1.原理
小波变换的计算方法:
1)一维信号:
例如:有a=[5,7,6,8]四个数,并使用b[4]数组来保存结果.
则一级Haar小波变换的结果为:
b[0]=(a[0]+a[1])/2, b[2]=(a[0]-a[1])/2
b[1]=(a[2]+a[3])/2, b[3]=(a[2]-a[3])/2
⚠️计算差均值时也有看见a[1]-a[0]的,只要保持一致应该都可以
由此可知,Haar变换采用的原理是:
A)低频采用和均值,即b[0]和b[1],和均值中均值存储了图像的整体信息
B)高频采用差均值,即b[2]和b[3],用于记录图像的细节信息,这样在重构时能够恢复图像的全部信息
因此上面的例子中
b[0] = (5+7)/2 = 6 , b[1] = (6+8)/2 = 6, b[2] = (5-7)/2 = -1, b[3] = (6-8)/2 = -1
如果要继续进行多级的小波变换:
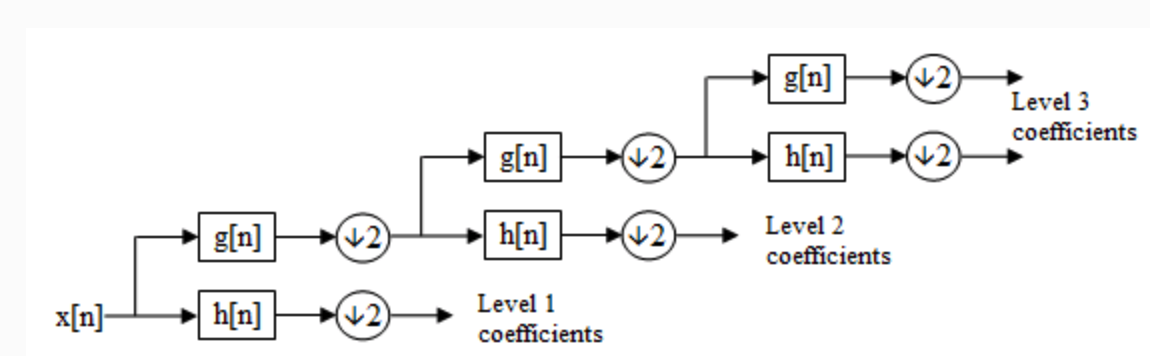
如上图可见是对低频的信息继续进行haar小波变换
2)二维
对于二维haar小波,我们通常一次分解形成了整体图像,水平细节,垂直细节,对角细节。首先我们按照一维haar小波分解的原理,按照行顺序对行进行处理,然后按照列顺序对行处理结果进行同样的处理
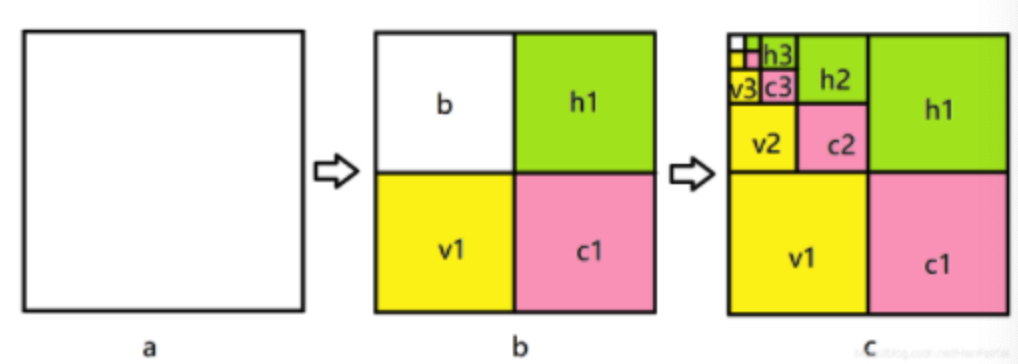
用图像表述如图所示:图中a表示原图,图b表示经过一级小波变换的结果,h1 表示水平反向的细节,v1 表示竖直方向的细节,c1表示对角线方向的细节,b表示下2采样的图像。图c中表示继续进行了三次Haar小波变换的结果:
详细过程经过下面的代码来解释
2.实现
1)
代码:https://github.com/lpj0/MWCNN_PyTorch/blob/master/model/common.py:
原图为:
中间有个问题,就是逆向重构的时候发现并没有成功,得到的结果是:

于是对操作的数据进行了一番输出:
#coding:utf-8 import torch.nn as nn import torch def dwt_init(x): print('-------------- origin ---------------') print(x[:,0,:,:]) x01 = x[:, :, 0::2, :] / 2 x02 = x[:, :, 1::2, :] / 2 x1 = x01[:, :, :, 0::2] x2 = x02[:, :, :, 0::2] x3 = x01[:, :, :, 1::2] x4 = x02[:, :, :, 1::2] x_LL = x1 + x2 + x3 + x4 x_HL = -x1 - x2 + x3 + x4 x_LH = -x1 + x2 - x3 + x4 x_HH = x1 - x2 - x3 + x4 print('---------------- LL ------------------') print(x_LL[:,0,:,:]) print() print('---------------- HL ------------------') print(x_HL[:,0,:,:]) print() print('---------------- LH ------------------') print(x_LH[:,0,:,:]) print() print('---------------- HH ------------------') print(x_HH[:,0,:,:]) return torch.cat((x_LL, x_HL, x_LH, x_HH), 1) # 使用哈尔 haar 小波变换来实现二维逆向离散小波 def iwt_init(x): r = 2 in_batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width = x.size() # print([in_batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width]) #[1, 12, 56, 56] out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width = in_batch, int(in_channel / (r**2)), r * in_height, r * in_width # print(out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width) #1 3 112 112 x1 = x[:, 0:out_channel, :, :] / 2 print('-------------- enter iwt ---------------') print(x1[:,0,:,:]) x2 = x[:, out_channel:out_channel * 2, :, :] / 2 x3 = x[:, out_channel * 2:out_channel * 3, :, :] / 2 x4 = x[:, out_channel * 3:out_channel * 4, :, :] / 2 # print(x1.shape) #torch.Size([1, 3, 56, 56]) # print(x2.shape) #torch.Size([1, 3, 56, 56]) # print(x3.shape) #torch.Size([1, 3, 56, 56]) # print(x4.shape) #torch.Size([1, 3, 56, 56]) # h = torch.zeros([out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width]).float().cuda() h = torch.zeros([out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width]).float() h[:, :, 0::2, 0::2] = x1 - x2 - x3 + x4 h[:, :, 1::2, 0::2] = x1 - x2 + x3 - x4 h[:, :, 0::2, 1::2] = x1 + x2 - x3 - x4 h[:, :, 1::2, 1::2] = x1 + x2 + x3 + x4 print('-------------- back ---------------') print(h[:,0,:,:]) return h # 二维离散小波 class DWT(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(DWT, self).__init__() self.requires_grad = False # 信号处理,非卷积运算,不需要进行梯度求导 def forward(self, x): return dwt_init(x) # 逆向二维离散小波 class IWT(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(IWT, self).__init__() self.requires_grad = False def forward(self, x): return iwt_init(x) if __name__ == '__main__': import os, cv2, torchvision from PIL import Image import numpy as np from torchvision import transforms as trans img = Image.open('./1.jpg') transform = trans.Compose([ trans.ToTensor() ]) img = transform(img).unsqueeze(0) dwt = DWT() change_img_tensor = dwt(img) # print(change_img_tensor.shape) #torch.Size([1, 12, 56, 56]) print('-------------- after dwt ---------------') print(change_img_tensor[:,0,:,:]) for i in range(change_img_tensor.size(1)//3): torchvision.utils.save_image(change_img_tensor[:,i*3:i*3+3:,:], os.path.join('./', 'change_{}.jpg'.format(i))) iwt = IWT() back_img_tensor = iwt(change_img_tensor) print(back_img_tensor.shape) torchvision.utils.save_image(back_img_tensor, 'back.jpg')
返回:
(deeplearning) bogon:learning user$ python delete.py -------------- origin --------------- tensor([[[0.9020, 0.9882, 0.9216, ..., 0.7176, 0.7843, 0.8431], [0.8941, 0.9608, 0.9255, ..., 0.7490, 0.7569, 0.7490], [0.8980, 0.9333, 0.8863, ..., 0.6941, 0.7333, 0.7608], ..., [0.1373, 0.1373, 0.1451, ..., 0.9529, 0.9686, 0.9804], [0.1451, 0.1451, 0.1490, ..., 0.9294, 0.9373, 0.9569], [0.1373, 0.1412, 0.1451, ..., 0.9137, 0.9020, 0.9176]]]) ---------------- LL ------------------ tensor([[[1.8725, 1.8569, 1.9314, ..., 1.4176, 1.4510, 1.5667], [1.8294, 1.7588, 1.5118, ..., 1.4490, 1.4314, 1.5137], [1.9039, 1.6059, 1.0412, ..., 1.2765, 1.4588, 1.5039], ..., [0.3078, 0.3216, 0.3490, ..., 1.8784, 1.8333, 1.7627], [0.2647, 0.3059, 0.3784, ..., 1.7510, 1.8725, 1.9137], [0.2843, 0.3020, 0.3922, ..., 1.8941, 1.8549, 1.8569]]]) ---------------- HL ------------------ tensor([[[ 0.0765, 0.0098, 0.0059, ..., 0.0098, 0.0157, 0.0255], [ 0.0294, -0.0294, -0.0922, ..., -0.0098, 0.0078, 0.0235], [-0.0412, -0.1588, -0.0725, ..., 0.0569, 0.0314, -0.0059], ..., [-0.0137, 0.0196, 0.0039, ..., 0.0275, -0.0412, 0.0098], [-0.0020, 0.0196, 0.0176, ..., 0.0216, 0.0216, 0.0039], [ 0.0020, 0.0078, 0.0314, ..., 0.0039, -0.0118, 0.0176]]]) ---------------- LH ------------------ tensor([[[-0.0176, 0.0098, -0.0176, ..., -0.0137, 0.0392, -0.0608], [-0.0020, -0.0098, -0.1510, ..., 0.1078, 0.0745, 0.0196], [ 0.0176, -0.1392, -0.0882, ..., -0.0059, 0.0588, 0.0725], ..., [-0.0255, -0.0078, 0.0118, ..., -0.0431, 0.0216, -0.0098], [ 0.0098, 0.0000, 0.0020, ..., 0.0020, -0.0020, 0.0353], [-0.0059, -0.0039, 0.0039, ..., 0.0549, 0.0039, -0.0373]]]) ---------------- HH ------------------ tensor([[[-0.0098, 0.0059, -0.0216, ..., 0.0216, -0.0078, -0.0333], [-0.0059, -0.0255, -0.0294, ..., 0.0137, -0.0235, -0.0039], [-0.0373, -0.0373, 0.0608, ..., -0.0020, 0.0196, -0.0098], ..., [ 0.0059, 0.0039, 0.0039, ..., 0.0118, 0.0137, -0.0137], [ 0.0020, -0.0039, 0.0020, ..., -0.0098, 0.0137, 0.0078], [ 0.0020, 0.0000, 0.0039, ..., 0.0000, -0.0196, -0.0020]]]) -------------- after dwt --------------- tensor([[[1.8725, 1.8569, 1.9314, ..., 1.4176, 1.4510, 1.5667], [1.8294, 1.7588, 1.5118, ..., 1.4490, 1.4314, 1.5137], [1.9039, 1.6059, 1.0412, ..., 1.2765, 1.4588, 1.5039], ..., [0.3078, 0.3216, 0.3490, ..., 1.8784, 1.8333, 1.7627], [0.2647, 0.3059, 0.3784, ..., 1.7510, 1.8725, 1.9137], [0.2843, 0.3020, 0.3922, ..., 1.8941, 1.8549, 1.8569]]]) -------------- enter iwt --------------- tensor([[[127.5000, 127.5000, 127.5000, ..., 127.5000, 127.5000, 127.5000], [127.5000, 127.5000, 127.5000, ..., 127.5000, 127.5000, 127.5000], [127.5000, 127.5000, 127.5000, ..., 127.5000, 127.5000, 127.5000], ..., [ 39.5000, 41.2500, 44.7500, ..., 127.5000, 127.5000, 127.5000], [ 34.0000, 39.2500, 48.5000, ..., 127.5000, 127.5000, 127.5000], [ 36.5000, 38.7500, 50.2500, ..., 127.5000, 127.5000, 127.5000]]]) -------------- back --------------- tensor([[[117.5000, 137.5000, 125.5000, ..., 124.5000, 124.0000, 131.0000], [117.5000, 137.5000, 126.5000, ..., 135.0000, 124.0000, 131.0000], [123.5000, 131.5000, 127.5000, ..., 119.0000, 121.5000, 128.0000], ..., [ 35.0000, 36.0000, 36.7500, ..., 132.5000, 130.2500, 134.2500], [ 36.5000, 36.5000, 37.7500, ..., 126.7500, 125.0000, 130.0000], [ 35.5000, 37.5000, 37.2500, ..., 128.2500, 125.0000, 130.0000]]]) torch.Size([1, 3, 112, 112])
发现输入iwt的结果变化了,突然想起来torchvision.utils.save_image函数是会对数据进行处理的
解决办法就是调整下顺序即可
重新运行一遍:
#coding:utf-8 import torch.nn as nn import torch def dwt_init(x): x01 = x[:, :, 0::2, :] / 2 x02 = x[:, :, 1::2, :] / 2 x1 = x01[:, :, :, 0::2] x2 = x02[:, :, :, 0::2] x3 = x01[:, :, :, 1::2] x4 = x02[:, :, :, 1::2] x_LL = x1 + x2 + x3 + x4 x_HL = -x1 - x2 + x3 + x4 x_LH = -x1 + x2 - x3 + x4 x_HH = x1 - x2 - x3 + x4 return torch.cat((x_LL, x_HL, x_LH, x_HH), 1) # 使用哈尔 haar 小波变换来实现二维逆向离散小波 def iwt_init(x): r = 2 in_batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width = x.size() # print([in_batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width]) #[1, 12, 56, 56] out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width = in_batch, int(in_channel / (r**2)), r * in_height, r * in_width # print(out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width) #1 3 112 112 x1 = x[:, 0:out_channel, :, :] / 2 x2 = x[:, out_channel:out_channel * 2, :, :] / 2 x3 = x[:, out_channel * 2:out_channel * 3, :, :] / 2 x4 = x[:, out_channel * 3:out_channel * 4, :, :] / 2 # print(x1.shape) #torch.Size([1, 3, 56, 56]) # print(x2.shape) #torch.Size([1, 3, 56, 56]) # print(x3.shape) #torch.Size([1, 3, 56, 56]) # print(x4.shape) #torch.Size([1, 3, 56, 56]) # h = torch.zeros([out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width]).float().cuda() h = torch.zeros([out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width]).float() h[:, :, 0::2, 0::2] = x1 - x2 - x3 + x4 h[:, :, 1::2, 0::2] = x1 - x2 + x3 - x4 h[:, :, 0::2, 1::2] = x1 + x2 - x3 - x4 h[:, :, 1::2, 1::2] = x1 + x2 + x3 + x4 return h # 二维离散小波 class DWT(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(DWT, self).__init__() self.requires_grad = False # 信号处理,非卷积运算,不需要进行梯度求导 def forward(self, x): return dwt_init(x) # 逆向二维离散小波 class IWT(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(IWT, self).__init__() self.requires_grad = False def forward(self, x): return iwt_init(x) if __name__ == '__main__': import os, cv2, torchvision from PIL import Image import numpy as np from torchvision import transforms as trans # img = cv2.imread('./1.jpg') # print(img.shape) # img = Image.fromarray(img.astype(np.uint8)) img = Image.open('./1.jpg') transform = trans.Compose([ trans.ToTensor() ]) img = transform(img).unsqueeze(0) dwt = DWT() change_img_tensor = dwt(img) iwt = IWT() back_img_tensor = iwt(change_img_tensor) print(back_img_tensor.shape) # print(change_img_tensor.shape) #torch.Size([1, 12, 56, 56]) #合并成一张4格的图 h = torch.zeros([4,3,change_img_tensor.size(2),change_img_tensor.size(2)]).float() for i in range(change_img_tensor.size(1)//3): h[i,:,:,:] = change_img_tensor[:,i*3:i*3+3:,:] #分别保存为一个图片 torchvision.utils.save_image(change_img_tensor[:,i*3:i*3+3:,:], os.path.join('./', 'change_{}.jpg'.format(i))) change_img_grid = torchvision.utils.make_grid(h, 2) #一行2张图片 torchvision.utils.save_image(change_img_grid, 'change_img_grid.jpg') torchvision.utils.save_image(back_img_tensor, 'back.jpg')
小波变换后的结果为:
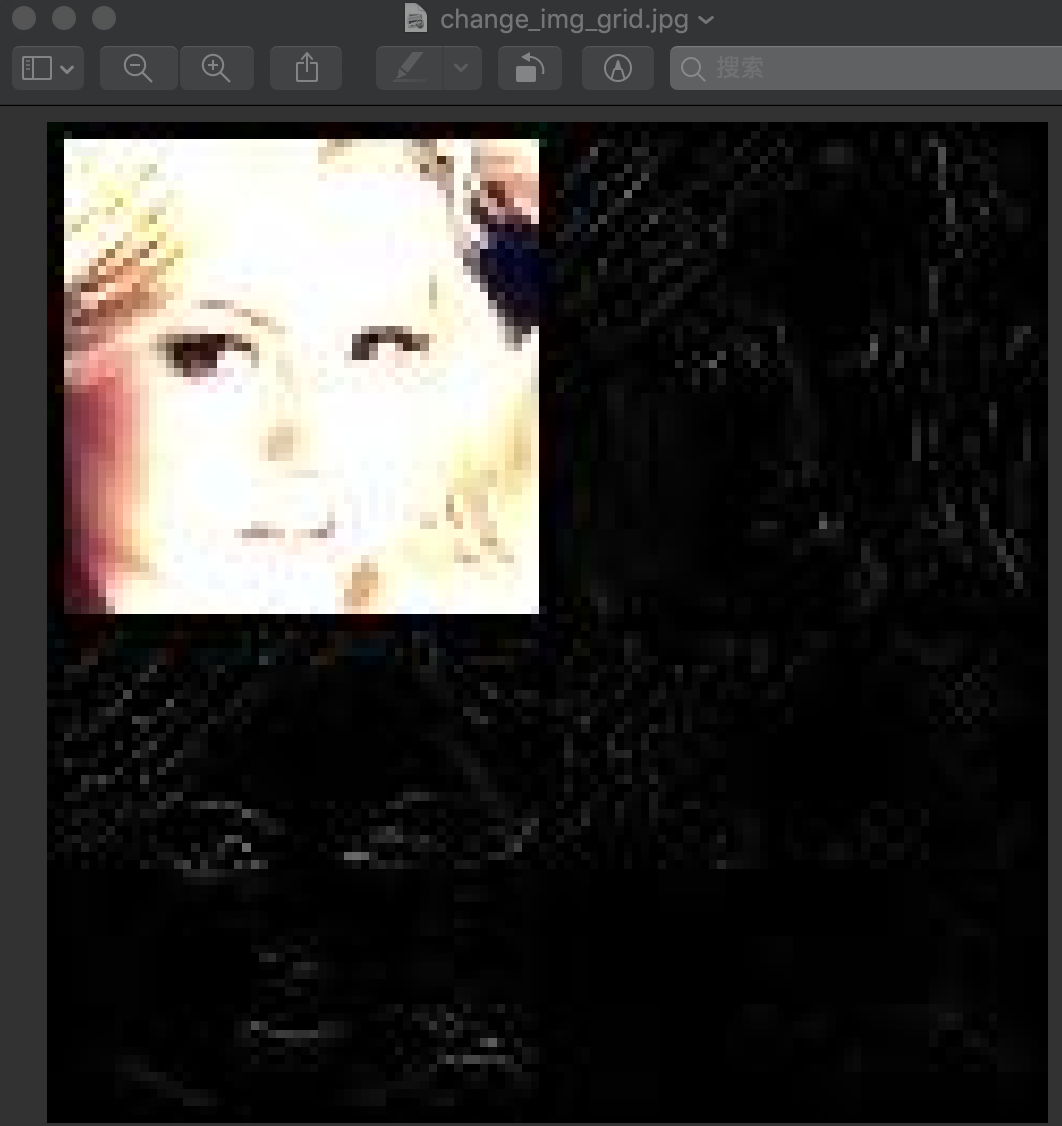
重构的图为:
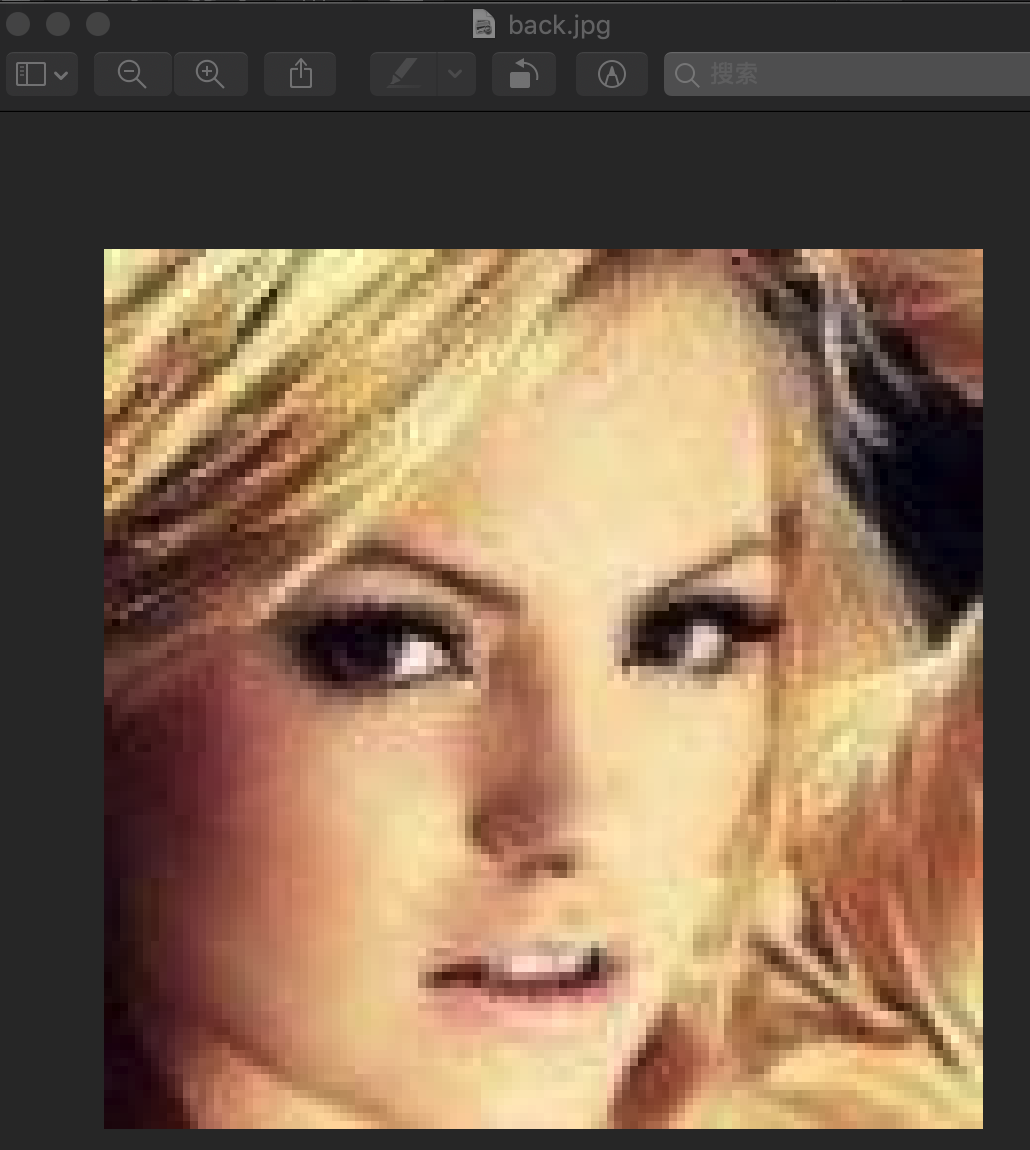
2)对代码进行解释
1》dwt
def dwt_init(x): x01 = x[:, :, 0::2, :] / 2 x02 = x[:, :, 1::2, :] / 2 x1 = x01[:, :, :, 0::2] x2 = x02[:, :, :, 0::2] x3 = x01[:, :, :, 1::2] x4 = x02[:, :, :, 1::2] x_LL = x1 + x2 + x3 + x4 x_HL = -x1 - x2 + x3 + x4 x_LH = -x1 + x2 - x3 + x4 x_HH = x1 - x2 - x3 + x4 return torch.cat((x_LL, x_HL, x_LH, x_HH), 1)
首先:
x01 = x[:, :, 0::2, :] / 2 x02 = x[:, :, 1::2, :] / 2
将矩阵分为偶数行和奇数行,并将所有值都除以2,这样后面只要进行求和和求差即可,因为已经求均值了
然后下面的:
x1 = x01[:, :, :, 0::2] x2 = x02[:, :, :, 0::2] x3 = x01[:, :, :, 1::2] x4 = x02[:, :, :, 1::2]
就是分为偶数列和奇数列,假设矩阵为6*6大小,那么就将该矩阵分成了4个3*3大小的x1、x2、x3和x4,如下图所示:
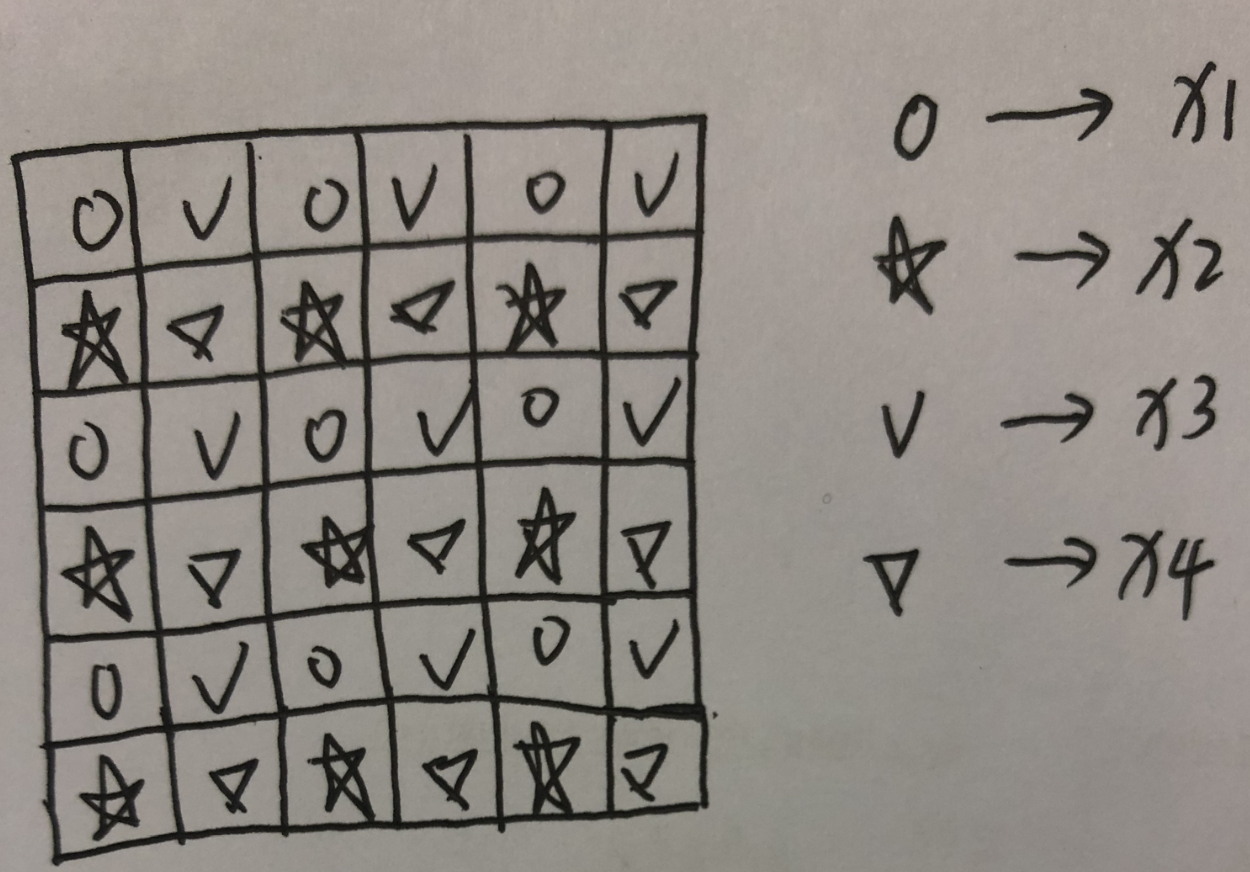
那么接下来在进行的计算就是进行行、列的和、差变换了:
x_LL = x1 + x2 + x3 + x4 x_HL = -x1 - x2 + x3 + x4 x_LH = -x1 + x2 - x3 + x4 x_HH = x1 - x2 - x3 + x4
再用一张图说明:

2》iwt
def iwt_init(x): r = 2 in_batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width = x.size() # print([in_batch, in_channel, in_height, in_width]) #[1, 12, 56, 56] out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width = in_batch, int(in_channel / (r**2)), r * in_height, r * in_width # print(out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width) #1 3 112 112 x1 = x[:, 0:out_channel, :, :] / 2 x2 = x[:, out_channel:out_channel * 2, :, :] / 2 x3 = x[:, out_channel * 2:out_channel * 3, :, :] / 2 x4 = x[:, out_channel * 3:out_channel * 4, :, :] / 2 # print(x1.shape) #torch.Size([1, 3, 56, 56]) # print(x2.shape) #torch.Size([1, 3, 56, 56]) # print(x3.shape) #torch.Size([1, 3, 56, 56]) # print(x4.shape) #torch.Size([1, 3, 56, 56]) # h = torch.zeros([out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width]).float().cuda() h = torch.zeros([out_batch, out_channel, out_height, out_width]).float() h[:, :, 0::2, 0::2] = x1 - x2 - x3 + x4 h[:, :, 1::2, 0::2] = x1 - x2 + x3 - x4 h[:, :, 0::2, 1::2] = x1 + x2 - x3 - x4 h[:, :, 1::2, 1::2] = x1 + x2 + x3 + x4 return h
在这里的行x1=x_LL/2, x2=x_HL/2, x3=x_LH/2, x4=x_HH/2
所以我们想重构,其实就是从这些值中恢复dwt中的x1,x2,x3,x4,分别放到h对应的位置变为原来的矩阵,如x1对应的是h[:, :, 0::2, 0::2],如下图所示:
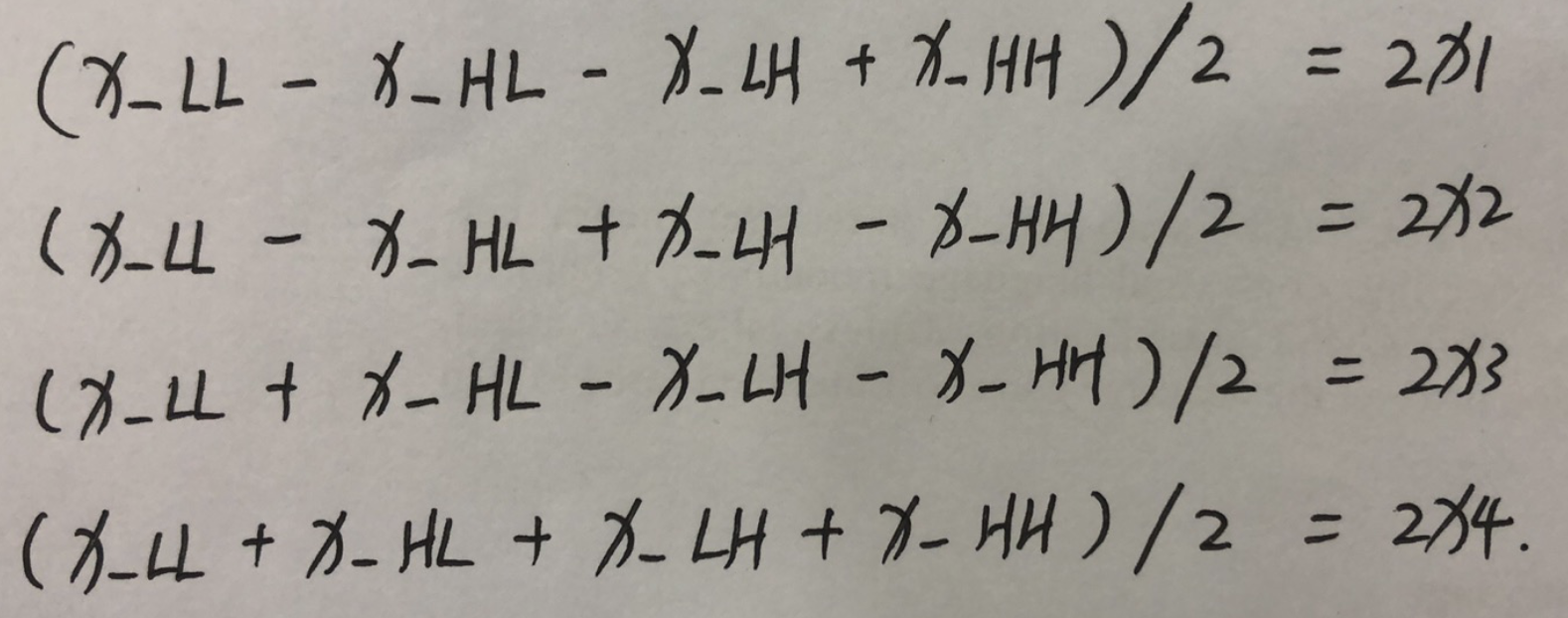
这就是重构的方法
过程中遇到的一点问题pytorch图像处理的问题