一、imguag简介
备选参考的图片扩大框架:kears Imagedatagenerator
参考文档
https://imgaug.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
https://github.com/aleju/imgaug
python3.7
numpy1.17.0
参数选择:
- 如果可能,应使用最近邻插值或线性插值,因为它们比其他选项要快得多。使用插值的大多数增强器提供
order参数(0 =最近邻,1 =线性)或interpolation参数(“最近邻”,“线性”)。 keep_size=True在所有更改图像尺寸的增强器中,默认设置为使用。这很方便,因为它可以确保图像尺寸不会因扩展而改变。但是,它的确会导致明显的性能下降,通常不仅仅使带宽减半。keep_size=False尽可能尝试 。您仍然可以在扩充后或使用来手动调整图像的大小KeepSizeByResize(Sequential(<augmenters>))。- 当增强器提供以用户定义的方式填充新创建的像素的模式(例如
pad_mode=constant,Pad以指定的恒定颜色填充所有填充的像素)时,使用edge代替constant通常不会带来明显的性能损失。
具体的增强器建议:
- 对于存在元素级同级的增强器(例如
Multiply和MultiplyElementwise),元素级增强器通常比非元素级的显着慢。 - 如果需要模糊处理,
AverageBlur是最快的选择,其次是GaussianBlur。 - 在较粗糙的图像(例如
CoarseDropoutvsDropout)上运行的增强器可能比其非粗略的兄弟姐妹快得多。 - 对比度归一化增强器在性能上均具有可比性,但基于直方图的增强器明显较慢。
PiecewiseAffine是一个非常慢的增幅器,通常应由ElasticTransformation代替,ElasticTransformation可以实现类似的输出,并且速度要快得多。Superpixels是一个相当缓慢的增强器,通常应该包装起来,例如Sometimes不要经常使用它并降低其性能影响。- 除天气
FastSnowyLandscape增速器外,其他增速器都相当缓慢,仅在合理时才使用。
图片
以下数字代表小图像(64x64x3)和大图像(224x224x3)。B=1表示的批量大小1,B=128其中一个128。
https://imgaug.readthedocs.io/en/latest/source/performance.html
二、安装imguag
官网文档:https://imgaug.readthedocs.io/en/latest/source/installation.html
在anaconda上安装
conda config --add channels conda-forge
conda install imgaug三、imguag使用方法
https://blog.csdn.net/limiyudianzi/article/details/86497305
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38451119/article/details/82417412
例一:边界框编#边界框
import imgaug as ia import imgaug.augmenters as iaa from imgaug.augmentables.bbs import BoundingBox, BoundingBoxesOnImage ia.seed(1) image = ia.quokka(size=(256, 256)) bbs = BoundingBoxesOnImage([ BoundingBox(x1=65, y1=100, x2=200, y2=150), BoundingBox(x1=150, y1=80, x2=200, y2=130) ], shape=image.shape) seq = iaa.Sequential([ iaa.Multiply((1.2, 1.5)), # change brightness, doesn't affect BBs iaa.Affine( translate_px={"x": 40, "y": 60}, scale=(1.2, 1.2) ) # 在x / y轴上平移40 / 60px,缩放到50-70%,影响BB ]) # Augment BBs and images. image_aug, bbs_aug = seq(image=image, bounding_boxes=bbs) # print coordinates before/after augmentation (see below) # use .x1_int, .y_int, ... to get integer coordinates for i in range(len(bbs.bounding_boxes)): before = bbs.bounding_boxes[i] after = bbs_aug.bounding_boxes[i] print("BB %d: (%.4f, %.4f, %.4f, %.4f) -> (%.4f, %.4f, %.4f, %.4f)" % ( i, before.x1, before.y1, before.x2, before.y2, after.x1, after.y1, after.x2, after.y2) ) # image with BBs before/after augmentation (shown below) image_before = bbs.draw_on_image(image, size=2) image_after = bbs_aug.draw_on_image(image_aug, size=2, color=[0, 0, 255]) path_name='F:/esint/smoking_Recognition/test/starzhai' #设置自己的保存路径
img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image_before) time.sleep(1) #以当前时间命名,每隔一秒保存一次图片 img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image_after) #能够进行的操作 平移,放缩,旋转(?怎么整?)
实现效果:
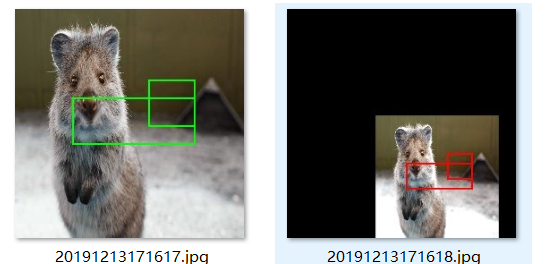
例二:热力图变换
#热力图 import imageio import numpy as np import imgaug as ia import imgaug.augmenters as iaa from imgaug.augmentables.heatmaps import HeatmapsOnImage ia.seed(1) # Load an example image (uint8, 128x128x3). image = ia.quokka(size=(128, 128), extract="square") depth = np.linspace(0, 50, 128).astype(np.float32) # 128 values from 0.0 to 50.0 depth = np.tile(depth.reshape(1, 128), (128, 1)) # change to a horizontal gradient depth[64-2:64+2, 16:128-16] = 0.75 * 50.0 # line from left to right depth[16:128-16, 64-2:64+2] = 1.0 * 50.0 # line from top to bottom depth = HeatmapsOnImage(depth, shape=image.shape, min_value=0.0, max_value=50.0) depth = depth.avg_pool(2) # Define our augmentation pipeline. seq = iaa.Sequential([ iaa.Dropout([0.05, 0.2]), # drop 5% or 20% of all pixels iaa.Sharpen((0.0, 1.0)), # sharpen the image iaa.Affine(rotate=(-45, 45)), # rotate by -45 to 45 degrees (affects heatmaps) iaa.ElasticTransformation(alpha=50, sigma=5) # apply water effect (affects heatmaps) ], random_order=True) # Augment images and heatmaps. images_aug = [] heatmaps_aug = [] for _ in range(5): images_aug_i, heatmaps_aug_i = seq(image=image, heatmaps=depth) images_aug.append(images_aug_i) heatmaps_aug.append(heatmaps_aug_i) cells = [] for image_aug, heatmap_aug in zip(images_aug, heatmaps_aug): cells.append(image) # column 1 cells.append(image_aug) # column 2 cells.append(heatmap_aug.draw_on_image(image_aug)[0]) # column 3 cells.append(heatmap_aug.draw(size=image_aug.shape[:2])[0]) # column 4 cells.append(heatmap_aug.draw(size=image_aug.shape[:2], cmap=None)[0]) # column 5 path_name='F:/esint/smoking_Recognition/test/starzhai' img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image_aug) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,heatmap_aug.draw_on_image(image_aug)[0]) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,heatmap_aug.draw(size=image_aug.shape[:2])[0]) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,heatmap_aug.draw(size=image_aug.shape[:2], cmap=None)[0]) time.sleep(1)
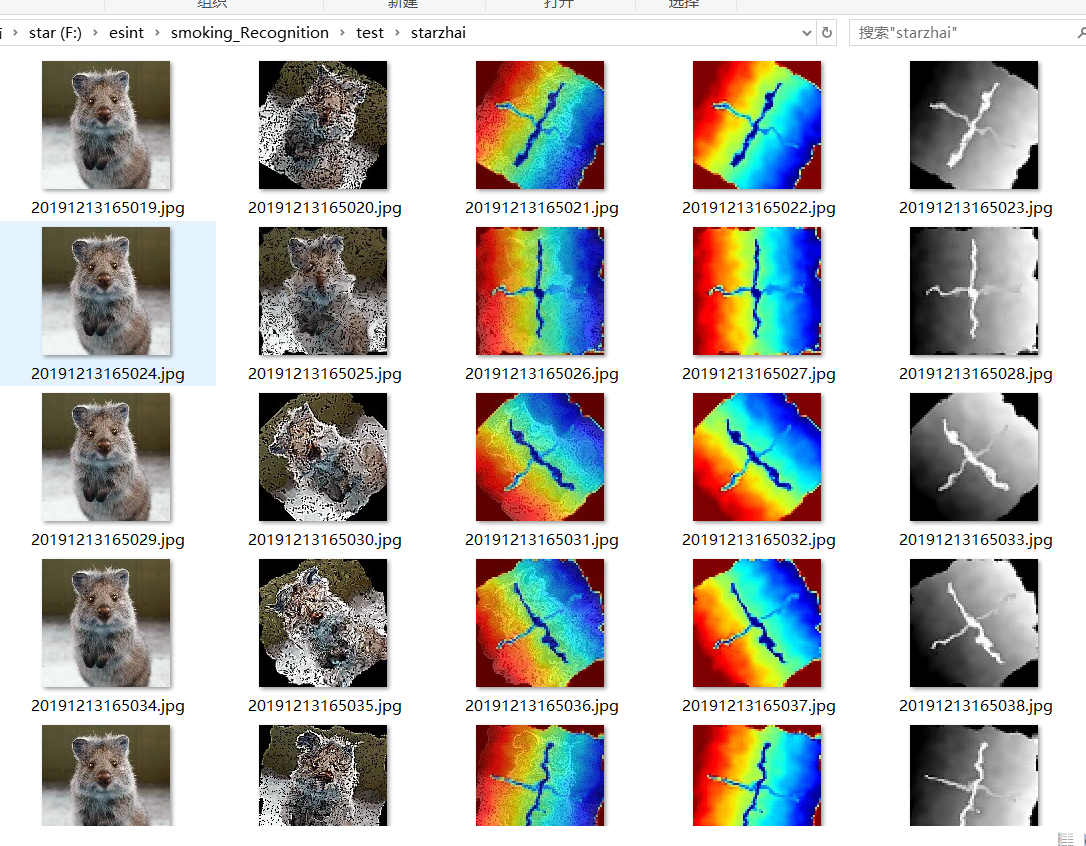
voc数据集的扩增方法
https://blog.csdn.net/coooo0l/article/details/84492916
2.数据变换类别
iaa.AdditiveGaussianNoise(scale=0.2*255)1#加噪声
iaa.GaussianBlur(sigma=(0.0, 3.0)1#变模糊
iaa.AllChannelsCLAHE(clip_limit=(1, 10))#图像增强
iaa.Affine(rotate=-45)#左旋转45度
iaa.Affine(rotate=45)#右旋转45度
iaa.Affine(scale=(0.4, 0.7))#Scale images to a value of 50 to 150% of their original size变大
iaa.Affine(scale=(1.3, 1.6))#Scale images to a value of 50 to 150% of their original size#缩小
iaa.GammaContrast((0.5, 2.0), per_channel=True)#色相变暗
iaa.Grayscale(alpha=(0.0, 1.0))#色相变灰
iaa.PiecewiseAffine(scale=(0.01, 0.05))#扭曲图像
四、批量处理图片生成对应xml文件详细实现过程
①默认老鼠图片以及标注框坐标,输出10张图片及其标注框坐标
#边界框 import imgaug as ia import imgaug.augmenters as iaa from imgaug.augmentables.bbs import BoundingBox, BoundingBoxesOnImage import time import cv2 #图像归一化 ia.seed(1) image = ia.quokka(size=(256, 256)) bbs = BoundingBoxesOnImage([ BoundingBox(x1=65, y1=100, x2=200, y2=150), BoundingBox(x1=150, y1=80, x2=200, y2=130) ], shape=image.shape) #aug1=iaa.Affine(rotate=45)#右旋转45度 #seq = iaa.Sequential([ aug1=iaa.AdditiveGaussianNoise(scale=0.2*255)#加噪声 aug2=iaa.GaussianBlur(sigma=(0.0, 3.0)) #变模糊 aug3=iaa.AllChannelsCLAHE(clip_limit=(1,10))#图像增强 aug4=iaa.Affine(rotate=-45)#左旋转45度 aug5=iaa.Affine(rotate=45)#右旋转45度 aug6=iaa.Affine(scale=(0.4, 0.7))#Scale images to a value of 50 to 150% of their original size变大 aug7=iaa.Affine(scale=(1.3, 1.6))#Scale images to a value of 50 to 150% of their original size#缩小 aug8=iaa.GammaContrast((2.5, 2.5), per_channel=True)#色相变暗 aug9=iaa.Grayscale(alpha=(0.9))#色相变灰 aug10=iaa.PiecewiseAffine(scale=(0.08))#扭曲图像 #]) #image_aug, bbs_aug = aug1(image=image, bounding_boxes=bbs) image1,bbs1=aug1(image=image, bounding_boxes=bbs) image2,bbs2=aug2(image=image, bounding_boxes=bbs) image3,bbs3=aug3(image=image, bounding_boxes=bbs) image4,bbs4=aug4(image=image, bounding_boxes=bbs) image5,bbs5=aug5(image=image, bounding_boxes=bbs) image6,bbs6=aug6(image=image, bounding_boxes=bbs) image7,bbs7=aug7(image=image, bounding_boxes=bbs) image8,bbs8=aug8(image=image, bounding_boxes=bbs) image9,bbs9=aug9(image=image, bounding_boxes=bbs) image10,bbs10=aug10(image=image, bounding_boxes=bbs) for i in range(len(bbs.bounding_boxes)): before = bbs.bounding_boxes[i] after = bbs_aug.bounding_boxes[i] print("BB %d: (%.4f, %.4f, %.4f, %.4f) -> (%.4f, %.4f, %.4f, %.4f)" % ( i, before.x1, before.y1, before.x2, before.y2, after.x1, after.y1, after.x2, after.y2) ) #画标注框 #image_before = bbs.draw_on_image(image, size=2) #image_after = bbs_aug.draw_on_image(image_aug, size=2, color=[0, 0, 255]) image1 = bbs1.draw_on_image(image1, size=2) image2 = bbs2.draw_on_image(image2, size=2) image3 = bbs3.draw_on_image(image3, size=2) image4 = bbs4.draw_on_image(image4, size=2) image5 = bbs5.draw_on_image(image5, size=2) image6 = bbs6.draw_on_image(image6, size=2) image7 = bbs7.draw_on_image(image7, size=2) image8 = bbs8.draw_on_image(image8, size=2) image9 = bbs9.draw_on_image(image9, size=2) image10 = bbs10.draw_on_image(image10, size=2) path_name='F:/esint/smoking_Recognition/test/imgaug' img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image1) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image2) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image3) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image4) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image5) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image6) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image7) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image8) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image9) time.sleep(1) img_name = '%s/%s.jpg'%(path_name,time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S",time.localtime())) cv2.imwrite(img_name,image10)
②更改输入图片,更改色阶(不要发紫的颜色)
③通过xml文件中的矩形框信息在图片上画框
④生成图片和对应的xml文件
⑤检测xml文件中的信息是否准确的落在原图合适的位置上
⑥批量生成图片及其对应的xml文件(使xml文件名与图片名一一对应)