背景
由项目中需要根据一些已有数据学习出一个y=ax+b的一元二项式,给定了x,y的一些样本数据,通过梯度下降或最小二乘法做多项式拟合得到a、b,解决该问题时,首先想到的是通过spark mllib去学习,可是结果并不理想:少量的文档,参数也很难调整。于是转变了解决问题的方式:采用了最小二乘法做多项式拟合。
最小二乘法多项式拟合描述下: (以下参考:https://blog.csdn.net/funnyrand/article/details/46742561)
假设给定的数据点和其对应的函数值为 (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ... (xm, ym),需要做的就是得到一个多项式函数f(x) = a0 * x + a1 * pow(x, 2) + .. + an * pow(x, n),使其对所有给定x所计算出的f(x)与实际对应的y值的差的平方和最小,也就是计算多项式的各项系数 a0, a1, ... an.
根据最小二乘法的原理,该问题可转换为求以下线性方程组的解:Ga = B,
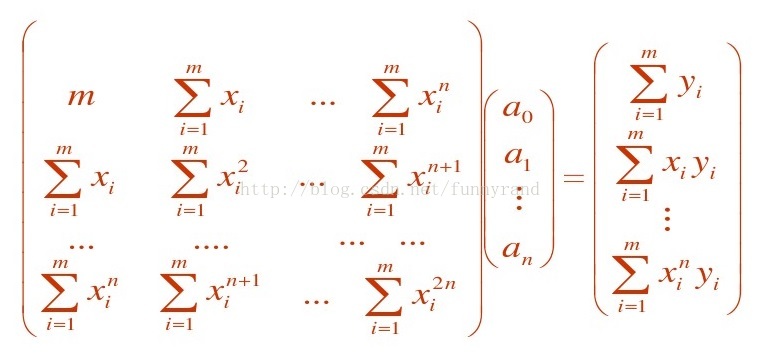
所以从编程的角度来说需要做两件事情:
1)确定线性方程组的各个系数:
确定系数比较简单,对给定的 (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ... (xm, ym) 做相应的计算即可,相关代码:
private void compute() {
...
}
2)解线性方程组:
解线性方程组稍微复杂,这里用到了高斯消元法,基本思想是通过递归做矩阵转换,逐渐减少求解的多项式系数的个数,相关代码:
private double[] calcLinearEquation(double[][] a, double[] b) {
...
}
Java代码
1 public class JavaLeastSquare { 2 private double[] x; 3 private double[] y; 4 private double[] weight; 5 private int n; 6 private double[] coefficient; 7 8 /** 9 * Constructor method. 10 * @param x Array of x 11 * @param y Array of y 12 * @param n The order of polynomial 13 */ 14 public JavaLeastSquare(double[] x, double[] y, int n) { 15 if (x == null || y == null || x.length < 2 || x.length != y.length 16 || n < 2) { 17 throw new IllegalArgumentException( 18 "IllegalArgumentException occurred."); 19 } 20 this.x = x; 21 this.y = y; 22 this.n = n; 23 weight = new double[x.length]; 24 for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++) { 25 weight[i] = 1; 26 } 27 compute(); 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * Constructor method. 32 * @param x Array of x 33 * @param y Array of y 34 * @param weight Array of weight 35 * @param n The order of polynomial 36 */ 37 public JavaLeastSquare(double[] x, double[] y, double[] weight, int n) { 38 if (x == null || y == null || weight == null || x.length < 2 39 || x.length != y.length || x.length != weight.length || n < 2) { 40 throw new IllegalArgumentException( 41 "IllegalArgumentException occurred."); 42 } 43 this.x = x; 44 this.y = y; 45 this.n = n; 46 this.weight = weight; 47 compute(); 48 } 49 50 /** 51 * Get coefficient of polynomial. 52 * @return coefficient of polynomial 53 */ 54 public double[] getCoefficient() { 55 return coefficient; 56 } 57 58 /** 59 * Used to calculate value by given x. 60 * @param x x 61 * @return y 62 */ 63 public double fit(double x) { 64 if (coefficient == null) { 65 return 0; 66 } 67 double sum = 0; 68 for (int i = 0; i < coefficient.length; i++) { 69 sum += Math.pow(x, i) * coefficient[i]; 70 } 71 return sum; 72 } 73 74 /** 75 * Use Newton's method to solve equation. 76 * @param y y 77 * @return x 78 */ 79 public double solve(double y) { 80 return solve(y, 1.0d); 81 } 82 83 /** 84 * Use Newton's method to solve equation. 85 * @param y y 86 * @param startX The start point of x 87 * @return x 88 */ 89 public double solve(double y, double startX) { 90 final double EPS = 0.0000001d; 91 if (coefficient == null) { 92 return 0; 93 } 94 double x1 = 0.0d; 95 double x2 = startX; 96 do { 97 x1 = x2; 98 x2 = x1 - (fit(x1) - y) / calcReciprocal(x1); 99 } while (Math.abs((x1 - x2)) > EPS); 100 return x2; 101 } 102 103 /* 104 * Calculate the reciprocal of x. 105 * @param x x 106 * @return the reciprocal of x 107 */ 108 private double calcReciprocal(double x) { 109 if (coefficient == null) { 110 return 0; 111 } 112 double sum = 0; 113 for (int i = 1; i < coefficient.length; i++) { 114 sum += i * Math.pow(x, i - 1) * coefficient[i]; 115 } 116 return sum; 117 } 118 119 /* 120 * This method is used to calculate each elements of augmented matrix. 121 */ 122 private void compute() { 123 if (x == null || y == null || x.length <= 1 || x.length != y.length 124 || x.length < n || n < 2) { 125 return; 126 } 127 double[] s = new double[(n - 1) * 2 + 1]; 128 for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { 129 for (int j = 0; j < x.length; j++) { 130 s[i] += Math.pow(x[j], i) * weight[j]; 131 } 132 } 133 double[] b = new double[n]; 134 for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) { 135 for (int j = 0; j < x.length; j++) { 136 b[i] += Math.pow(x[j], i) * y[j] * weight[j]; 137 } 138 } 139 double[][] a = new double[n][n]; 140 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 141 for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { 142 a[i][j] = s[i + j]; 143 } 144 } 145 146 // Now we need to calculate each coefficients of augmented matrix 147 coefficient = calcLinearEquation(a, b); 148 } 149 150 /* 151 * Calculate linear equation. 152 * The matrix equation is like this: Ax=B 153 * @param a two-dimensional array 154 * @param b one-dimensional array 155 * @return x, one-dimensional array 156 */ 157 private double[] calcLinearEquation(double[][] a, double[] b) { 158 if (a == null || b == null || a.length == 0 || a.length != b.length) { 159 return null; 160 } 161 162 for (double[] x : a) { 163 if (x == null || x.length != a.length) 164 return null; 165 } 166 167 int len = a.length - 1; 168 double[] result = new double[a.length]; 169 170 if (len == 0) { 171 result[0] = b[0] / a[0][0]; 172 return result; 173 } 174 175 double[][] aa = new double[len][len]; 176 double[] bb = new double[len]; 177 int posx = -1, posy = -1; 178 for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++) { 179 for (int j = 0; j <= len; j++) 180 if (a[i][j] != 0.0d) { 181 posy = j; 182 break; 183 } 184 if (posy != -1) { 185 posx = i; 186 break; 187 } 188 } 189 if (posx == -1) { 190 return null; 191 } 192 193 int count = 0; 194 for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++) { 195 if (i == posx) { 196 continue; 197 } 198 bb[count] = b[i] * a[posx][posy] - b[posx] * a[i][posy]; 199 int count2 = 0; 200 for (int j = 0; j <= len; j++) { 201 if (j == posy) { 202 continue; 203 } 204 aa[count][count2] = a[i][j] * a[posx][posy] - a[posx][j] * a[i][posy]; 205 count2++; 206 } 207 count++; 208 } 209 210 // Calculate sub linear equation 211 double[] result2 = calcLinearEquation(aa, bb); 212 213 // After sub linear calculation, calculate the current coefficient 214 double sum = b[posx]; 215 count = 0; 216 for (int i = 0; i <= len; i++) { 217 if (i == posy) { 218 continue; 219 } 220 sum -= a[posx][i] * result2[count]; 221 result[i] = result2[count]; 222 count++; 223 } 224 result[posy] = sum / a[posx][posy]; 225 return result; 226 } 227 228 public static void main(String[] args) { 229 JavaLeastSquare eastSquareMethod = new JavaLeastSquare( 230 new double[]{ 231 2, 14, 20, 25, 26, 34, 232 47, 87, 165, 265, 365, 465, 233 565, 665 234 }, 235 new double[]{ 236 0.7 * 2 + 20 + 0.4, 237 0.7 * 14 + 20 + 0.5, 238 0.7 * 20 + 20 + 3.4, 239 0.7 * 25 + 20 + 5.8, 240 0.7 * 26 + 20 + 8.27, 241 0.7 * 34 + 20 + 0.4, 242 243 0.7 * 47 + 20 + 0.1, 244 0.7 * 87 + 20, 245 0.7 * 165 + 20, 246 0.7 * 265 + 20, 247 0.7 * 365 + 20, 248 0.7 * 465 + 20, 249 250 0.7 * 565 + 20, 251 0.7 * 665 + 20 252 }, 253 2); 254 255 double[] coefficients = eastSquareMethod.getCoefficient(); 256 for (double c : coefficients) { 257 System.out.println(c); 258 } 259 260 // 测试 261 System.out.println(eastSquareMethod.fit(4)); 262 } 263 }
输出结果:
com.datangmobile.biz.leastsquare.JavaLeastSquare
22.27966881467629
0.6952475907448203
25.06065917765557
Process finished with exit code 0
使用开源库
也可使用Apache开源库commons math(http://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-math/userguide/fitting.html),提供的功能更强大:
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-math3</artifactId> <version>3.5</version> </dependency>
实现代码:
import org.apache.commons.math3.fitting.PolynomialCurveFitter; import org.apache.commons.math3.fitting.WeightedObservedPoints; public class WeightedObservedPointsTest { public static void main(String[] args) { final WeightedObservedPoints obs = new WeightedObservedPoints(); obs.add(2, 0.7 * 2 + 20 + 0.4); obs.add(12, 0.7 * 12 + 20 + 0.3); obs.add(32, 0.7 * 32 + 20 + 3.4); obs.add(34 , 0.7 * 34 + 20 + 5.8); obs.add(58 , 0.7 * 58 + 20 + 8.4); obs.add(43 , 0.7 * 43 + 20 + 0.28); obs.add(27 , 0.7 * 27 + 20 + 0.4); // Instantiate a two-degree polynomial fitter. final PolynomialCurveFitter fitter = PolynomialCurveFitter.create(2); // Retrieve fitted parameters (coefficients of the polynomial function). final double[] coeff = fitter.fit(obs.toList()); for (double c : coeff) { System.out.println(c); } } }
测试输出结果:
20.47425047847121
0.6749744063035112
0.002523043547711147
Process finished with exit code 0
使用org.ujmp(矩阵)实现最小二乘法:
pom.xml中需要引入org.ujmp
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.dtgroup</groupId> <artifactId>dtgroup</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <repositories> <repository> <id>limaven</id> <name>aliyun maven</name> <url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url> <layout>default</layout> <releases> <enabled>true</enabled> </releases> <snapshots> <enabled>false</enabled> </snapshots> </repository> </repositories> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.ujmp</groupId> <artifactId>ujmp-core</artifactId> <version>0.3.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
java代码:
/** * 采用最小二乘法多项式拟合方式,获取多项式的系数。 * @param sampleCount 采样点个数 * @param fetureCount 多项式的系数 * @param samples 采样点集合 * **/ private static void leastsequare(int sampleCount, int fetureCout, List<Sample> samples) { // 构件 2*2矩阵 存储X,元素值都为1.0000的矩阵 Matrix matrixX = DenseMatrix.Factory.ones(sampleCount, fetureCout); for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) { matrixX.setAsDouble(samples.get(i).getX(), i, 1); } // System.out.println(matrixX); System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); // 构件 2*2矩阵 存储X Matrix matrixY = DenseMatrix.Factory.ones(sampleCount, 1); for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) { matrixY.setAsDouble(samples.get(i).getY(), i, 0); } // System.out.println(matrixY); // 对X进行转置 Matrix matrixXTrans = matrixX.transpose(); // System.out.println(matrixXTrans); // 乘积运算:x*转转置后x:matrixXTrans*matrixX Matrix matrixMtimes = matrixXTrans.mtimes(matrixX); System.out.println(matrixMtimes); System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); // 求逆 Matrix matrixMtimesInv = matrixMtimes.inv(); System.out.println(matrixMtimesInv); // x转置后结果*求逆结果 System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); Matrix matrixMtimesInvMtimes = matrixMtimesInv.mtimes(matrixXTrans); System.out.println(matrixMtimesInvMtimes); System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); Matrix theta = matrixMtimesInvMtimes.mtimes(matrixY); System.out.println(theta); }
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { /** * y=ax+b * * a(0,1] b[5,20] * * x[0,500] y>=5 */ // y= 0.8d*x+15 // 当x不变动时,y对应有多个值;此时把y求均值。 List<Sample> samples = new ArrayList<Sample>(); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 1 + 15 + 1, 1d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 4 + 15 + 0.8, 4d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 3 + 15 + 0.7, 3d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 24 + 15 + 0.4, 24d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 5 + 15 + 0.3, 5d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 10 + 15 + 0.4, 10d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 14 + 15 + 0.2, 14d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 7 + 15 + 0.3, 7d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 1000 + 23 + 0.3, 70d)); int sampleCount = samples.size(); int fetureCout = 2; leastsequare(sampleCount, fetureCout, samples); }
过滤样本中的噪点:
public static void main(String[] args) { /** * y=ax+b * * a(0,1] b[5,20] * * x[0,500] y>=5 */ // y= 0.8d*x+15 // 当x不变动时,y对应有多个值;此时把y求均值。 List<Sample> samples = new ArrayList<Sample>(); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 1 + 15 + 1, 1d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 4 + 15 + 0.8, 4d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 3 + 15 + 0.7, 3d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 24 + 15 + 0.4, 24d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 5 + 15 + 0.3, 5d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 10 + 15 + 0.4, 10d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 14 + 15 + 0.2, 14d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 7 + 15 + 0.3, 7d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 1000 + 23 + 0.3, 70d)); // samples = filterSample(samples); sortSample(samples); FilterSampleByGradientResult result = filterSampleByGradient(0, samples); while (result.isComplete() == false) { List<Sample> newSamples=result.getSamples(); sortSample(newSamples); result = filterSampleByGradient(result.getIndex(), newSamples); } samples = result.getSamples(); for (Sample sample : samples) { System.out.println(sample); } int sampleCount = samples.size(); int fetureCout = 2; leastsequare(sampleCount, fetureCout, samples); } /** * 对采样点进行排序,按照x排序,升序排列 * @param samples 采样点集合 * **/ private static void sortSample(List<Sample> samples) { samples.sort(new Comparator<Sample>() { public int compare(Sample o1, Sample o2) { if (o1.getX() > o2.getX()) { return 1; } else if (o1.getX() <= o2.getX()) { return -1; } return 0; } }); } /** * 过滤采样点中的噪点(采样过滤方式:double theta=(y2-y1)/(x2-x1),theta就是一个斜率,根据该值范围来过滤。) * @param index 记录上次过滤索引 * @param samples 采样点集合(将从其中过滤掉噪点) * **/ private static FilterSampleByGradientResult filterSampleByGradient(int index, List<Sample> samples) { int sampleSize = samples.size(); for (int i = index; i < sampleSize - 1; i++) { double delta_x = samples.get(i).getX() - samples.get(i + 1).getX(); double delta_y = samples.get(i).getY() - samples.get(i + 1).getY(); // 距离小于2米 if (Math.abs(delta_x) < 1) { double newY = (samples.get(i).getY() + samples.get(i + 1).getY()) / 2; double newX = samples.get(i).getX(); samples.remove(i); samples.remove(i + 1); samples.add(new Sample(newY, newX)); return new FilterSampleByGradientResult(false, i, samples); } else { double gradient = delta_y / delta_x; if (gradient > 1.5) { if (i == 0) { // double newY = (samples.get(i).getY() + samples.get(i // + 1).getY()) / 2; // double newX = (samples.get(i).getX() + samples.get(i // + 1).getX()) / 2; // samples.remove(i); // samples.add(new Sample(newY, newX)); } else { samples.remove(i + 1); } return new FilterSampleByGradientResult(false, i, samples); } } } return new FilterSampleByGradientResult(true, 0, samples); }
使用距离来处理过滤:
private static List<Sample> filterSample(List<Sample> samples) { // x={x1,x2,x3...xn} // u=E(x) ---x的期望(均值)为 u // 6=sqrt(pow((x1-u),2)+pow((x2-u),2)+pow((x3-u),2)+...+pow((xn-u),2)) // 6为x的标准差,标准差=sqrt(方差) // 剔除噪点可以采用: // 若xi不属于(u-3*6,u+3*6),则认为它是噪点。 // 另外一种方案,对x/y都做上边的处理,之后如果两个结果为and 或者 or操作来选取是否剔除。 // 用点的方式来过滤数据,求出一个中值点,求其他点到该点的距离。 int sampleCount = samples.size(); double sumX = 0d; double sumY = 0d; for (Sample sample : samples) { sumX += sample.getX(); sumY += sample.getY(); } // 求中心点 double centerX = (sumX / sampleCount); double centerY = (sumY / sampleCount); List<Double> distanItems = new ArrayList<Double>(); // 计算出所有点距离该中心点的距离 for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) { Sample sample = samples.get(i); Double xyPow2 = Math.pow(sample.getX() - centerX, 2) + Math.pow(sample.getY() - centerY, 2); distanItems.add(Math.sqrt(xyPow2)); } // 以下对根据距离(所有点距离中心点的距离)进行筛选 double sumDistan = 0d; double distanceU = 0d; for (Double distance : distanItems) { sumDistan += distance; } distanceU = sumDistan / sampleCount; double deltaPowSum = 0d; double distanceTheta = 0d; // sqrt(pow((x1-u),2)+pow((x2-u),2)+pow((x3-u),2)+...+pow((xn-u),2)) for (Double distance : distanItems) { deltaPowSum += Math.pow((distance - distanceU), 2); } distanceTheta = Math.sqrt(deltaPowSum); // 剔除噪点可以采用: // 若xi不属于(u-3*6,u+3*6),则认为它是噪点。 double minDistance = distanceU - 0.5 * distanceTheta; double maxDistance = distanceU + 0.5 * distanceTheta; List<Integer> willbeRemoveIdxs = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i = distanItems.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { Double distance = distanItems.get(i); if (distance <= minDistance || distance >= maxDistance) { willbeRemoveIdxs.add(i); System.out.println("will be remove " + i); } } for (int willbeRemoveIdx : willbeRemoveIdxs) { samples.remove(willbeRemoveIdx); } return samples; }
实际业务测试:


package com.zjanalyse.spark.maths; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.List; import org.ujmp.core.DenseMatrix; import org.ujmp.core.Matrix; public class LastSquare { /** * y=ax+b a(0,1] b[5,20] x[0,500] y>=5 */ public static void main(String[] args) { // y= 0.8d*x+15 // 当x不变动时,y对应有多个值;此时把y求均值。 List<Sample> samples = new ArrayList<Sample>(); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 11 + 15 + 1, 11d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 24 + 15 + 0.8, 24d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 33 + 15 + 0.7, 33d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 24 + 15 + 0.4, 24d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 47 + 15 + 0.3, 47d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 60 + 15 + 0.4, 60d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 14 + 15 + 0.2, 14d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 57 + 15 + 0.3, 57d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 70 + 60 + 0.3, 70d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 80 + 60 + 0.3, 80d)); samples.add(new Sample(0.8d * 40 + 30 + 0.3, 40d)); sortSample(samples); System.out.println("原始样本数据"); for (Sample sample : samples) { System.out.println(sample); } System.out.println("开始“所有点”通过“业务数据取值范围”剔除:"); // 按照业务过滤。。。 filterByBusiness(samples); System.out.println("结束“所有点”通过“业务数据取值范围”剔除:"); for (Sample sample : samples) { System.out.println(sample); } int sampleCount = samples.size(); int fetureCout = 2; System.out.println("第一次拟合。。。"); Matrix theta = leastsequare(sampleCount, fetureCout, samples); double wear_loss = theta.getAsDouble(0, 0); double path_loss = theta.getAsDouble(1, 0); System.out.println("wear loss " + wear_loss); System.out.println("path loss " + path_loss); System.out.println("开始“所有点”与“第一多项式拟合结果直线方式距离方差”剔除:"); samples = filterSample(wear_loss, path_loss, samples); System.out.println("结束“所有点”与“第一多项式拟合结果直线方式距离方差”剔除:"); for (Sample sample : samples) { System.out.println(sample); } System.out.println("第二次拟合。。。"); sampleCount = samples.size(); fetureCout = 2; if (sampleCount >= 2) { theta = leastsequare(sampleCount, fetureCout, samples); wear_loss = theta.getAsDouble(0, 0); path_loss = theta.getAsDouble(1, 0); System.out.println("wear loss " + wear_loss); System.out.println("path loss " + path_loss); } System.out.println("complete..."); } /** * 按照业务过滤有效值范围 */ private static void filterByBusiness(List<Sample> samples) { for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) { double x = samples.get(i).getX(); double y = samples.get(i).getY(); if (x >= 500) { System.out.println(x + " x值超出有效值范围[0,500)"); samples.remove(i); i--; } // y= 0.8d*x+15 else if (y < 0 * x + 5 || y > 1 * x + 30) { System.out.println( y + " y值超出有效值范围[(0*x+5),(1*x+30)]其中x=" + x + ",也就是:[" + (0 * x + 5) + "," + (1 * x + 30) + ")"); samples.remove(i); i--; } } } /** * Description 点到直线的距离 * * @param x1 * 点横坐标 * @param y1 * 点纵坐标 * @param A * 直线方程一般式系数A * @param B * 直线方程一般式系数B * @param C * 直线方程一般式系数C * @return 点到之间的距离 * @see 点0,1到之前y=x+0的距离 <br> * double distance = getDistanceOfPerpendicular(0,0, -1, 1, 0);<br> * System.out.println(distance);<br> */ private static double getDistanceOfPerpendicular(double x1, double y1, double A, double B, double C) { double distance = Math.abs((A * x1 + B * y1 + C) / Math.sqrt(A * A + B * B)); return distance; } private static List<Sample> filterSample(double wear_loss, double path_loss, List<Sample> samples) { // x={x1,x2,x3...xn} // u=E(x) ---x的期望(均值)为 u // 6=sqrt(pow((x1-u),2)+pow((x2-u),2)+pow((x3-u),2)+...+pow((xn-u),2)) // 6为x的标准差,标准差=sqrt(方差) // 剔除噪点可以采用: // 若xi不属于(u-3*6,u+3*6),则认为它是噪点。 // 求出所有点距离第一次拟合结果的直线方程的距离 int sampleCount = samples.size(); List<Double> distanItems = new ArrayList<Double>(); // 计算出所有点距离该中心点的距离 for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) { Sample sample = samples.get(i); double distance = getDistanceOfPerpendicular(sample.getX(), sample.getY(), path_loss, -1, wear_loss); distanItems.add(Math.sqrt(distance)); } // 以下对根据距离(所有点距离中心点的距离)进行筛选 double sumDistan = 0d; double distanceU = 0d; for (Double distance : distanItems) { sumDistan += distance; } distanceU = sumDistan / sampleCount; double deltaPowSum = 0d; double distanceTheta = 0d; // sqrt(pow((x1-u),2)+pow((x2-u),2)+pow((x3-u),2)+...+pow((xn-u),2)) for (Double distance : distanItems) { deltaPowSum += Math.pow((distance - distanceU), 2); } distanceTheta = Math.sqrt(deltaPowSum); // 剔除噪点可以采用: // 若xi不属于(u-3*6,u+3*6),则认为它是噪点。 double minDistance = distanceU - 0.25 * distanceTheta; double maxDistance = distanceU + 0.25 * distanceTheta; List<Integer> willbeRemoveIdxs = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i = distanItems.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { Double distance = distanItems.get(i); if (distance <= minDistance || distance >= maxDistance) { System.out.println(distance + " out of range [" + minDistance + "," + maxDistance + "]"); willbeRemoveIdxs.add(i); } else { System.out.println(distance); } } for (int willbeRemoveIdx : willbeRemoveIdxs) { Sample sample = samples.get(willbeRemoveIdx); System.out.println("remove " + sample); samples.remove(willbeRemoveIdx); } return samples; } /** * 对采样点进行排序,按照x排序,升序排列 * * @param samples * 采样点集合 **/ private static void sortSample(List<Sample> samples) { samples.sort(new Comparator<Sample>() { public int compare(Sample o1, Sample o2) { if (o1.getX() > o2.getX()) { return 1; } else if (o1.getX() <= o2.getX()) { return -1; } return 0; } }); } /** * Description 采用最小二乘法多项式拟合方式,获取多项式的系数。 * * @param sampleCount * 采样点个数 * @param fetureCount * 多项式的系数 * @param samples * 采样点集合 **/ private static Matrix leastsequare(int sampleCount, int fetureCout, List<Sample> samples) { // 构件 2*2矩阵 存储X,元素值都为1.0000的矩阵 Matrix matrixX = DenseMatrix.Factory.ones(sampleCount, fetureCout); for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) { matrixX.setAsDouble(samples.get(i).getX(), i, 1); } // System.out.println(matrixX); // System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); // 构件 2*2矩阵 存储X Matrix matrixY = DenseMatrix.Factory.ones(sampleCount, 1); for (int i = 0; i < samples.size(); i++) { matrixY.setAsDouble(samples.get(i).getY(), i, 0); } // System.out.println(matrixY); // 对X进行转置 Matrix matrixXTrans = matrixX.transpose(); // System.out.println(matrixXTrans); // 乘积运算:x*转转置后x:matrixXTrans*matrixX Matrix matrixMtimes = matrixXTrans.mtimes(matrixX); // System.out.println(matrixMtimes); // System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); // 求逆 Matrix matrixMtimesInv = matrixMtimes.inv(); // System.out.println(matrixMtimesInv); // x转置后结果*求逆结果 // System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); Matrix matrixMtimesInvMtimes = matrixMtimesInv.mtimes(matrixXTrans); // System.out.println(matrixMtimesInvMtimes); // System.out.println("--------------------------------------"); Matrix theta = matrixMtimesInvMtimes.mtimes(matrixY); // System.out.println(theta); return theta; } }