RocketMQ 是阿里巴巴开源的分布式消息中间件,它借鉴了 Kafka 实现,支持消息订阅与发布、顺序消息、事务消息、定时消息、消息回溯、死信队列等功能。RocketMQ 架构上主要分为四部分,如下图所示:
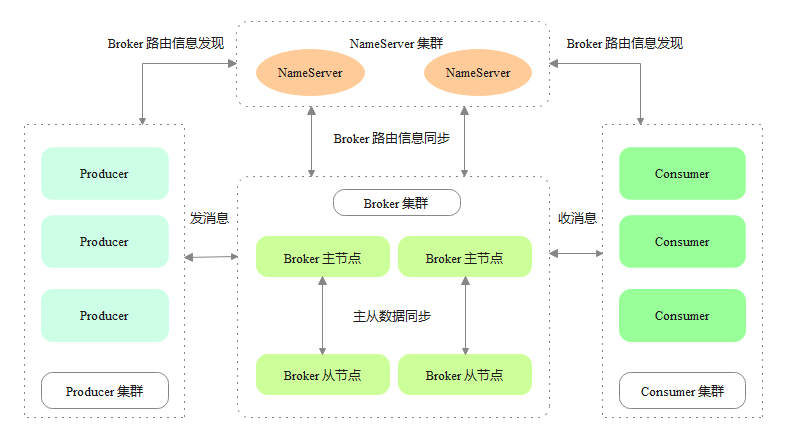
Producer:消息生产者,支持分布式集群方式部署。
Consumer:消息消费者,支持分布式集群方式部署。
NameServer:名字服务,是一个非常简单的 Topic 路由注册中心,支持 Broker 的动态注册与发现,Producer 和 Consumer 通过 NameServer 动态感知 Broker 的路由信息。
Broker:Broker 主要负责消息的存储、转发和查询。
本文基于 Apache RocketMQ 4.9.1 版本剖析 Broker 中的消息存储模块是如何设计的。
二、存储架构RocketMQ 的消息文件路径如图所示。
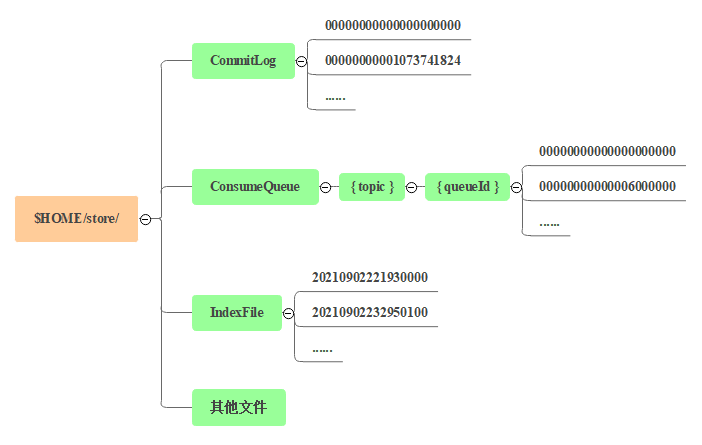
CommitLog
消息主体以及元数据的存储主体,存储 Producer 端写入的消息主体内容,消息内容不是定长的。单个文件大小默认1G, 文件名长度为 20 位,左边补零,剩余为起始偏移量,比如 00000000000000000000 代表了第一个文件,起始偏移量为 0,文件大小为 1G=1073741824;当第一个文件写满了,第二个文件为 00000000001073741824,起始偏移量为 1073741824,以此类推。
ConsumeQueue
消息消费队列,Consumequeue 文件可以看成是基于 CommitLog 的索引文件。ConsumeQueue 文件采取定长设计,每一个条目共 20 个字节,分别为 8 字节的 CommitLog 物理偏移量、4 字节的消息长度、8 字节 tag hashcode,单个文件由 30W 个条目组成,可以像数组一样随机访问每一个条目,每个 ConsumeQueue 文件大小约 5.72M。
IndexFile
索引文件,提供了一种可以通过 key 或时间区间来查询消息的方法。单个 IndexFile 文件大小约为 400M,一个 IndexFile 可以保存 2000W 个索引,IndexFile 的底层存储设计类似 JDK 的 HashMap 数据结构。
其他文件:包括 config 文件夹,存放运行时配置信息;abort 文件,说明 Broker 是否正常关闭;checkpoint 文件,存储 Commitlog、ConsumeQueue、Index 文件最后一次刷盘时间戳。这些不在本文讨论的范围。
同 Kafka 相比,Kafka 每个 Topic 的每个 partition 对应一个文件,顺序写入,定时刷盘。但一旦单个 Broker 的 Topic 过多,顺序写将退化为随机写。而 RocketMQ 单个 Broker 所有 Topic 在同一个 CommitLog 中顺序写,是能够保证严格顺序写。RocketMQ 读取消息需要从 ConsumeQueue 中拿到消息实际物理偏移再去 CommitLog 读取消息内容,会造成随机读取。
2.1 Page Cache 和 mmap
在正式介绍 Broker 消息存储模块实现前,先说明下 Page Cache 和 mmap 这两个概念。
Page Cache 是 OS 对文件的缓存,用于加速对文件的读写。一般来说,程序对文件进行顺序读写的速度几乎接近于内存的读写速度,主要原因就是由于 OS 使用 Page Cache 机制对读写访问操作进行了性能优化,将一部分的内存用作 Page Cache。对于数据的写入,OS 会先写入至 Cache 内,随后通过异步的方式由 pdflush 内核线程将 Cache 内的数据刷盘至物理磁盘上。对于数据的读取,如果一次读取文件时出现未命中 Page Cache 的情况,OS 从物理磁盘上访问读取文件的同时,会顺序对其他相邻块的数据文件进行预读取。
mmap 是将磁盘上的物理文件直接映射到用户态的内存地址中,减少了传统 IO 将磁盘文件数据在操作系统内核地址空间的缓冲区和用户应用程序地址空间的缓冲区之间来回进行拷贝的性能开销。Java NIO 中的 FileChannel 提供了 map() 方法可以实现 mmap。FileChannel (文件通道)和 mmap (内存映射) 读写性能比较可以参照这篇文章。
2.2 Broker 模块
下图是 Broker 存储架构图,展示了 Broker 模块从收到消息到返回响应业务流转过程。
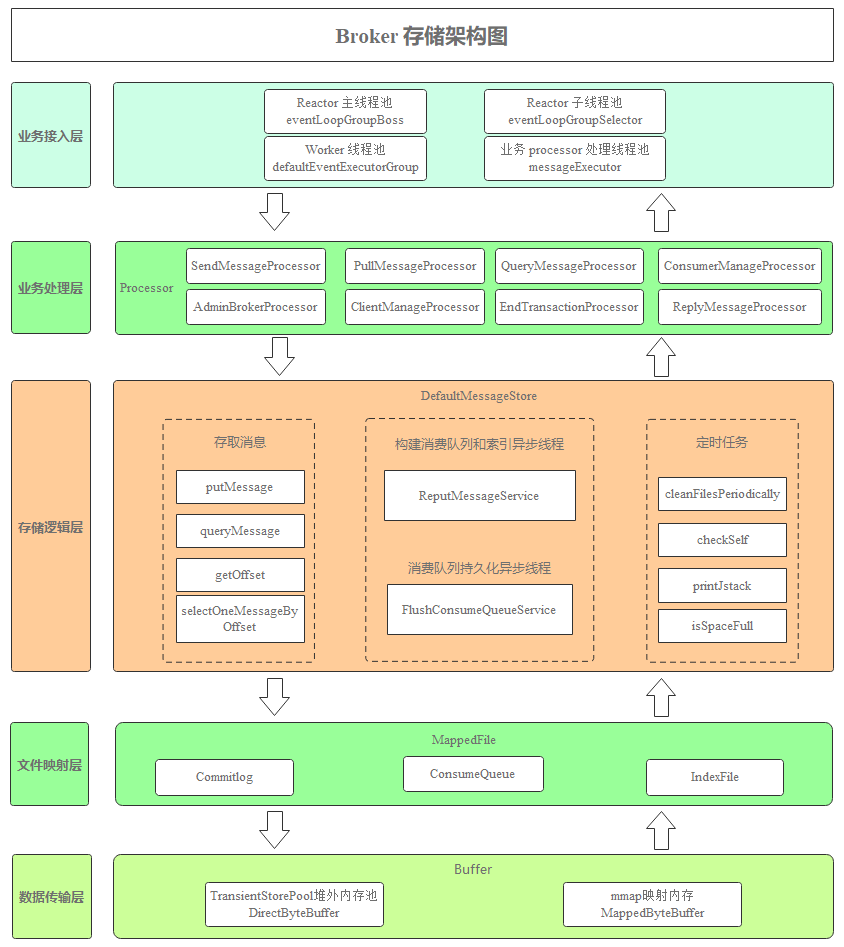
业务接入层:RocketMQ 基于 Netty 的 Reactor 多线程模型实现了底层通信。Reactor 主线程池 eventLoopGroupBoss 负责创建 TCP 连接,默认只有一个线程。连接建立后,再丢给 Reactor 子线程池 eventLoopGroupSelector 进行读写事件的处理。
defaultEventExecutorGroup 负责 SSL 验证、编解码、空闲检查、网络连接管理。然后根据 RomotingCommand 的业务请求码 code 去 processorTable 这个本地缓存变量中找到对应的 processor,封装成 task 任务后,提交给对应的业务 processor 处理线程池来执行。Broker 模块通过这四级线程池提升系统吞吐量。
业务处理层:处理各种通过 RPC 调用过来的业务请求,其中:
SendMessageProcessor 负责处理 Producer 发送消息的请求;
PullMessageProcessor 负责处理 Consumer 消费消息的请求;
QueryMessageProcessor 负责处理按照消息 Key 等查询消息的请求。
存储逻辑层:DefaultMessageStore 是 RocketMQ 的存储逻辑核心类,提供消息存储、读取、删除等能力。
文件映射层:把 Commitlog、ConsumeQueue、IndexFile 文件映射为存储对象 MappedFile。
数据传输层:支持基于 mmap 内存映射进行读写消息,同时也支持基于 mmap 进行读取消息、堆外内存写入消息的方式进行读写消息。
下面章节将从源码角度来剖析 RocketMQ 是如何实现高性能存储。
三、消息写入以单个消息生产为例,消息写入时序逻辑如下图,业务逻辑如上文 Broker 存储架构所示在各层之间进行流转。
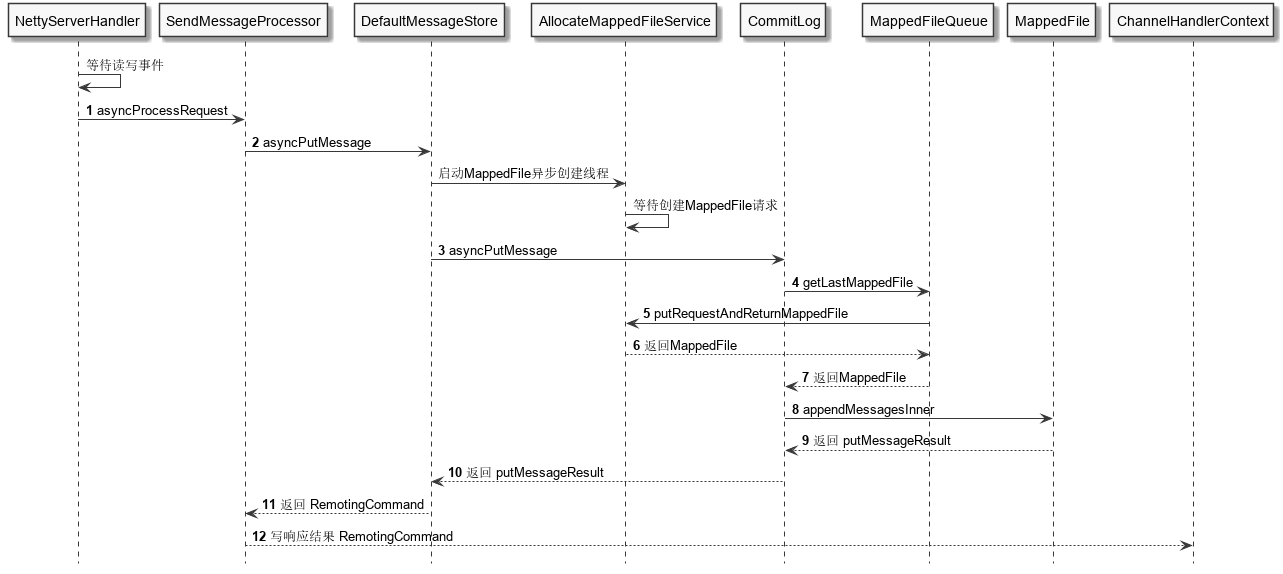
最底层消息写入核心代码在 CommitLog 的 asyncPutMessage 方法中,主要分为获取 MappedFile、往缓冲区写消息、提交刷盘请求三步。需要注意的是在这三步前后有自旋锁或 ReentrantLock 的加锁、释放锁,保证单个 Broker 写消息是串行的。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.CommitLog::asyncPutMessage
public CompletableFuture<PutMessageResult> asyncPutMessage(final MessageExtBrokerInner msg) {
...
putMessageLock.lock(); //spin or ReentrantLock ,depending on store config
try {
//获取最新的 MappedFile
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile();
...
//向缓冲区写消息
result = mappedFile.appendMessage(msg, this.appendMessageCallback, putMessageContext);
...
//提交刷盘请求
CompletableFuture<PutMessageStatus> flushResultFuture = submitFlushRequest(result, msg);
...
} finally {
putMessageLock.unlock();
}
...
}
下面介绍这三步具体做了什么事情。
3.1 MappedFile 初始化
在 Broker 初始化时会启动管理 MappedFile 创建的 AllocateMappedFileService 异步线程。消息处理线程 和 AllocateMappedFileService 线程通过队列 requestQueue 关联。
消息写入时调用 AllocateMappedFileService 的 putRequestAndReturnMappedFile 方法往 requestQueue 放入提交创建 MappedFile 请求,这边会同时构建两个 AllocateRequest 放入队列。
AllocateMappedFileService 线程循环从 requestQueue 获取 AllocateRequest 来创建 MappedFile。消息处理线程通过 CountDownLatch 等待获取第一个 MappedFile 创建成功就返回。
当消息处理线程需要再次创建 MappedFile 时,此时可以直接获取之前已预创建的 MappedFile。这样通过预创建 MappedFile ,减少文件创建等待时间。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.AllocateMappedFileService::putRequestAndReturnMappedFile
public MappedFile putRequestAndReturnMappedFile(String nextFilePath, String nextNextFilePath, int fileSize) {
//请求创建 MappedFile
AllocateRequest nextReq = new AllocateRequest(nextFilePath, fileSize);
boolean nextPutOK = this.requestTable.putIfAbsent(nextFilePath, nextReq) == null;
...
//请求预先创建下一个 MappedFile
AllocateRequest nextNextReq = new AllocateRequest(nextNextFilePath, fileSize);
boolean nextNextPutOK = this.requestTable.putIfAbsent(nextNextFilePath, nextNextReq) == null;
...
//获取本次创建 MappedFile
AllocateRequest result = this.requestTable.get(nextFilePath);
...
}
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.AllocateMappedFileService::run
public void run() {
..
while (!this.isStopped() && this.mmapOperation()) {
}
...
}
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.AllocateMappedFileService::mmapOperation
private boolean mmapOperation() {
...
//从队列获取 AllocateRequest
req = this.requestQueue.take();
...
//判断是否开启堆外内存池
if (messageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {
//开启堆外内存的 MappedFile
mappedFile = ServiceLoader.load(MappedFile.class).iterator().next();
mappedFile.init(req.getFilePath(), req.getFileSize(), messageStore.getTransientStorePool());
} else {
//普通 MappedFile
mappedFile = new MappedFile(req.getFilePath(), req.getFileSize());
}
...
//MappedFile 预热
if (mappedFile.getFileSize() >= this.messageStore.getMessageStoreConfig()
.getMappedFileSizeCommitLog()
&&
this.messageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isWarmMapedFileEnable()) {
mappedFile.warmMappedFile(this.messageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType(),
this.messageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushLeastPagesWhenWarmMapedFile());
}
req.setMappedFile(mappedFile);
...
}
每次新建普通 MappedFile 请求,都会创建 mappedByteBuffer,下面代码展示了 Java mmap 是如何实现的。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.MappedFile::init
private void init(final String fileName, final int fileSize) throws IOException {
...
this.fileChannel = new RandomAccessFile(this.file, "rw").getChannel();
this.mappedByteBuffer = this.fileChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, fileSize);
...
}
如果开启堆外内存,即 transientStorePoolEnable = true 时,mappedByteBuffer 只是用来读消息,堆外内存用来写消息,从而实现对于消息的读写分离。堆外内存对象不是每次新建 MappedFile 都需要创建,而是系统启动时根据堆外内存池大小就初始化好了。每个堆外内存 DirectByteBuffer 都与 CommitLog 文件大小相同,通过锁定住该堆外内存,确保不会被置换到虚拟内存中去。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.TransientStorePool
public void init() {
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
//分配与 CommitLog 文件大小相同的堆外内存
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(fileSize);
final long address = ((DirectBuffer) byteBuffer).address();
Pointer pointer = new Pointer(address);
//锁定堆外内存,确保不会被置换到虚拟内存中去
LibC.INSTANCE.mlock(pointer, new NativeLong(fileSize));
availableBuffers.offer(byteBuffer);
}
}
上面的 mmapOperation 方法中有段 MappedFile 预热逻辑。为什么需要文件预热呢?文件预热怎么做的呢?
因为通过 mmap 映射,只是建立了进程虚拟内存地址与物理内存地址之间的映射关系,并没有将 Page Cache 加载至内存。读写数据时如果没有命中写 Page Cache 则发生缺页中断,从磁盘重新加载数据至内存,这样会影响读写性能。为了防止缺页异常,阻止操作系统将相关的内存页调度到交换空间(swap space),RocketMQ 通过对文件预热,文件预热实现如下。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.MappedFile::warmMappedFile
public void warmMappedFile(FlushDiskType type, int pages) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = this.mappedByteBuffer.slice();
int flush = 0;
//通过写入 1G 的字节 0 来让操作系统分配物理内存空间,如果没有填充值,操作系统不会实际分配物理内存,防止在写入消息时发生缺页异常
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < this.fileSize; i += MappedFile.OS_PAGE_SIZE, j++) {
byteBuffer.put(i, (byte) 0);
// force flush when flush disk type is sync
if (type == FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH) {
if ((i / OS_PAGE_SIZE) - (flush / OS_PAGE_SIZE) >= pages) {
flush = i;
mappedByteBuffer.force();
}
}
//prevent gc
if (j % 1000 == 0) {
Thread.sleep(0);
}
}
//force flush when prepare load finished
if (type == FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH) {
mappedByteBuffer.force();
}
...
this.mlock();
}
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.MappedFile::mlock
public void mlock() {
final long beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
final long address = ((DirectBuffer) (this.mappedByteBuffer)).address();
Pointer pointer = new Pointer(address);
//通过系统调用 mlock 锁定该文件的 Page Cache,防止其被交换到 swap 空间
int ret = LibC.INSTANCE.mlock(pointer, new NativeLong(this.fileSize));
//通过系统调用 madvise 给操作系统建议,说明该文件在不久的将来要被访问
int ret = LibC.INSTANCE.madvise(pointer, new NativeLong(this.fileSize), LibC.MADV_WILLNEED);
}
综上所述,RocketMQ 每次都预创建一个文件来减少文件创建延迟,通过文件预热避免了读写时缺页异常。
3.2 消息写入
3.2.1 写入 CommitLog
CommitLog 中每条消息存储的逻辑视图如下图所示, TOTALSIZE 是整个消息占用存储空间大小。
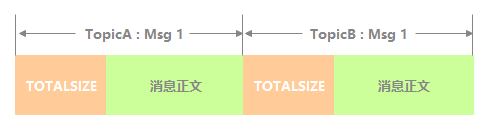
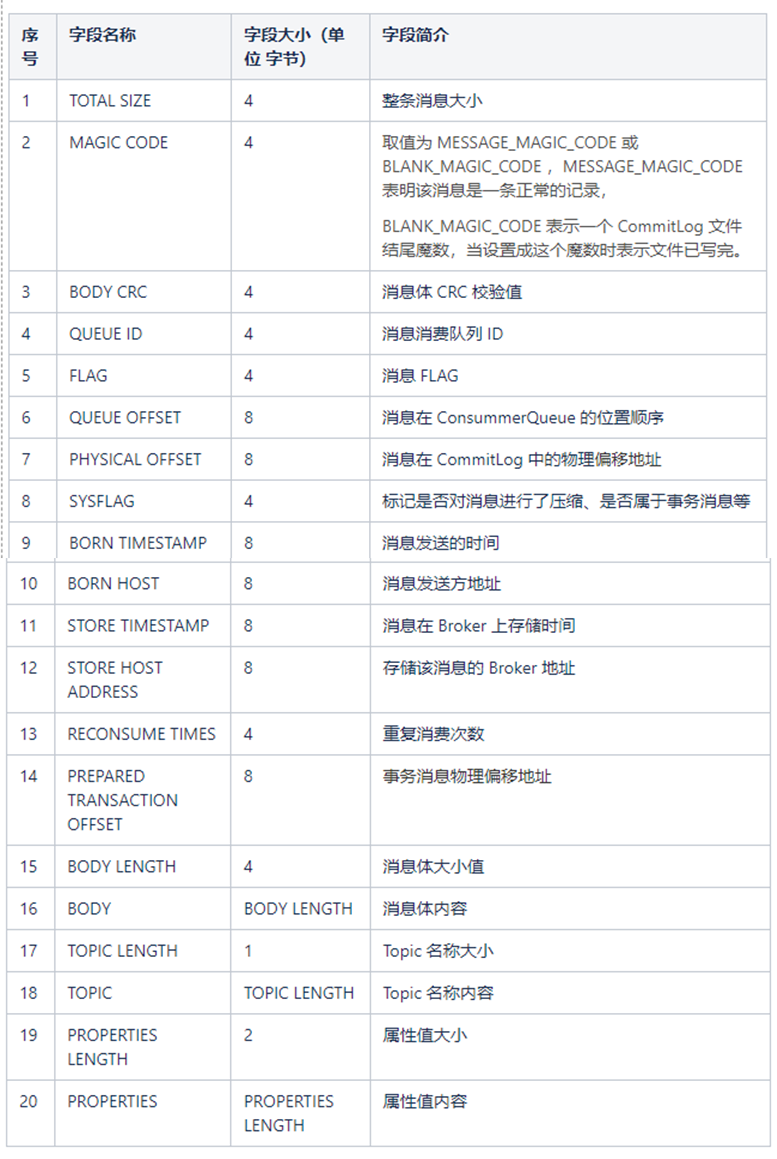
下面表格说明下每条消息包含哪些字段,以及这些字段占用空间大小和字段简介。
消息的写入是调用MappedFile 的 appendMessagesInner方法。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.MappedFile::appendMessagesInner
public AppendMessageResult appendMessagesInner(final MessageExt messageExt, final AppendMessageCallback cb,
PutMessageContext putMessageContext) {
//判断使用 DirectBuffer 还是 MappedByteBuffer 进行写操作
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = writeBuffer != null ? writeBuffer.slice() : this.mappedByteBuffer.slice();
..
byteBuffer.position(currentPos);
AppendMessageResult result = cb.doAppend(this.getFileFromOffset(), byteBuffer, this.fileSize - currentPos,
(MessageExtBrokerInner) messageExt, putMessageContext);
..
return result;
}
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.CommitLog::doAppend
public AppendMessageResult doAppend(final long fileFromOffset, final ByteBuffer byteBuffer, final int maxBlank,
final MessageExtBrokerInner msgInner, PutMessageContext putMessageContext) {
...
ByteBuffer preEncodeBuffer = msgInner.getEncodedBuff();
...
//这边只是将消息写入缓冲区,还未实际刷盘
byteBuffer.put(preEncodeBuffer);
msgInner.setEncodedBuff(null);
...
return result;
}
至此,消息最终写入 ByteBuffer,还没有持久到磁盘,具体何时持久化,下一小节会具体讲刷盘机制。这边有个疑问 ConsumeQueue 和 IndexFile 是怎么写入的?
答案是在存储架构图中存储逻辑层的 ReputMessageService。MessageStore 在初始化的时候,会启动一个 ReputMessageService 异步线程,它启动后便会在循环中不断调用 doReput 方法,用来通知 ConsumeQueue 和 IndexFile 进行更新。ConsumeQueue 和 IndexFile 之所以可以异步更新是因为 CommitLog 中保存了恢复 ConsumeQueue 和 IndexFile 所需队列和 Topic 等信息,即使 Broker 服务异常宕机,Broker 重启后可以根据 CommitLog 恢复 ConsumeQueue 和IndexFile。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.DefaultMessageStore.ReputMessageService::run
public void run() {
...
while (!this.isStopped()) {
Thread.sleep(1);
this.doReput();
}
...
}
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.DefaultMessageStore.ReputMessageService::doReput
private void doReput() {
...
//获取CommitLog中存储的新消息
DispatchRequest dispatchRequest =
DefaultMessageStore.this.commitLog.checkMessageAndReturnSize(result.getByteBuffer(), false, false);
int size = dispatchRequest.getBufferSize() == -1 ? dispatchRequest.getMsgSize() : dispatchRequest.getBufferSize();
if (dispatchRequest.isSuccess()) {
if (size > 0) {
//如果有新消息,则分别调用 CommitLogDispatcherBuildConsumeQueue、CommitLogDispatcherBuildIndex 进行构建 ConsumeQueue 和 IndexFile
DefaultMessageStore.this.doDispatch(dispatchRequest);
}
...
}
3.2.2 写入 ConsumeQueue
如下图所示,ConsumeQueue 每一条记录共 20 个字节,分别为 8 字节的 CommitLog 物理偏移量、4 字节的消息长度、8字节 tag hashcode。
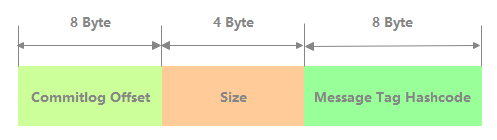
ConsumeQueue 记录持久化逻辑如下。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.ConsumeQueue::putMessagePositionInfo
private boolean putMessagePositionInfo(final long offset, final int size, final long tagsCode,
final long cqOffset) {
...
this.byteBufferIndex.flip();
this.byteBufferIndex.limit(CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE);
this.byteBufferIndex.putLong(offset);
this.byteBufferIndex.putInt(size);
this.byteBufferIndex.putLong(tagsCode);
final long expectLogicOffset = cqOffset * CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE;
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile(expectLogicOffset);
if (mappedFile != null) {
...
return mappedFile.appendMessage(this.byteBufferIndex.array());
}
}
3.2.3 写入 IndexFile
IndexFile 的文件逻辑结构如下图所示,类似于 JDK 的 HashMap 的数组加链表结构。主要由 Header、Slot Table、Index Linked List 三部分组成。
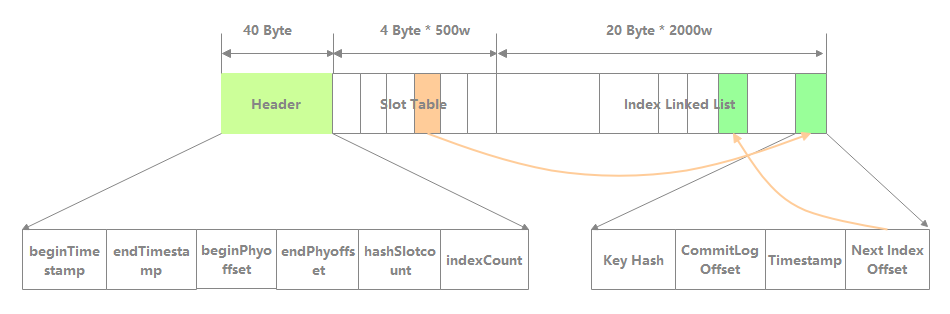
Header:IndexFile 的头部,占 40 个字节。主要包含以下字段:
beginTimestamp:该 IndexFile 文件中包含消息的最小存储时间。
endTimestamp:该 IndexFile 文件中包含消息的最大存储时间。
beginPhyoffset:该 IndexFile 文件中包含消息的最小 CommitLog 文件偏移量。
endPhyoffset:该 IndexFile 文件中包含消息的最大 CommitLog 文件偏移量。
hashSlotcount:该 IndexFile 文件中包含的 hashSlot 的总数。
indexCount:该 IndexFile 文件中已使用的 Index 条目个数。
Slot Table:默认包含 500w 个 Hash 槽,每个 Hash 槽存储的是相同 hash 值的第一个 IndexItem 存储位置 。
Index Linked List:默认最多包含 2000w 个 IndexItem。其组成如下所示:
Key Hash:消息 key 的 hash,当根据 key 搜索时比较的是其 hash,在之后会比较 key 本身。
CommitLog Offset:消息的物理位移。
Timestamp:该消息存储时间与第一条消息的时间戳的差值。
Next Index Offset:发生 hash 冲突后保存的下一个 IndexItem 的位置。
Slot Table 中每个 hash 槽存放的是 IndexItem 在 Index Linked List 的位置,如果 hash 冲突时,新的 IndexItem 插入链表头, 它的 Next Index Offset 中存放之前链表头 IndexItem 位置,同时覆盖 Slot Table 中的 hash 槽为最新 IndexItem 位置。代码如下:
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.index.IndexFile::putKey
public boolean putKey(final String key, final long phyOffset, final long storeTimestamp) {
int keyHash = indexKeyHashMethod(key);
int slotPos = keyHash % this.hashSlotNum;
int absSlotPos = IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + slotPos * hashSlotSize;
...
//从 Slot Table 获取当前最新消息位置
int slotValue = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absSlotPos);
...
int absIndexPos =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize
+ this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() * indexSize;
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos, keyHash);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putLong(absIndexPos + 4, phyOffset);
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8, (int) timeDiff);
//存放之前链表头 IndexItem 位置
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4, slotValue);
//更新 Slot Table 中 hash 槽的值为最新消息位置
this.mappedByteBuffer.putInt(absSlotPos, this.indexHeader.getIndexCount());
if (this.indexHeader.getIndexCount() <= 1) {
this.indexHeader.setBeginPhyOffset(phyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setBeginTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
}
if (invalidIndex == slotValue) {
this.indexHeader.incHashSlotCount();
}
this.indexHeader.incIndexCount();
this.indexHeader.setEndPhyOffset(phyOffset);
this.indexHeader.setEndTimestamp(storeTimestamp);
return true;
...
}
综上所述一个完整的消息写入流程包括:同步写入 Commitlog 文件缓存区,异步构建 ConsumeQueue、IndexFile 文件。
3.3 消息刷盘
RocketMQ 消息刷盘主要分为同步刷盘和异步刷盘。
(1) 同步刷盘:只有在消息真正持久化至磁盘后 RocketMQ 的 Broker 端才会真正返回给 Producer 端一个成功的 ACK 响应。同步刷盘对 MQ 消息可靠性来说是一种不错的保障,但是性能上会有较大影响,一般金融业务使用该模式较多。
(2) 异步刷盘:能够充分利用 OS 的 Page Cache 的优势,只要消息写入 Page Cache 即可将成功的 ACK 返回给 Producer 端。消息刷盘采用后台异步线程提交的方式进行,降低了读写延迟,提高了 MQ 的性能和吞吐量。异步刷盘包含开启堆外内存和未开启堆外内存两种方式。
在 CommitLog 中提交刷盘请求时,会根据当前 Broker 相关配置决定是同步刷盘还是异步刷盘。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.CommitLog::submitFlushRequest
public CompletableFuture<PutMessageStatus> submitFlushRequest(AppendMessageResult result, MessageExt messageExt) {
//同步刷盘
if (FlushDiskType.SYNC_FLUSH == this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getFlushDiskType()) {
final GroupCommitService service = (GroupCommitService) this.flushCommitLogService;
if (messageExt.isWaitStoreMsgOK()) {
GroupCommitRequest request = new GroupCommitRequest(result.getWroteOffset() + result.getWroteBytes(),
this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getSyncFlushTimeout());
service.putRequest(request);
return request.future();
} else {
service.wakeup();
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK);
}
}
//异步刷盘
else {
if (!this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isTransientStorePoolEnable()) {
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
} else {
//开启堆外内存的异步刷盘
commitLogService.wakeup();
}
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK);
}
}
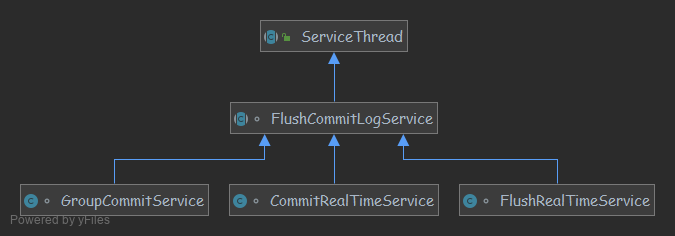
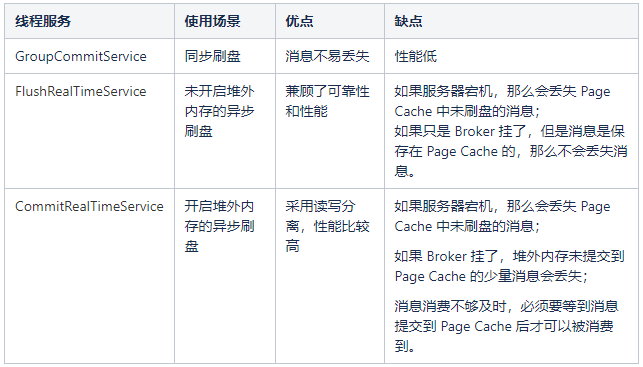
GroupCommitService、FlushRealTimeService、CommitRealTimeService 三者继承关系如图;
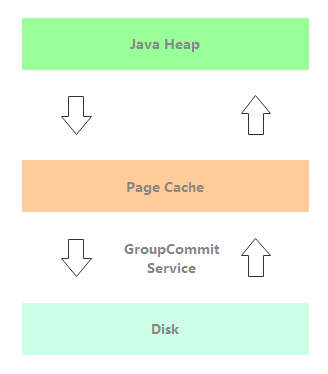
GroupCommitService:同步刷盘线程。如下图所示,消息写入到 Page Cache 后通过 GroupCommitService 同步刷盘,消息处理线程阻塞等待刷盘结果。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.CommitLog.GroupCommitService::run
public void run() {
...
while (!this.isStopped()) {
this.waitForRunning(10);
this.doCommit();
}
...
}
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.CommitLog.GroupCommitService::doCommit
private void doCommit() {
...
for (GroupCommitRequest req : this.requestsRead) {
boolean flushOK = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getFlushedWhere() >= req.getNextOffset();
for (int i = 0; i < 2 && !flushOK; i++) {
CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(0);
flushOK = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.getFlushedWhere() >= req.getNextOffset();
}
//唤醒等待刷盘完成的消息处理线程
req.wakeupCustomer(flushOK ? PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK : PutMessageStatus.FLUSH_DISK_TIMEOUT);
}
...
}
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.MappedFile::flush
public int flush(final int flushLeastPages) {
if (this.isAbleToFlush(flushLeastPages)) {
...
//使用到了 writeBuffer 或者 fileChannel 的 position 不为 0 时用 fileChannel 进行强制刷盘
if (writeBuffer != null || this.fileChannel.position() != 0) {
this.fileChannel.force(false);
} else {
//使用 MappedByteBuffer 进行强制刷盘
this.mappedByteBuffer.force();
}
...
}
}
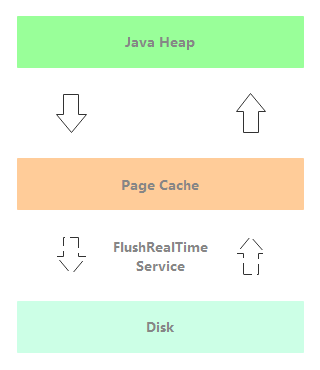
FlushRealTimeService:未开启堆外内存的异步刷盘线程。如下图所示,消息写入到 Page Cache 后,消息处理线程立即返回,通过 FlushRealTimeService 异步刷盘。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.CommitLog.FlushRealTimeService
public void run() {
...
//判断是否需要周期性进行刷盘
if (flushCommitLogTimed) {
//固定休眠 interval 时间间隔
Thread.sleep(interval);
} else {
// 如果被唤醒就刷盘,非周期性刷盘
this.waitForRunning(interval);
}
...
// 这边和 GroupCommitService 用的是同一个强制刷盘方法
CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.flush(flushPhysicQueueLeastPages);
...
}
CommitRealTimeService:开启堆外内存的异步刷盘线程。如下图所示,消息处理线程把消息写入到堆外内存后立即返回。后续先通过 CommitRealTimeService 把消息由堆外内存异步提交至 Page Cache,再由 FlushRealTimeService 线程异步刷盘。
注意:在消息异步提交至 Page Cache 后,业务就可以从 MappedByteBuffer 读取到该消息。
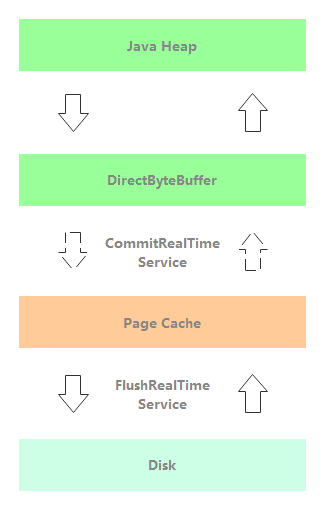
消息写入到堆外内存 writeBuffer 后,会通过 isAbleToCommit 方法判断是否积累到至少提交页数(默认4页)。如果页数达到最小提交页数,则批量提交;否则还是驻留在堆外内存,这边有丢失消息风险。通过这种批量操作,读和写的 Page Cahe 会间隔数页,降低了 Page Cahe 读写冲突的概率,实现了读写分离。具体实现逻辑如下:
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.CommitLog.CommitRealTimeService
class CommitRealTimeService extends FlushCommitLogService {
@Override
public void run() {
while (!this.isStopped()) {
...
int commitDataLeastPages = CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getCommitCommitLogLeastPages();
...
//把消息 commit 到内存缓冲区,最终调用的是 MappedFile::commit0 方法,只有达到最少提交页数才能提交成功,否则还在堆外内存中
boolean result = CommitLog.this.mappedFileQueue.commit(commitDataLeastPages);
if (!result) {
//唤醒 flushCommitLogService,进行强制刷盘
flushCommitLogService.wakeup();
}
...
this.waitForRunning(interval);
}
}
}
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.MappedFile::commit0
protected void commit0() {
int writePos = this.wrotePosition.get();
int lastCommittedPosition = this.committedPosition.get();
//消息提交至 Page Cache,并未实际刷盘
if (writePos - lastCommittedPosition > 0) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = writeBuffer.slice();
byteBuffer.position(lastCommittedPosition);
byteBuffer.limit(writePos);
this.fileChannel.position(lastCommittedPosition);
this.fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
this.committedPosition.set(writePos);
}
}
下面总结一下三种刷盘机制的使用场景及优缺点。
消息读取逻辑相比写入逻辑简单很多,下面着重分析下根据 offset 查询消息和根据 key 查询消息是如何实现的。
4.1 根据 offset 查询
读取消息的过程就是先从 ConsumeQueue 中找到消息在 CommitLog 的物理偏移地址,然后再从 CommitLog 文件中读取消息的实体内容。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.DefaultMessageStore::getMessage
public GetMessageResult getMessage(final String group, final String topic, final int queueId, final long offset,
final int maxMsgNums,
final MessageFilter messageFilter) {
long nextBeginOffset = offset;
GetMessageResult getResult = new GetMessageResult();
final long maxOffsetPy = this.commitLog.getMaxOffset();
//找到对应的 ConsumeQueue
ConsumeQueue consumeQueue = findConsumeQueue(topic, queueId);
...
//根据 offset 找到对应的 ConsumeQueue 的 MappedFile
SelectMappedBufferResult bufferConsumeQueue = consumeQueue.getIndexBuffer(offset);
status = GetMessageStatus.NO_MATCHED_MESSAGE;
long maxPhyOffsetPulling = 0;
int i = 0;
//能返回的最大信息大小,不能大于 16M
final int maxFilterMessageCount = Math.max(16000, maxMsgNums * ConsumeQueue.CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE);
for (; i < bufferConsumeQueue.getSize() && i < maxFilterMessageCount; i += ConsumeQueue.CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE) {
//CommitLog 物理地址
long offsetPy = bufferConsumeQueue.getByteBuffer().getLong();
int sizePy = bufferConsumeQueue.getByteBuffer().getInt();
maxPhyOffsetPulling = offsetPy;
...
//根据 offset 和 size 从 CommitLog 拿到具体的 Message
SelectMappedBufferResult selectResult = this.commitLog.getMessage(offsetPy, sizePy);
...
//将 Message 放入结果集
getResult.addMessage(selectResult);
status = GetMessageStatus.FOUND;
}
//更新 offset
nextBeginOffset = offset + (i / ConsumeQueue.CQ_STORE_UNIT_SIZE);
long diff = maxOffsetPy - maxPhyOffsetPulling;
long memory = (long) (StoreUtil.TOTAL_PHYSICAL_MEMORY_SIZE
* (this.messageStoreConfig.getAccessMessageInMemoryMaxRatio() / 100.0));
getResult.setSuggestPullingFromSlave(diff > memory);
...
getResult.setStatus(status);
getResult.setNextBeginOffset(nextBeginOffset);
return getResult;
}
4.2 根据 key 查询
读取消息的过程就是用 topic 和 key 找到 IndexFile 索引文件中的一条记录,根据记录中的 CommitLog 的 offset 从 CommitLog 文件中读取消息的实体内容。
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.DefaultMessageStore::queryMessage
public QueryMessageResult queryMessage(String topic, String key, int maxNum, long begin, long end) {
QueryMessageResult queryMessageResult = new QueryMessageResult();
long lastQueryMsgTime = end;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
//获取 IndexFile 索引文件中记录的消息在 CommitLog 文件物理偏移地址
QueryOffsetResult queryOffsetResult = this.indexService.queryOffset(topic, key, maxNum, begin, lastQueryMsgTime);
...
for (int m = 0; m < queryOffsetResult.getPhyOffsets().size(); m++) {
long offset = queryOffsetResult.getPhyOffsets().get(m);
...
MessageExt msg = this.lookMessageByOffset(offset);
if (0 == m) {
lastQueryMsgTime = msg.getStoreTimestamp();
}
...
//在 CommitLog 文件获取消息内容
SelectMappedBufferResult result = this.commitLog.getData(offset, false);
...
queryMessageResult.addMessage(result);
...
}
}
return queryMessageResult;
}
在 IndexFile 索引文件,查找 CommitLog 文件物理偏移地址实现如下:
//org.apache.rocketmq.store.index.IndexFile::selectPhyOffset
public void selectPhyOffset(final List<Long> phyOffsets, final String key, final int maxNum,
final long begin, final long end, boolean lock) {
int keyHash = indexKeyHashMethod(key);
int slotPos = keyHash % this.hashSlotNum;
int absSlotPos = IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + slotPos * hashSlotSize;
//获取相同 hash 值 key 的第一个 IndexItme 存储位置,即链表的首节点
int slotValue = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absSlotPos);
//遍历链表节点
for (int nextIndexToRead = slotValue; ; ) {
if (phyOffsets.size() >= maxNum) {
break;
}
int absIndexPos =
IndexHeader.INDEX_HEADER_SIZE + this.hashSlotNum * hashSlotSize
+ nextIndexToRead * indexSize;
int keyHashRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos);
long phyOffsetRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getLong(absIndexPos + 4);
long timeDiff = (long) this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8);
int prevIndexRead = this.mappedByteBuffer.getInt(absIndexPos + 4 + 8 + 4);
if (timeDiff < 0) {
break;
}
timeDiff *= 1000L;
long timeRead = this.indexHeader.getBeginTimestamp() + timeDiff;
boolean timeMatched = (timeRead >= begin) && (timeRead <= end);
//符合条件的结果加入 phyOffsets
if (keyHash == keyHashRead && timeMatched) {
phyOffsets.add(phyOffsetRead);
}
if (prevIndexRead <= invalidIndex
|| prevIndexRead > this.indexHeader.getIndexCount()
|| prevIndexRead == nextIndexToRead || timeRead < begin) {
break;
}
//继续遍历链表
nextIndexToRead = prevIndexRead;
}
...
}
本文从源码的角度介绍了 RocketMQ 存储系统的核心模块实现,包括存储架构、消息写入和消息读取。
RocketMQ 把所有 Topic 下的消息都写入到 CommitLog 里面,实现了严格的顺序写。通过文件预热防止 Page Cache 被交换到 swap 空间,减少读写文件时缺页中断。使用 mmap 对 CommitLog 文件进行读写,将对文件的操作转化为直接对内存地址进行操作,从而极大地提高了文件的读写效率。
对于性能要求高、数据一致性要求不高的场景下,可以通过开启堆外内存,实现读写分离,提升磁盘的吞吐量。总之,存储模块的学习需要对操作系统原理有一定了解。作者采用的性能极致优化方案值得我们好好学习。
六、参考文献作者:vivo互联网服务器团队-Zhang Zhenglin