Rootkit是一种特殊的恶意软件,它的功能是在安装目标上隐藏自身及指定的文件、进程和网络链接等信息,比较多见到的是Rootkit一般都和木马、后门等其他恶意程序结合使用。Rootkit一词更多地是指被作为驱动程序,加载到操作系统内核中的恶意软件。
chkrootkit简介chkrootkit是一个linux下检RootKit的脚本,在某些检测中会调用当前目录的检测程序
下载源码:ftp://ftp.pangeia.com.br/pub/seg/pac/chkrootkit.tar.gz
解压后执行 make 命令,就可以使用了
一般直接运行,一旦有INFECTED,说明可能被植入了RootKit
./chkrootkit | grep INFECTED
首先删除别名,确保接下来的一些操作不会用了被RootKit改变了的别名
### workaround for some Bourne shell implementations
unalias login > /dev/null 2>&1
unalias ls > /dev/null 2>&1
unalias netstat > /dev/null 2>&1
unalias ps > /dev/null 2>&1
unalias dirname > /dev/null 2>&1
一开始会检测一些必要的命令是否可用,可执行,因为检测基于这些命令
cmdlist="
awk
cut
echo
egrep
find
head
id
ls
netstat
ps
sed
ssh
strings
uname
"
接下来就是检测ps的参数ax好不好使,好使就使用ax,不好使就用-fe
# Check if ps command is ok
if ${ps} ax >/dev/null 2>&1 ; then
ps_cmd="ax"
else
ps_cmd="-fe"
fi
当然还需检测你是否是root,就根据你的id号是否为0
if [ `${id} | ${cut} -d= -f2 | ${cut} -d( -f1` -ne 0 ]; then
echo "$0 need root privileges"
exit 1
fi
接下来就是默认执行所有测试,当然你也可以指定测试的命令
if [ $# -gt 0 ]
then
### perform only tests supplied as arguments
for arg in $*
do
### check if is a valid test name
if echo "${TROJAN} ${TOOLS}"|
${egrep} -v "${L_REGEXP}$arg${R_REGEXP}" > /dev/null 2>&1
then
echo >&2 "$0: \`$arg': not a known test"
exit 1
fi
done
LIST=$*
else
### this is the default: perform all tests
LIST="${TROJAN} ${TOOLS}"
fi
接下来只是对是否开启调试模式,用户是否指定了要检测的根目录进行处理
if [ "${DEBUG}" = "t" ]; then
set -x
fi
if [ "${ROOTDIR}" != "/" ]; then
### remove trailing `/'
ROOTDIR=`echo ${ROOTDIR} | ${sed} -e 's//*$//g'`
for dir in ${pth}
do
if echo ${dir} | ${egrep} '^/' > /dev/null 2>&1
then
newpth="${newpth} ${ROOTDIR}${dir}"
else
newpth="${newpth} ${ROOTDIR}/${dir}"
fi
done
pth=${newpth}
ROOTDIR="${ROOTDIR}/"
fi
最后便是循环调用各个check函数进行处理了
for cmd in ${LIST}
do
if echo "${TROJAN}" |
${egrep} "${L_REGEXP}$cmd${R_REGEXP}" > /dev/null 2>&1
then
if [ "${EXPERT}" != "t" -a "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then
printn "Checking \`${cmd}'... "
fi
chk_${cmd}
STATUS=$?
### quiet mode
if [ "${QUIET}" = "t" ]; then
### show only INFECTED status
if [ ${STATUS} -eq 0 ]; then
echo "Checking \`${cmd}'... INFECTED"
fi
continue
fi
case $STATUS in
0) echo "INFECTED";;
1) echo "not infected";;
2) echo "not tested";;
3) echo "not found";;
4) echo "infected but disabled";;
5) ;; ### expert mode
esac
else
### external tool
if [ "${EXPERT}" != "t" -a "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then
printn "Checking \`$cmd'... "
fi
${cmd}
fi
done
那么接下来每个check方法到底是怎么检测的呢?接下来
检测方法通过分析脚本,总结出检测方法如下:
- 搜索通用的ROOTKIT特征的字符串
- 对某种特定的rootkits,或者命令的特殊的感染特征进行检测
- 对某种特定的rootkits的生成的特定文件的检测
- 对程序的SUID位的设置进行检测
- 对ldsopreload的检测
- 查找可疑的log文件
- 查找可疑的php文件
- 检测.history文件
- 检测有无程序监听了一些可疑的端口
- 检测Linux可加载内核模块
- 检测有无隐藏进程
- 检测目录的软链接异常
- 检测网络接口的异常
- 检测用户的登录日志
- 检测上一次登录
- 检测可疑的没有tty记录的进程
下面对上面这些方法结合脚本代码进行简单说明
搜索通用的ROOTKIT特征的字符串
搜索的是下面的比较通用的ROOTKIT字符串
# Many trojaned commands have this label
GENERIC_ROOTKIT_LABEL="^/bin/.*sh$|bash|elite$|vejeta|.ark|iroffer"
可以看到前两个都是shell相关的,相关的示例代码如下:
chk_chfn () {
STATUS=${NOT_INFECTED}
CMD=`loc chfn chfn $pth`
[ ${?} -ne 0 ] && return ${NOT_FOUND}
if [ "${EXPERT}" = "t" ]; then
expertmode_output "${strings} -a ${CMD}"
return 5
fi
case "${SYSTEM}" in
Linux)
if ${strings} -a ${CMD} | ${egrep} "${GENERIC_ROOTKIT_LABEL}"
>/dev/null 2>&1
then
STATUS=${INFECTED}
fi;;
FreeBSD)
[ `echo $V | ${awk} '{ if ( $1 >= 5.0) print 1; else print 0 }'` -eq 1 ] && n=1 || n=2
if [ `${strings} -a ${CMD} |
${egrep} -c "${GENERIC_ROOTKIT_LABEL}"` -ne $n ]
then
STATUS=${INFECTED}
fi;;
esac
return ${STATUS}
}
程序针对Linux和FreeBSD系统分开处理,都是通过strings获取二进制程序中的字符串,再使用egrep命令去正则匹配,匹配成功就将返回值STATUS设置为INFECTED这个常量(这个在文件开头处定义了)
对某种特定的rootkits,或者命令的特殊的感染特征进行检测
比如这个amd命令的某个感染特征
chk_amd () {
STATUS=${NOT_INFECTED}
AMD_INFECTED_LABEL="blah"
CMD=`loc amd amd $pth`
if [ ! -x "${CMD}" ]; then
return ${NOT_FOUND}
fi
if [ "${EXPERT}" = "t" ]; then
expertmode_output "${strings} -a ${CMD}"
return 5
fi
if ${strings} -a ${CMD} | ${egrep} "${AMD_INFECTED_LABEL}" >/dev/null 2>&1
then
STATUS=${INFECTED}
fi
return ${STATUS}
}
下面这个检测crontab的nobody用户,并且定时任务中有数字的, 可能是Lupper.Worm
当然还是有CRONTAB_I_L这个特殊的检测
chk_crontab () {
STATUS=${NOT_INFECTED}
CRONTAB_I_L="crontab.*666"
CMD=`loc crontab crontab $pth`
if [ ! -r ${CMD} ]
then
return ${NOT_FOUND}
fi
if [ "${EXPERT}" = "t" ]; then
expertmode_output "${CMD} -l -u nobody"
return 5
fi
# slackware's crontab have a bug
if ( ${CMD} -l -u nobody | $egrep [0-9] ) >/dev/null 2>&1 ; then
${echo} "Warning: crontab for nobody found, possible Lupper.Worm... "
if ${CMD} -l -u nobody 2>/dev/null | ${egrep} $CRONTAB_I_L >/dev/null 2>&1
then
STATUS=${INFECTED}
fi
fi
return ${STATUS}
}
对Ramen Worm进行特征匹配
if ${egrep} "^asp" ${ROOTDIR}etc/inetd.conf >/dev/null 2>&1; then
echo "Warning: Possible Ramen Worm installed in inetd.conf"
STATUS=${INFECTED}
fi
对某种特定的rootkits生成的特定文件的检测
如下面的HiDrootkit和t0rn
### HiDrootkit
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then printn
"Searching for HiDrootkit's default dir... "; fi
if [ -d ${ROOTDIR}var/lib/games/.k ]
then
echo "Possible HiDrootkit installed"
else
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then echo "nothing found"; fi
fi
### t0rn
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then printn
"Searching for t0rn's default files and dirs... "; fi
if [ -f ${ROOTDIR}etc/ttyhash -o -f ${ROOTDIR}sbin/xlogin -o
-d ${ROOTDIR}usr/src/.puta -o -r ${ROOTDIR}lib/ldlib.tk -o
-d ${ROOTDIR}usr/info/.t0rn ]
then
echo "Possible t0rn rootkit installed"
else
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then echo "nothing found"; fi
fi
对程序的SUID位的设置进行检测
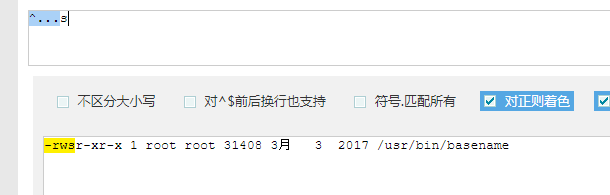
chk_basename () {
STATUS=${NOT_INFECTED}
CMD=`loc basename basename $pth`
if [ "${EXPERT}" = "t" ]; then
expertmode_output "${strings} -a ${CMD}"
expertmode_output "${ls} -l ${CMD}"
return 5
fi
if ${strings} -a ${CMD} | ${egrep} "${GENERIC_ROOTKIT_LABEL}" > /dev/null 2>&1
then
STATUS=${INFECTED}
fi
[ "$SYSTEM" != "OSF1" ] &&
{
if ${ls} -l ${CMD} | ${egrep} "^...s" > /dev/null 2>&1
then
STATUS=${INFECTED}
fi
}
return ${STATUS}
}
这个除了检测有无关键字,还检测SUID位有无设置
对ldsopreload的检测
chk_ldsopreload() {
STATUS=${NOT_INFECTED}
CMD="${ROOTDIR}lib/libshow.so ${ROOTDIR}lib/libproc.a"
if [ "${SYSTEM}" = "Linux" ]
then
if [ ! -x ./strings-static ]; then
printn "can't exec ./strings-static, "
return ${NOT_TESTED}
fi
if [ "${EXPERT}" = "t" ]; then
expertmode_output "./strings-static -a ${CMD}"
return 5
fi
### strings must be a statically linked binary.
if ./strings-static -a ${CMD} > /dev/null 2>&1
then
STATUS=${INFECTED}
fi
else
STATUS=${NOT_TESTED}
fi
return ${STATUS}
}
检测是否有libshow.so,libproc.a,有就说明感染了恶意so文件
可以看到为了保险起见,作者使用的是自己目录下静态编译的strings进行检测
查找可疑的log文件
例子如下:
files=`${find} ${ROOTDIR}dev ${ROOTDIR}tmp ${ROOTDIR}lib ${ROOTDIR}etc ${ROOTDIR}var
${findargs} ( -name "tcp.log" -o -name ".linux-sniff" -o -name "sniff-l0g" -o -name "core_" )
2>/dev/null`
if [ "${files}" = "" ]
then
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then echo "nothing found"; fi
else
echo
echo ${files}
fi
查找可疑的php文件
查找一些可疑的php文件
###
### Suspect PHP files
###
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then
printn "Searching for suspect PHP files... "; fi
files="`${find} ${ROOTDIR}tmp ${ROOTDIR}var/tmp ${findargs} -name '*.php' 2> /dev/null`"
if [ `echo abc | head -n 1` = "abc" ]; then
fileshead="`${find} ${ROOTDIR}tmp ${ROOTDIR}var/tmp ${findargs} -type f -exec head -n 1 {} ; | $egrep '#!.*php' 2> /dev/null`"
else
fileshead="`${find} ${ROOTDIR}tmp ${ROOTDIR}var/tmp ${findargs} -type f -exec head -1 {} ; | grep '#!.*php' 2> /dev/null`"
fi
if [ "${files}" = "" -a "${fileshead}" = "" ]; then
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then echo "nothing found"; fi
else
echo
echo "${files}"
echo "${fileshead}"
fi
检测.history文件
看看history有没有被清空了,或者软连接到其他地方了
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then
printn "Searching for anomalies in shell history files... "; fi
files=""
if [ ! -z "${SHELL}" -a ! -z "${HOME}" ]; then
files=`${find} ${ROOTDIR}${HOME} ${findargs} -name '.*history' -size 0`
[ ! -z "${files}" ] &&
echo "Warning: \`${files}' file size is zero"
files1=`${find} ${ROOTDIR}${HOME} ${findargs} -name '.*history' ( -links 2 -o -type l )`
[ ! -z "${files1}" ] &&
echo "Warning: \`${files1}' is linked to another file"
fi
if [ -z "${files}" -a -z "${files1}" ]; then
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then echo "nothing found"; fi
fi
检测有无程序监听了一些可疑的端口
检测代码如下:
bindshell () {
PORT="114|145|465|511|600|1008|1524|1999|1978|2881|3049|3133|3879|4000|4369|5190|5665|6667|10008|12321|23132|27374|29364|30999|31336|31337|37998|45454|47017|47889|60001|7222"
OPT="-an"
PI=""
if [ "${ROOTDIR}" != "/" ]; then
echo "not tested"
return ${NOT_TESTED}
fi
if [ "${EXPERT}" = "t" ]; then
expertmode_output "${netstat} ${OPT}"
return 5
fi
for P in `echo $PORT | ${sed} 's/|/ /g'`; do
if ${netstat} "${OPT}" | ${egrep} "^tcp.*LIST|^udp" | ${egrep}
"[.:]${P}[^0-9.:]" >/dev/null 2>&1
then
PI="${PI} ${P}"
fi
done
if [ "${PI}" != "" ]
then
echo "INFECTED PORTS: ($PI)"
else
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then echo "not infected"; fi
fi
}
检测Linux可加载内核模块
lkm ()
{
prog=""
if [ ( "${SYSTEM}" = "Linux" -o ( "${SYSTEM}" = "FreeBSD" -a
`echo ${V} | ${awk} '{ if ($1 > 4.3 || $1 < 6.0) print 1; else print 0 }'` -eq 1 ) ) -a "${ROOTDIR}" = "/" ]; then
[ -x ./chkproc -a "`find /proc | wc -l`" -gt 1 ] && prog="./chkproc"
[ -x ./chkdirs ] && prog="$prog ./chkdirs"
if [ "$prog" = "" ]; then
echo "not tested: can't exec $prog"
return ${NOT_TESTED}
fi
if [ "${EXPERT}" = "t" ]; then
[ -r /proc/$KALLSYMS ] && ${egrep} -i "adore|sebek" < /proc/$KALLSYMS 2>/dev/null
[ -d /proc/knark ] && ${ls} -la /proc/knark 2> /dev/null
PV=`$ps -V 2>/dev/null| $cut -d " " -f 3 |${awk} -F . '{ print $1 "." $2 $3 }' | ${awk} '{ if ($0 > 3.19) print 3; else if ($0 < 2.015) print 1; else print 2 }'`
[ "$PV" = "" ] && PV=2
[ "${SYSTEM}" = "SunOS" ] && PV=0
expertmode_output "./chkproc -v -v -p $PV"
return 5
fi
### adore LKM
[ -r /proc/$KALLSYMS ] &&
if `${egrep} -i adore < /proc/$KALLSYMS >/dev/null 2>&1`; then
echo "Warning: Adore LKM installed"
fi
### sebek LKM (Adore based)
[ -r /proc/$KALLSYMS ] &&
if `${egrep} -i sebek < /proc/$KALLSYMS >/dev/null 2>&1`; then
echo "Warning: Sebek LKM installed"
fi
### knark LKM
if [ -d /proc/knark ]; then
echo "Warning: Knark LKM installed"
fi
PV=`$ps -V 2>/dev/null| $cut -d " " -f 3 |${awk} -F . '{ print $1 "." $2 $3 }' | ${awk} '{ if ($0 > 3.19) print 3; else if ($0 < 2.11) print 1; else print 2 }'`
[ "$PV" = "" ] && PV=2
[ "${SYSTEM}" = "SunOS" ] && PV=0
if [ "${DEBUG}" = "t" ]; then
${echo} "*** PV=$PV ***"
fi
if ./chkproc -p ${PV}; then
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then echo "chkproc: nothing detected"; fi
else
echo "chkproc: Warning: Possible LKM Trojan installed"
fi
dirs="/tmp"
for i in /usr/share /usr/bin /usr/sbin /lib; do
[ -d $i ] && dirs="$dirs $i"
done
if ./chkdirs $dirs; then
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then echo "chkdirs: nothing detected"; fi
else
echo "chkdirs: Warning: Possible LKM Trojan installed"
fi
else
if [ "${QUIET}" != "t" ]; then echo "chkproc: not tested"; fi
fi
}
loadable kernel module (LKM),这个是检测内核模块的 ,看看有无adore,sebek这些内核模块
之后调用chkproc,chkdirs进行检测,这两个下面检测有无隐藏进程,会说到
检测有无隐藏进程
这个代码在chkproc.c中,它通过暴力递归,看看有没有/proc目录存在,而ps查不出来的进程,那么就说明有进程隐藏了
/* Brute force */
strcpy(buf, "/proc/");
retps = retdir = 0;
for (i = FIRST_PROCESS; i <= MAX_PROCESSES; i++)
{
// snprintf(&buf[6], 6, "%d", i);
snprintf(&buf[6], 8, "%d", i);
if (!chdir(buf))
{
if (!dirproc[i] && !psproc[i])
{
#if defined(__linux__)
if (!isathread[i]) {
#endif
retdir++;
if (verbose)
printf ("PID %5d(%s): not in readdir output
", i, buf);
#if defined(__linux__)
}
#endif
}
if (!psproc[i] ) /* && !kill(i, 0)) */
{
#if defined(__linux__)
if(!isathread[i]) {
#endif
retps++;
if (verbose)
printf ("PID %5d: not in ps output
", i);
#if defined(__linux__)
}
#endif
}
检测目录的软链接异常
chkdirs比较的是父目录的软链接数和子目录的个数
正常情况下,父目录的软链接数 = 子目录的个数 + 2
if (!linkcount) {
if (lstat(".", &statinfo)) {
fprintf(stderr, "lstat(%s): %s
", fullpath, strerror(errno));
goto abort;
}
linkcount = statinfo.st_nlink; //获取符号链接数
}
if (!(dirhandle = opendir("."))) {
fprintf(stderr, "opendir(%s): %s
", fullpath, strerror(errno));
goto abort;
}
numdirs = 0;
dl = (struct dirinfolist *)NULL;
while ((finfo = readdir(dirhandle))) {
if (!strcmp(finfo->d_name, ".") || !strcmp(finfo->d_name, ".."))
continue;
if (lstat(finfo->d_name, &statinfo)) {
fprintf(stderr, "lstat(%s/%s): %s
",
fullpath, finfo->d_name, strerror(errno));
closedir(dirhandle);
goto abort;
}
if (S_ISDIR(statinfo.st_mode)) { //判断是否是目录
numdirs++;
if (norecurse) continue; /* just count subdirs if "-n" */
/* Otherwise, keep a list of all directories found that have link
count > 2 (indicating directory contains subdirectories). We'll
call check_dir() on each of these subdirectories in a moment...
*/
if (statinfo.st_nlink > 2) {
dptr = dl;
if (!(dl = (struct dirinfolist *)malloc(sizeof(struct dirinfolist)))) {
fprintf(stderr, "malloc() failed: %s
", strerror(errno));
norecurse = 1;
while (dptr) {
dl = dptr->dil_next;
free((void *)dptr);
dptr = dl;
}
continue;
}
strncpy(dl->dil_name, finfo->d_name, sizeof(dl->dil_name));
dl->dil_lc = statinfo.st_nlink;
dl->dil_next = dptr;
}
}
}
closedir(dirhandle);
/* Parent directory link count had better equal #subdirs+2... */
diff = linkcount - numdirs - 2; //
if (diff) printf("%d %s
", diff, fullpath);
检测网络接口的异常
sniffer () {
if [ "${ROOTDIR}" != "/" ]; then
echo "not tested"
return ${NOT_TESTED}
fi
if [ "$SYSTEM" = "SunOS" ]; then
return ${NOT_TESTED}
fi
if [ "${EXPERT}" = "t" ]; then
expertmode_output "./ifpromisc" -v
return 5
fi
if [ ! -x ./ifpromisc ]; then
echo "not tested: can't exec ./ifpromisc"
return ${NOT_TESTED}
else
[ "${QUIET}" != "t" ] && ./ifpromisc -v || ./ifpromisc -q
fi
}
这个是对网络接口的检测,看看有无开启网卡混杂模式(英语:promiscuous mode)
而PF_PACKET可以操作链路层的数据,可以读取和发送链路层的数据包
./ifpromisc -v
ens3: PF_PACKET(/sbin/dhclient)
virbr0: not promisc and no PF_PACKET sockets
docker0: not promisc and no PF_PACKET sockets
br-47a3d838588a: not promisc and no PF_PACKET sockets
检测用户的登录日志
检测用户的登录相关的log文件
SunOS使用的是check_wtmpx,比较的文件是/var/adm/wtmp,/var/adm/wtmpx,check_wtmpx部分代码,比较这两个文件的一些差异,比如下面的比较uid
if ( memcmp( utmp_entry.ut_id, utmpx_entry.ut_id, 4 ) != 0 )
{
fprintf( stderr, "[ %u ] utmp_entry.ut_id != utmpx_entry.ut_id
", wtmp_read_counter );
break;
}
其他linux检测的是var/log/wtmp或者var/adm/wtmp
chkwtmp部分代码,查看有无删除了登录时间
gettimeofday(&mytime, &dummy);
act_time=mytime.tv_sec;
wtmpfile[127]='