ref就是RemoteActorRef,那么RemoteActorRef是不是一个ActorRefWithCell呢?
private[akka] class RemoteActorRef private[akka] ( remote: RemoteTransport, val localAddressToUse: Address, val path: ActorPath, val getParent: InternalActorRef, props: Option[Props], deploy: Option[Deploy]) extends InternalActorRef with RemoteRef
那么rec就会走到case _的逻辑,也就是把消息转发给了前面创建的RemoteActorRef,我们来看看这个示例是如何实现tell的。
override def !(message: Any)(implicit sender: ActorRef = Actor.noSender): Unit = {
if (message == null) throw InvalidMessageException("Message is null")
try remote.send(message, OptionVal(sender), this) catch handleException(message, sender)
}
RemoteActorRef这个类,通过remote把消息发送出去了,那么remote是什么呢?RemoteTransport是不是很熟悉?在ActorSystem启动的时候我们分析过这个对象,它是Remoting类的实例,Remoting里面send方法是怎样的呢?
override def send(message: Any, senderOption: OptionVal[ActorRef], recipient: RemoteActorRef): Unit = endpointManager match {
case Some(manager) ⇒ manager.tell(Send(message, senderOption, recipient), sender = senderOption getOrElse Actor.noSender)
case None ⇒ throw new RemoteTransportExceptionNoStackTrace("Attempted to send remote message but Remoting is not running.", null)
}
它又把消息转发给了manager,而manager就是endpointManager。endpointManager是不是也比较眼熟呢?前面文章中我们也见到过,这是一个EndpointManager实例,而EndpointManager是一个Actor。请注意这里用Send又对message进行了封装。EndpointManager是如何对Send消息进行反应的呢?
case s @ Send(message, senderOption, recipientRef, _) ⇒
val recipientAddress = recipientRef.path.address
def createAndRegisterWritingEndpoint(): ActorRef = {
endpoints.registerWritableEndpoint(
recipientAddress,
uid = None,
createEndpoint(
recipientAddress,
recipientRef.localAddressToUse,
transportMapping(recipientRef.localAddressToUse),
settings,
handleOption = None,
writing = true))
}
endpoints.writableEndpointWithPolicyFor(recipientAddress) match {
case Some(Pass(endpoint, _)) ⇒
endpoint ! s
case Some(Gated(timeOfRelease)) ⇒
if (timeOfRelease.isOverdue()) createAndRegisterWritingEndpoint() ! s
else extendedSystem.deadLetters ! s
case Some(Quarantined(uid, _)) ⇒
// timeOfRelease is only used for garbage collection reasons, therefore it is ignored here. We still have
// the Quarantined tombstone and we know what UID we don't want to accept, so use it.
createAndRegisterWritingEndpoint() ! s
case None ⇒
createAndRegisterWritingEndpoint() ! s
}
分析以上逻辑,简单来看,会先判断是不是存在一个endpoint,如果存在说明链接已经建立,可以直接发送,否则出于其他状态,就重新创建endpoint,然后把消息转发给该endpoint。
def registerWritableEndpoint(address: Address, uid: Option[Int], endpoint: ActorRef): ActorRef =
addressToWritable.get(address) match {
case Some(Pass(e, _)) ⇒
throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"Attempting to overwrite existing endpoint [$e] with [$endpoint]")
case _ ⇒
// note that this overwrites Quarantine marker,
// but that is ok since we keep the quarantined uid in addressToRefuseUid
addressToWritable += address → Pass(endpoint, uid)
writableToAddress += endpoint → address
endpoint
}
registerWritableEndpoint没有太复杂的逻辑,就是查询addressToWritable这个HashMap,如果不存在则把对应的endpoint加入缓存,并返回endpoint。而endpoint是通过createEndpoint创建的。
private def createEndpoint(
remoteAddress: Address,
localAddress: Address,
transport: AkkaProtocolTransport,
endpointSettings: RemoteSettings,
handleOption: Option[AkkaProtocolHandle],
writing: Boolean): ActorRef = {
require(transportMapping contains localAddress, "Transport mapping is not defined for the address")
// refuseUid is ignored for read-only endpoints since the UID of the remote system is already known and has passed
// quarantine checks
val refuseUid = endpoints.refuseUid(remoteAddress)
if (writing) context.watch(context.actorOf(
RARP(extendedSystem).configureDispatcher(ReliableDeliverySupervisor.props(
handleOption,
localAddress,
remoteAddress,
refuseUid,
transport,
endpointSettings,
AkkaPduProtobufCodec,
receiveBuffers)).withDeploy(Deploy.local),
"reliableEndpointWriter-" + AddressUrlEncoder(remoteAddress) + "-" + endpointId.next()))
else context.watch(context.actorOf(
RARP(extendedSystem).configureDispatcher(EndpointWriter.props(
handleOption,
localAddress,
remoteAddress,
refuseUid,
transport,
endpointSettings,
AkkaPduProtobufCodec,
receiveBuffers,
reliableDeliverySupervisor = None)).withDeploy(Deploy.local),
"endpointWriter-" + AddressUrlEncoder(remoteAddress) + "-" + endpointId.next()))
}
createEndpoint最终创建了ReliableDeliverySupervisor这个Actor,也就是说RemoteActorRef最终又把消息发送给了ReliableDeliverySupervisor,ReliableDeliverySupervisor收到消息去调用handleSend方法。
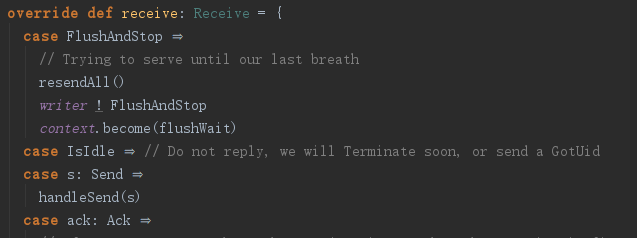
private def handleSend(send: Send): Unit =
if (send.message.isInstanceOf[SystemMessage]) {
val sequencedSend = send.copy(seqOpt = Some(nextSeq()))
tryBuffer(sequencedSend)
// If we have not confirmed the remote UID we cannot transfer the system message at this point just buffer it.
// GotUid will kick resendAll() causing the messages to be properly written.
// Flow control by not sending more when we already have many outstanding.
if (uidConfirmed && resendBuffer.nonAcked.size <= settings.SysResendLimit)
writer ! sequencedSend
} else writer ! send
除去特殊情况,用户发的普通消息又发送给了writer,艾玛我去,真是绕啊。writer是什么呢?
var writer: ActorRef = createWriter()
private def createWriter(): ActorRef = {
context.watch(context.actorOf(RARP(context.system).configureDispatcher(EndpointWriter.props(
handleOrActive = currentHandle,
localAddress = localAddress,
remoteAddress = remoteAddress,
refuseUid,
transport = transport,
settings = settings,
AkkaPduProtobufCodec,
receiveBuffers = receiveBuffers,
reliableDeliverySupervisor = Some(self))).withDeploy(Deploy.local), "endpointWriter"))
}
很显然这又是一个ACor!!!哎,继续查找EndpointWriter这个Actor喽
def receive = if (handle.isEmpty) initializing else writing
val writing: Receive = {
case s: Send ⇒
if (!writeSend(s)) {
enqueueInBuffer(s)
scheduleBackoffTimer()
context.become(buffering)
}
// We are in Writing state, so buffer is empty, safe to stop here
case FlushAndStop ⇒
flushAndStop()
case AckIdleCheckTimer if ackDeadline.isOverdue() ⇒
trySendPureAck()
}
这个Actor会先判断是否已经初始化,这里就假设初始化吧,初始化之后就会进入writing这个偏函数,对send类型的消息,又调用了writeSend函数。
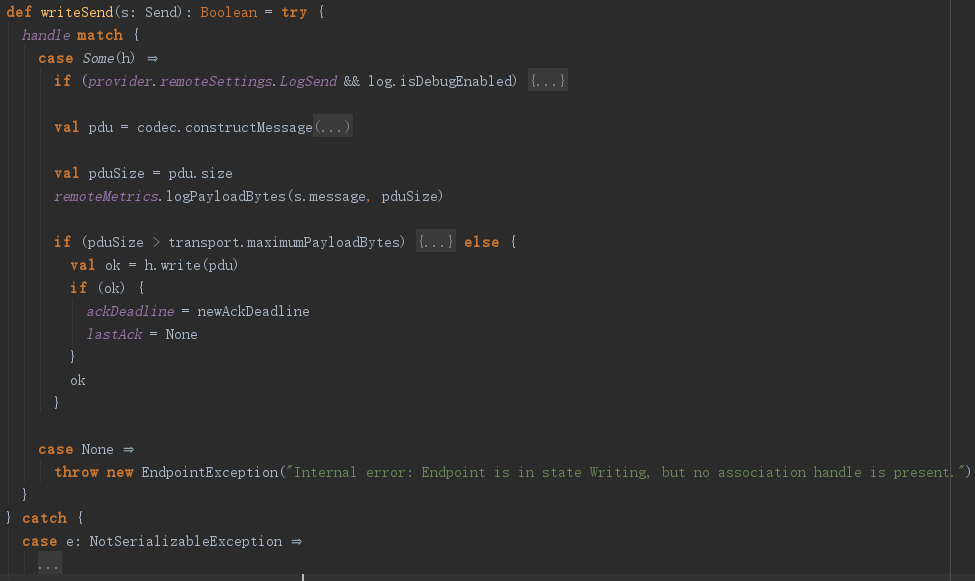
这个函数简单来看,就是调用codec对消息进行序列化,然后创建了一个pdu,最终把pdu通过handle的write发送出去。handle又是什么呢?
var handle: Option[AkkaProtocolHandle] = handleOrActive
private[remote] class AkkaProtocolHandle(
_localAddress: Address,
_remoteAddress: Address,
val readHandlerPromise: Promise[HandleEventListener],
_wrappedHandle: AssociationHandle,
val handshakeInfo: HandshakeInfo,
private val stateActor: ActorRef,
private val codec: AkkaPduCodec)
extends AbstractTransportAdapterHandle(_localAddress, _remoteAddress, _wrappedHandle, AkkaScheme) {
override def write(payload: ByteString): Boolean = wrappedHandle.write(codec.constructPayload(payload))
override def disassociate(): Unit = disassociate(Unknown)
def disassociate(info: DisassociateInfo): Unit = stateActor ! DisassociateUnderlying(info)
}
handle最终是一个AkkaProtocolHandle,这个对象我们不再具体分析,我们可以认为这是一个本地与远程地址链接的通道,通过这个通道就可以与远程actor发送消息了。
分析到这个地方,actorSelection与远程通信的过程大概就梳理清楚了。为了方便理解,作者特意辛苦的画了一个流程图,以供参考。细心的读者一定会问,那我的消息通过handle发送出去了,对方怎么接收呢?接收之后怎么发送到指定actor的邮箱呢?这一点我们后面再分析。
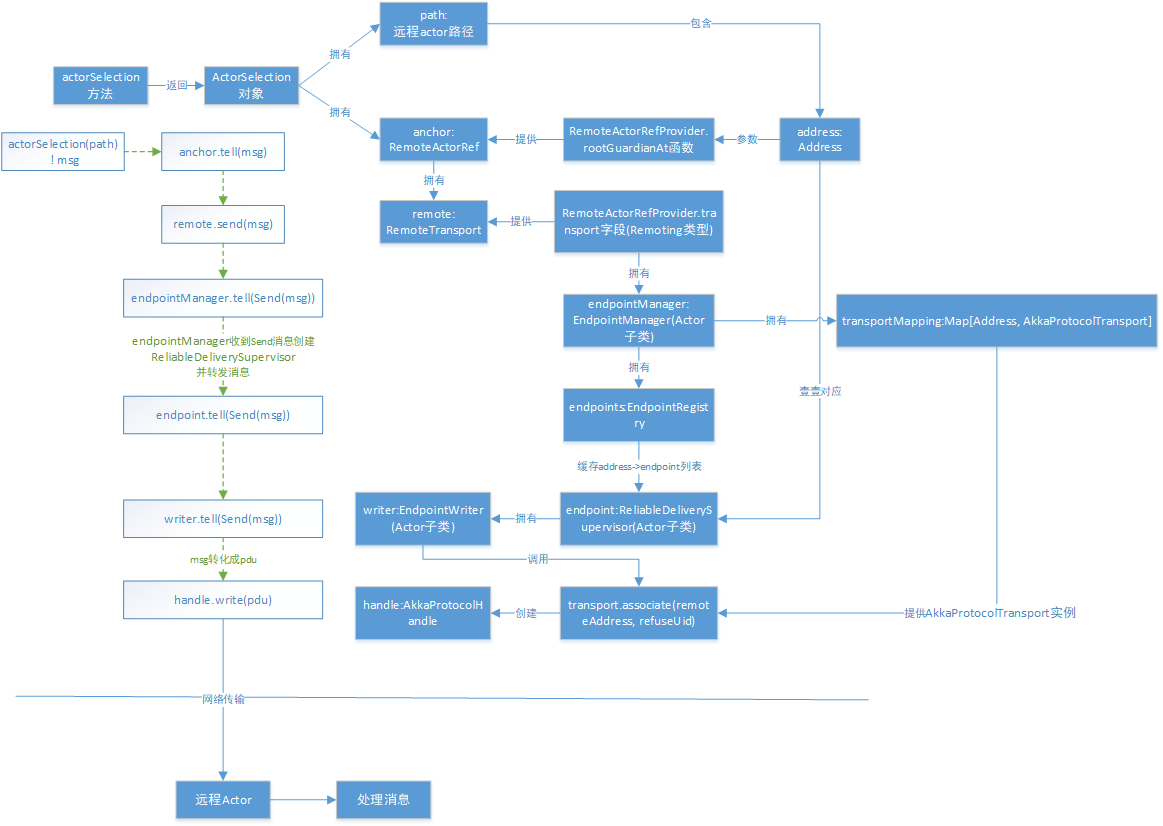
actorSelection分析清楚了,剩下的就是通过ActorRef发送消息了。那么如何得到远程Actor的ActorRef呢?当然是“问”它了啊,怎么“问”呢?发消息啊。发什么消息呢?
/** * A message all Actors will understand, that when processed will reply with * [[akka.actor.ActorIdentity]] containing the `ActorRef`. The `messageId` * is returned in the `ActorIdentity` message as `correlationId`. */ @SerialVersionUID(1L) final case class Identify(messageId: Any) extends AutoReceivedMessage with NotInfluenceReceiveTimeout
官网对Identify的注释非常清楚,这个消息继承了AutoReceivedMessage,所有的Actor都理解该消息,且受到该消息后会返回akka.actor.ActorIdentity消息,里面包含当前Actor的ActorRef。那么所有的Actor为啥都理解该消息呢?
//Memory consistency is handled by the Mailbox (reading mailbox status then processing messages, then writing mailbox status
final def invoke(messageHandle: Envelope): Unit = {
val influenceReceiveTimeout = !messageHandle.message.isInstanceOf[NotInfluenceReceiveTimeout]
try {
currentMessage = messageHandle
if (influenceReceiveTimeout)
cancelReceiveTimeout()
messageHandle.message match {
case msg: AutoReceivedMessage ⇒ autoReceiveMessage(messageHandle)
case msg ⇒ receiveMessage(msg)
}
currentMessage = null // reset current message after successful invocation
} catch handleNonFatalOrInterruptedException { e ⇒
handleInvokeFailure(Nil, e)
} finally {
if (influenceReceiveTimeout)
checkReceiveTimeout // Reschedule receive timeout
}
}
def autoReceiveMessage(msg: Envelope): Unit = {
if (system.settings.DebugAutoReceive)
publish(Debug(self.path.toString, clazz(actor), "received AutoReceiveMessage " + msg))
msg.message match {
case t: Terminated ⇒ receivedTerminated(t)
case AddressTerminated(address) ⇒ addressTerminated(address)
case Kill ⇒ throw ActorKilledException("Kill")
case PoisonPill ⇒ self.stop()
case sel: ActorSelectionMessage ⇒ receiveSelection(sel)
case Identify(messageId) ⇒ sender() ! ActorIdentity(messageId, Some(self))
}
}
如果读者看过我之前分析的文章对上面的代码一定还有印象,它是ActorCell里面处理消息的两个函数,invoke会先判断消息类型是不是AutoReceivedMessage,如果是就自己处理了,不会去调用开发者自定义的receive函数。而Identify属于AutoReceivedMessage,收到后给sender发送了ActorIdentity消息,该消息的第二个参数是当前Actor的ActorFef变量。这样本地的actor收到远程actor返回的ActorIdentity,就可以通过对方的ActorRef给它发送消息了。当然本地actor收到的ActorIdentity消息中,第二个参数应该是一个RemoteActorRef类型。如何通过RemoteActorRef发送消息,上文已经分析清楚了,其实actorSelection最终也是通过远程actor的ActorPath创建了对应的RemoteActorRef,来发送消息的。
至此给远程actor发消息的两种方法就讲解完毕了。其实还有第三种方式,就是在本地创建一个远程Actor,当然了最终还是需要通过RemoteActorRef发消息的,这个具体就不再详细介绍了。