在学完Collection接口,以及其下面的List接口,了解几种基本的集合实现类如ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector后,可以做一个简单的斗地主,这里记录一下使用ArrayList来模拟实现斗地主的组合牌洗牌发牌看牌动作。
案例分析
1. 组装54张扑克牌
2. 将54张牌顺序打乱
3. 三个玩家参与游戏,三人交替摸牌,每人17张牌,最后三张留作底牌。
4. 查看三人各自手中的牌(按照牌的大小排序)、底牌
组合牌
使用集合,循环遍历完成。
1 //1 组合牌 2 //定义一个集合保存一副牌 3 ArrayList<String> poker=new ArrayList<String>(); 4 //定义花色 5 String[] colors={"♠","♦","♣","♥"}; 6 //定义序号 7 String[] numbers={"3","4","5","6","7","8","9","10","J","Q","K","A","2"}; 8 //定义大小王 9 String[] joker=new String[]{"大王","小王"}; 10 //组合牌 11 for (String color : colors) { 12 for (String number : numbers) { 13 poker.add(color+number); 14 } 15 } 16 poker.add(joker[0]); 17 poker.add(joker[1]); 18 /*System.out.println(poker);//打桩测试*/
洗牌
使用Collections工具类的静态方法 public static void shuffle(List<?> list)完成。
1 //2 洗牌 2 Collections.shuffle(poker); 3 /*System.out.println(poker);*/
查看shuffle源码,发现底层调用了shuffle(list,rnd)方法,其中list为传入的集合,rnd为一个Random随机数类。另外Random是一个线程安全的类,在高并发情况下可能会导致性能下降,如果需要考虑高并发可以使用ThreadLocalRandom,如果是密码相关的应用使用SecureRandom。
1 public static void shuffle(List<?> list) { 2 Random rnd = r; 3 if (rnd == null) 4 r = rnd = new Random(); // harmless race. 5 shuffle(list, rnd); 6 }
继续查看shuffle方法,发现有两种情况,一种是list集合的大小小于5,或者list集合属于RandomAccess实例时执行swap方法,另外一种情况是先将list转换成一个数组,然后对数组进行随机交换。前一种情况是针对底层是数组的集合,如ArrayList,后面一种情况是针对底层是链表实现的集合,如LinkedList,两种选择只是选择更优的算法,让执行更快。
1 public static void shuffle(List<?> list, Random rnd) { 2 int size = list.size(); 3 if (size < SHUFFLE_THRESHOLD || list instanceof RandomAccess) { 4 for (int i=size; i>1; i--) 5 swap(list, i-1, rnd.nextInt(i)); 6 } else { 7 Object arr[] = list.toArray(); 8 9 // Shuffle array 10 for (int i=size; i>1; i--) 11 swap(arr, i-1, rnd.nextInt(i)); 12 13 // Dump array back into list 14 // instead of using a raw type here, it's possible to capture 15 // the wildcard but it will require a call to a supplementary 16 // private method 17 ListIterator it = list.listIterator(); 18 for (int i=0; i<arr.length; i++) { 19 it.next(); 20 it.set(arr[i]); 21 } 22 } 23 }
查看底层是数组的swap方法,以及for循环,发现先从数组最后一个元素开始比较,逐一往前面移动下标,直到第二个元素才停止交换。交换的就是当前位置的元素和当前位置之前的随机位置的元素,这点从rnd.nextInt(i)能够看出来。
1 public static void swap(List<?> list, int i, int j) { 2 // instead of using a raw type here, it's possible to capture 3 // the wildcard but it will require a call to a supplementary 4 // private method 5 final List l = list; 6 l.set(i, l.set(j, l.get(i))); 7 }
查看底层是链表的swap方法,就是交换相互位置的元素,交换情况跟上面类似,也是交换当前位置元素和当前位置之前随机位置的元素。
1 private static void swap(Object[] arr, int i, int j) { 2 Object tmp = arr[i]; 3 arr[i] = arr[j]; 4 arr[j] = tmp; 5 }
发牌
发牌需要创建4个容器接收牌。
1 //3 发牌,ArrayList底层是一个数组,根据索引来发牌 2 //定义三个集合,用于储存发的牌 3 ArrayList<String> player1=new ArrayList<String>(); 4 ArrayList<String> player2=new ArrayList<String>(); 5 ArrayList<String> player3=new ArrayList<String>(); 6 ArrayList<String> leftPoker=new ArrayList<String>();//底牌 7 //发牌 8 for (int i = 0; i < poker.size(); i++) { 9 //当索引为51时开始,不再发牌,留作底牌,其他发掉 10 if(i>=51){ 11 leftPoker.add(poker.get(i)); 12 }else if(i%3==0){ 13 player1.add(poker.get(i)); 14 }else if(i%3==1){ 15 player2.add(poker.get(i)); 16 }else if(i%3==2){ 17 player3.add(poker.get(i)); 18 } 19 }
看牌
看牌就是打印集合中的内容。
1 //4 看牌 2 System.out.println("赌王的牌:"+player1); 3 System.out.println("赌圣的牌:"+player2); 4 System.out.println("赌仙的牌:"+player3); 5 System.out.println("底牌"+leftPoker);
完整代码
 View Code
View Code控制台打印结果
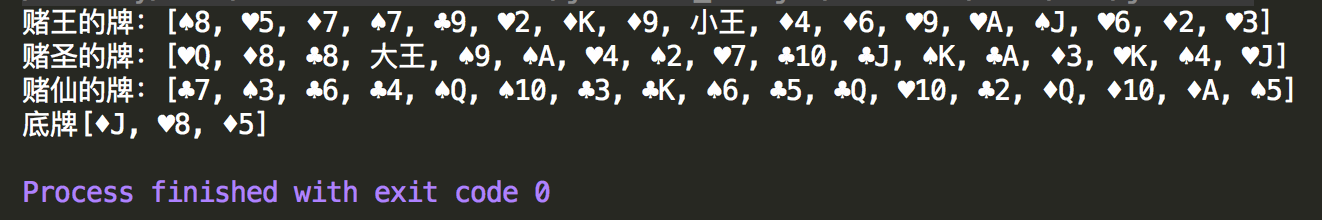
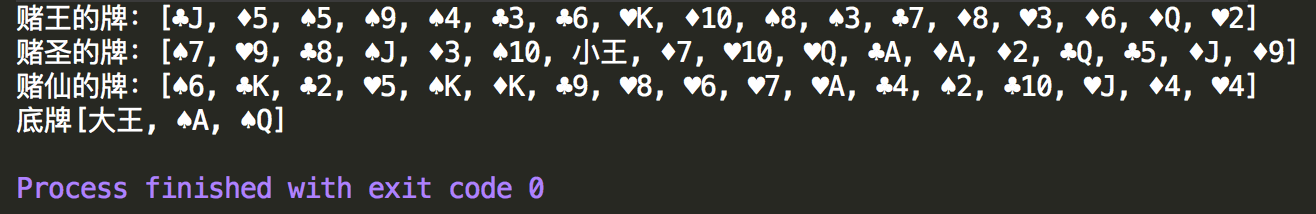
以上实现了一个简单的模拟斗地主发牌动作,加深对集合的理解。
参考博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38237873/article/details/83003422