Spring配置中,采用属性注入时,当创建IOC容器时,也直接创建对象,并且执行相对应的setter方法
Student.java


1 package com.scope; 2 3 public class Student { 4 private String name; 5 private String number; 6 public String getName() { 7 return name; 8 } 9 public void setName(String name) { 10 this.name = name; 11 System.out.println(name); 12 } 13 public String getNumber() { 14 return number; 15 } 16 public void setNumber(String number) { 17 this.number = number; 18 } 19 public Student() { 20 super(); 21 System.out.println("hello Student!"); 22 23 } 24 25 26 }
Main.java


1 package com.scope; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 public class Main { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans-scope.xml"); 9 10 } 11 }
beans-scope.xml


1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 5 6 <bean id="student1" class="com.scope.Student"> 7 <property name="name" value="Mary"></property> 8 <property name="number" value="1120143231"></property> 9 </bean> 10 <bean id="student2" class="com.scope.Student"> 11 <property name="name" value="Curry"></property> 12 <property name="number" value="1120111413"></property> 13 </bean> 14 15 </beans>
执行结果
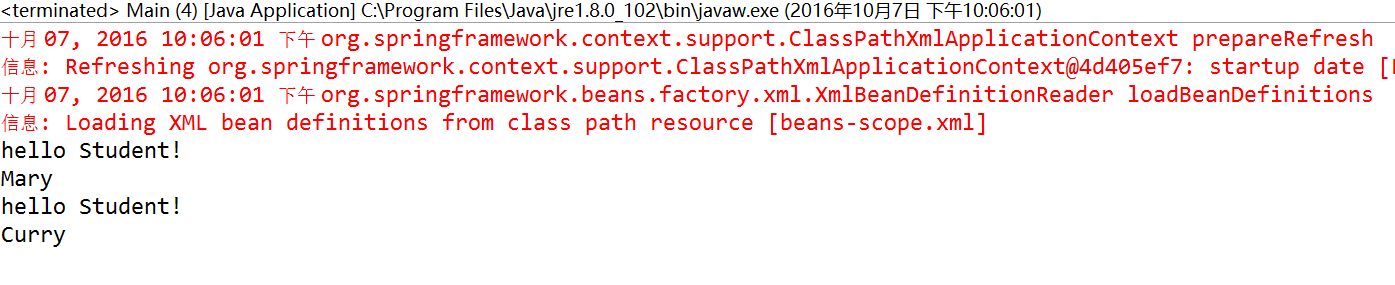
当创建IOC容器时,配置文件中有多少个bean就会创建多少个对象,并且执行相对应的setter函数。
我们对Main.java进行修改


1 package com.scope; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 public class Main { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans-scope.xml"); 9 Student student1 = (Student) ctx.getBean("student1"); 10 Student student2 = (Student) ctx.getBean("student1"); 11 System.out.println(student1 == student2); 12 } 13 }
执行结果:

当执行Student student1 = (Student) ctx.getBean("student1")时,并没有创建对象,只是创建了一个索引而已,Student1和Student2引用的是同一个对象。
以上就是单例模式,属性注入时,默认的就是单例模式,每个bean id只会创建一个对象,并且在创建IOC容器时,就创建对象和执行相对应的setter函数。
下面讲原型模式,即prototype模式。
Main.java


1 package com.scope; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 public class Main { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans-scope.xml"); 9 // Student student1 = (Student) ctx.getBean("student1"); 10 // Student student2 = (Student) ctx.getBean("student1"); 11 // System.out.println(student1 == student2); 12 } 13 }
beans-scope.xml


1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 5 6 <bean id="student1" class="com.scope.Student" scope="prototype"> 7 <property name="name" value="Mary"></property> 8 <property name="number" value="1120143231"></property> 9 </bean> 10 <bean id="student2" class="com.scope.Student" scope="prototype"> 11 <property name="name" value="Curry"></property> 12 <property name="number" value="1120111413"></property> 13 </bean> 14 15 </beans>
执行结果

采用prototype模式时,在创建IOC容器时,并没有创建相应的对象。我们继续对Main.java进行修改。


1 package com.scope; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 public class Main { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans-scope.xml"); 9 Student student1 = (Student) ctx.getBean("student1"); 10 Student student2 = (Student) ctx.getBean("student1"); 11 System.out.println(student1 == student2); 12 } 13 }
执行结果

在执行Student student1 = (Student) ctx.getBean("student1"); Student student2 = (Student) ctx.getBean("student1");创建了两个对象,所以输出了false。
采用prototype模式时,只有在获取bean时,才开始创建对象,获取多少次就创建多少个对象。