* Copyright (c) 2003, 2011, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. package java.util; import java.security.*; /** * A class that represents an immutable universally unique identifier (UUID). * A UUID represents a 128-bit value. * * <p> There exist different variants of these global identifiers. The methods * of this class are for manipulating the Leach-Salz variant, although the * constructors allow the creation of any variant of UUID (described below). * * <p> The layout of a variant 2 (Leach-Salz) UUID is as follows: * * The most significant long consists of the following unsigned fields: * <pre> * 0xFFFFFFFF00000000 time_low * 0x00000000FFFF0000 time_mid * 0x000000000000F000 version * 0x0000000000000FFF time_hi * </pre> * The least significant long consists of the following unsigned fields: * <pre> * 0xC000000000000000 variant * 0x3FFF000000000000 clock_seq * 0x0000FFFFFFFFFFFF node * </pre> * * <p> The variant field contains a value which identifies the layout of the * {@code UUID}. The bit layout described above is valid only for a {@code * UUID} with a variant value of 2, which indicates the Leach-Salz variant. * * <p> The version field holds a value that describes the type of this {@code * UUID}. There are four different basic types of UUIDs: time-based, DCE * security, name-based, and randomly generated UUIDs. These types have a * version value of 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively. * * <p> For more information including algorithms used to create {@code UUID}s, * see <a href="http://t.zoukankan.com/http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4122.txt"> <i>RFC 4122: A * Universally Unique IDentifier (UUID) URN Namespace</i></a>, section 4.2 * "Algorithms for Creating a Time-Based UUID". * * @since 1.5 */ public final class UUID implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<UUID> { /** * Explicit serialVersionUID for interoperability. */ private static final long serialVersionUID = -4856846361193249489L; /* * The most significant 64 bits of this UUID. * * @serial */ private final long mostSigBits; /* * The least significant 64 bits of this UUID. * * @serial */ private final long leastSigBits; /* * The random number generator used by this class to create random * based UUIDs. In a holder class to defer initialization until needed. */ private static class Holder { static final SecureRandom numberGenerator = new SecureRandom(); } // Constructors and Factories /* * Private constructor which uses a byte array to construct the new UUID. */ private UUID(byte[] data) { long msb = 0; long lsb = 0; assert data.length == 16 : "data must be 16 bytes in length"; for (int i=0; i<8; i++) msb = (msb << 8) | (data[i] & 0xff); for (int i=8; i<16; i++) lsb = (lsb << 8) | (data[i] & 0xff); this.mostSigBits = msb; this.leastSigBits = lsb; } /** * Constructs a new {@code UUID} using the specified data. {@code * mostSigBits} is used for the most significant 64 bits of the {@code * UUID} and {@code leastSigBits} becomes the least significant 64 bits of * the {@code UUID}. * * @param mostSigBits * The most significant bits of the {@code UUID} * * @param leastSigBits * The least significant bits of the {@code UUID} */ public UUID(long mostSigBits, long leastSigBits) { this.mostSigBits = mostSigBits; this.leastSigBits = leastSigBits; } /** * Static factory to retrieve a type 4 (pseudo randomly generated) UUID. * * The {@code UUID} is generated using a cryptographically strong pseudo * random number generator. * * @return A randomly generated {@code UUID} */ public static UUID randomUUID() { SecureRandom ng = Holder.numberGenerator; byte[] randomBytes = new byte[16]; ng.nextBytes(randomBytes); randomBytes[6] &= 0x0f; /* clear version */ randomBytes[6] |= 0x40; /* set to version 4 */ randomBytes[8] &= 0x3f; /* clear variant */ randomBytes[8] |= 0x80; /* set to IETF variant */ return new UUID(randomBytes); } /** * Static factory to retrieve a type 3 (name based) {@code UUID} based on * the specified byte array. * * @param name * A byte array to be used to construct a {@code UUID} * * @return A {@code UUID} generated from the specified array */ public static UUID nameUUIDFromBytes(byte[] name) { MessageDigest md; try { md = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5"); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException nsae) { throw new InternalError("MD5 not supported"); } byte[] md5Bytes = md.digest(name); md5Bytes[6] &= 0x0f; /* clear version */ md5Bytes[6] |= 0x30; /* set to version 3 */ md5Bytes[8] &= 0x3f; /* clear variant */ md5Bytes[8] |= 0x80; /* set to IETF variant */ return new UUID(md5Bytes); } /** * Creates a {@code UUID} from the string standard representation as * described in the {@link #toString} method. * * @param name * A string that specifies a {@code UUID} * * @return A {@code UUID} with the specified value * * @throws IllegalArgumentException * If name does not conform to the string representation as * described in {@link #toString} * */ public static UUID fromString(String name) { String[] components = name.split("-"); if (components.length != 5) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid UUID string: "+name); for (int i=0; i<5; i++) components[i] = "0x"+components[i]; long mostSigBits = Long.decode(components[0]).longValue(); mostSigBits <<= 16; mostSigBits |= Long.decode(components[1]).longValue(); mostSigBits <<= 16; mostSigBits |= Long.decode(components[2]).longValue(); long leastSigBits = Long.decode(components[3]).longValue(); leastSigBits <<= 48; leastSigBits |= Long.decode(components[4]).longValue(); return new UUID(mostSigBits, leastSigBits); } // Field Accessor Methods /** * Returns the least significant 64 bits of this UUID's 128 bit value. * * @return The least significant 64 bits of this UUID's 128 bit value */ public long getLeastSignificantBits() { return leastSigBits; } /** * Returns the most significant 64 bits of this UUID's 128 bit value. * * @return The most significant 64 bits of this UUID's 128 bit value */ public long getMostSignificantBits() { return mostSigBits; } /** * The version number associated with this {@code UUID}. The version * number describes how this {@code UUID} was generated. * * The version number has the following meaning: * <p><ul> * <li>1 Time-based UUID * <li>2 DCE security UUID * <li>3 Name-based UUID * <li>4 Randomly generated UUID * </ul> * * @return The version number of this {@code UUID} */ public int version() { // Version is bits masked by 0x000000000000F000 in MS long return (int)((mostSigBits >> 12) & 0x0f); } /** * The variant number associated with this {@code UUID}. The variant * number describes the layout of the {@code UUID}. * * The variant number has the following meaning: * <p><ul> * <li>0 Reserved for NCS backward compatibility * <li>2 <a href="http://t.zoukankan.com/http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc4122.txt">IETF RFC 4122</a> * (Leach-Salz), used by this class * <li>6 Reserved, Microsoft Corporation backward compatibility * <li>7 Reserved for future definition * </ul> * * @return The variant number of this {@code UUID} */ public int variant() { // This field is composed of a varying number of bits. // 0 - - Reserved for NCS backward compatibility // 1 0 - The IETF aka Leach-Salz variant (used by this class) // 1 1 0 Reserved, Microsoft backward compatibility // 1 1 1 Reserved for future definition. return (int) ((leastSigBits >>> (64 - (leastSigBits >>> 62))) & (leastSigBits >> 63)); } /** * The timestamp value associated with this UUID. * * <p> The 60 bit timestamp value is constructed from the time_low, * time_mid, and time_hi fields of this {@code UUID}. The resulting * timestamp is measured in 100-nanosecond units since midnight, * October 15, 1582 UTC. * * <p> The timestamp value is only meaningful in a time-based UUID, which * has version type 1. If this {@code UUID} is not a time-based UUID then * this method throws UnsupportedOperationException. * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException * If this UUID is not a version 1 UUID */ public long timestamp() { if (version() != 1) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not a time-based UUID"); } return (mostSigBits & 0x0FFFL) << 48 | ((mostSigBits >> 16) & 0x0FFFFL) << 32 | mostSigBits >>> 32; } /** * The clock sequence value associated with this UUID. * * <p> The 14 bit clock sequence value is constructed from the clock * sequence field of this UUID. The clock sequence field is used to * guarantee temporal uniqueness in a time-based UUID. * * <p> The {@code clockSequence} value is only meaningful in a time-based * UUID, which has version type 1. If this UUID is not a time-based UUID * then this method throws UnsupportedOperationException. * * @return The clock sequence of this {@code UUID} * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException * If this UUID is not a version 1 UUID */ public int clockSequence() { if (version() != 1) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not a time-based UUID"); } return (int)((leastSigBits & 0x3FFF000000000000L) >>> 48); } /** * The node value associated with this UUID. * * <p> The 48 bit node value is constructed from the node field of this * UUID. This field is intended to hold the IEEE 802 address of the machine * that generated this UUID to guarantee spatial uniqueness. * * <p> The node value is only meaningful in a time-based UUID, which has * version type 1. If this UUID is not a time-based UUID then this method * throws UnsupportedOperationException. * * @return The node value of this {@code UUID} * * @throws UnsupportedOperationException * If this UUID is not a version 1 UUID */ public long node() { if (version() != 1) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not a time-based UUID"); } return leastSigBits & 0x0000FFFFFFFFFFFFL; } // Object Inherited Methods /** * Returns a {@code String} object representing this {@code UUID}. * * <p> The UUID string representation is as described by this BNF: * <blockquote><pre> * {@code * UUID = <time_low> "-" <time_mid> "-" * <time_high_and_version> "-" * <variant_and_sequence> "-" * <node> * time_low = 4*<hexOctet> * time_mid = 2*<hexOctet> * time_high_and_version = 2*<hexOctet> * variant_and_sequence = 2*<hexOctet> * node = 6*<hexOctet> * hexOctet = <hexDigit><hexDigit> * hexDigit = * "0" | "1" | "2" | "3" | "4" | "5" | "6" | "7" | "8" | "9" * | "a" | "b" | "c" | "d" | "e" | "f" * | "A" | "B" | "C" | "D" | "E" | "F" * }</pre></blockquote> * * @return A string representation of this {@code UUID} */ public String toString() { return (digits(mostSigBits >> 32, 8) + "-" + digits(mostSigBits >> 16, 4) + "-" + digits(mostSigBits, 4) + "-" + digits(leastSigBits >> 48, 4) + "-" + digits(leastSigBits, 12)); } /** Returns val represented by the specified number of hex digits. */ private static String digits(long val, int digits) { long hi = 1L << (digits * 4); return Long.toHexString(hi | (val & (hi - 1))).substring(1); } /** * Returns a hash code for this {@code UUID}. * * @return A hash code value for this {@code UUID} */ public int hashCode() { long hilo = mostSigBits ^ leastSigBits; return ((int)(hilo >> 32)) ^ (int) hilo; } /** * Compares this object to the specified object. The result is {@code * true} if and only if the argument is not {@code null}, is a {@code UUID} * object, has the same variant, and contains the same value, bit for bit, * as this {@code UUID}. * * @param obj * The object to be compared * * @return {@code true} if the objects are the same; {@code false} * otherwise */ public boolean equals(Object obj) { if ((null == obj) || (obj.getClass() != UUID.class)) return false; UUID id = (UUID)obj; return (mostSigBits == id.mostSigBits && leastSigBits == id.leastSigBits); } // Comparison Operations /** * Compares this UUID with the specified UUID. * * <p> The first of two UUIDs is greater than the second if the most * significant field in which the UUIDs differ is greater for the first * UUID. * * @param val * {@code UUID} to which this {@code UUID} is to be compared * * @return -1, 0 or 1 as this {@code UUID} is less than, equal to, or * greater than {@code val} * */ public int compareTo(UUID val) { // The ordering is intentionally set up so that the UUIDs // can simply be numerically compared as two numbers return (this.mostSigBits < val.mostSigBits ? -1 : (this.mostSigBits > val.mostSigBits ? 1 : (this.leastSigBits < val.leastSigBits ? -1 : (this.leastSigBits > val.leastSigBits ? 1 : 0)))); } }
上面的是公司的UUID工具类源码,默认生成16位字节的随机数。
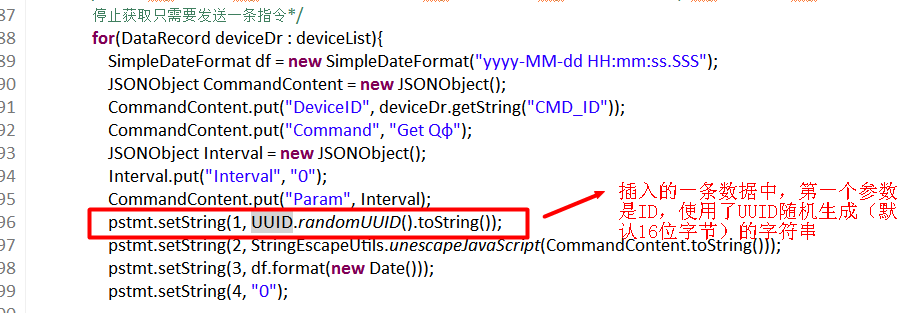
调用方式:UUID.randomUUID(),如下图所示:
下面的是网上找的一些方法,是否能生成唯一性?高并发下是否重复?本人没有测试过,无法保证生成随机数的唯一性:
import java.util.Random; import java.util.UUID; /** * * java通过UUID生成16位唯一订单号 * * * */ public class getOrredingIdUUID { public static String getOrderIdByUUId() { int first = new Random(10).nextInt(8) + 1; System.out.println(first); int hashCodeV = UUID.randomUUID().toString().hashCode(); if (hashCodeV < 0) {//有可能是负数 hashCodeV = -hashCodeV; } // 0 代表前面补充0 // 4 代表长度为4 // d 代表参数为正数型 return first + String.format("%015d", hashCodeV); } public static void main(String[] args) { String orderingID= getOrderIdByUUId(); System.out.println(orderingID); } }
/** * 获取16位随机字符串 * @return String */ public static String getUUID() { String uuid= UUID.randomUUID().toString(); char[] cs=new char[32]; char c=0; for(int i=uuid.length()/2,j=1;i-->0;){ if((c=uuid.charAt(i))!='-'){ cs[j++]=c; } } String uid=String.valueOf(cs); return uid; }
仅限一台服务器 关于多个表主键的生成,在不建议扩展主键长度的前提下,通过对时间戳加锁来解决主键重复问题 import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; import com.fto.sql.UniqueTimestamp; public class Test { public static UniqueTimestamp UT = new UniqueTimestamp(); public static String generateId() { synchronized (UT) { return StringUtils.leftPad(Long.toHexString(UT.getUniqueTimestamp()).toUpperCase(), 16, '0'); } } public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(generateId()); } }).start(); } } } 从100个线程同时执行的结果来看,没有重复,但是目前还有几个疑问: 1.会不会出现两次执行时间差小于时间戳最小单位? 2.虽然可能解决了问题,但是效率是否降低影响整体? 3.回到问题,除了此方法,是否可以生成16位唯一值? 补充下 package com.fto.sql; public class UniqueTimestamp { public static final char PRECISION_MILLISECOND = 'S'; public static final char PRECISION_SECOND = 's'; public static final char PRECISION_MINUTE = 'm'; private char precision = 'S'; private long ts = -1L; public UniqueTimestamp() {} public UniqueTimestamp(char prec) { if ((prec != 'S') && (prec != 's') && (prec != 'm')) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal argument for UniqueTimestamp. Only 'S', 's','m' can be used."); } this.precision = prec; } public synchronized long getUniqueTimestamp() { if (this.ts == -1L) { this.ts = getCurrentTimeValue(); } else { long t = getCurrentTimeValue(); if (t <= this.ts) { this.ts += 1L; } else { this.ts = t; } } return getReturnValue(this.ts); } private long getCurrentTimeValue() { long ts; switch (this.precision) { case 'S': default: ts = System.currentTimeMillis(); break; case 's': ts = System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000L; break; case 'm': ts = System.currentTimeMillis() / 60000L; } return ts; } private long getReturnValue(long ts) { switch (this.precision) { case 'S': default: return ts; case 's': return ts * 1000L; } return ts * 60000L; } } ———————————————————————————————————————————————— 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u011410116/java/article/details/79969926
网上收集的方法中,个人觉得最后一种方法可靠性相对比较高,不考虑集群的情况下,简单地处理了小量的并发问题。